Vidcoin SHALL be the next Bitcoin !!!

INTRODUCTION
Online media-streaming is one industry that has shown vivid signs to be the perfect replacement of
traditional telecast and radio broadcast. Researchers tracked 165 online video views and 1.53
billion logins over a year, and they found that total TV viewing over the internet grew by 388
percent in mid-2014 compared to the same time a year earlier. With websites like YouTube, the use
of online media streaming has been on the increase. People now have access to a massive archive of
media files, and even live broadcast.
Like every traditional online base technology there are numerous limitations in the way we stream
media files; this range from security issues, streaming speed, and monopoly of control by
companies that run such platforms. Streaming is absolutely on their terms, and the underlying
procedures on how these videos are accessed are their exclusive reserve. Also, the data controlled
by these platforms are usually vulnerable to damage or compromise since they operate a centralized
database and control server, which can be attacked or hacked.
The entire concept of any blockchain based technology is built immune to such limitations stated
above. From a decentralized database to the science of cryptography and a blockchain system of
sharing data; all of these systems are several steps further from the conventional way of sharing data
and interacting on the web.
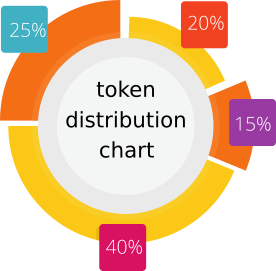
Vid-stream is a media streaming platform that is proposed to be built based on the blockchain
technology. It is meant to operate a decentralized database and control server. Also like all
blockchain based system, it is meant to be self-regulated and as transparent as can be. From the
pioneering blockchain based system, Bitcoin; Vid-stream will be built several steps away from its
limitations.
THE BASIC CONCEPT OF MEDIA STREAMING
The idea of streaming media is less than two decades old, and yet it has experienced impressive
growth. Using streaming technologies, the delivery of multimedia data over the Internet now
reaches many millions of people. Using their personal computers, offering live sport, music, news,
entertainment and on-demand is now just a few clicks away. With broadband networks being
deployed in many countries and media file compression technologies advancing rapidly, the quality
of media services over the Internet is increasing rapidly. A variety of user terminals can now be
deployed, ranging from office desktops to personal digital assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones.
There are two modes for the transmission of media over the Internet:
The download mode: the user can play the downloaded file only after the whole file has been
downloaded from a server to his/her computer. The full file transfer, in the download mode, can
often suffer unacceptably long transfer times, which depend on the size of the media file and the
bandwidth of the transport channel. For example, if downloaded from http://www.vidstream.com,
an MP3 audio file encoded at 128 kilobits/s and of 5 min duration will occupy 4.8 MB of the user's
hard disk. Using a 28.8k modem, it will take about 40 minutes to download the whole file 2.
The streaming mode: this could either be a live streaming or archived streaming. It involves the
continuous downloading and playing of a media file at the same time without waiting for a
complete download and also without saving the file during this process. In this process, the file is
broken into bits which constitute little kilobytes which are downloaded from a central database of
the media streaming site. Or it could be from a device where it is being recorded in real-time (that is
it is continuously being recorded, uploaded online and played by the end user in all of this process);
this is accessed from the web server of the live media streaming site through the media file's URL.
Below these two streaming methods are thoroughly explained:
Live streaming
This involves the access and playing of a media file that is at that time being broadcasted over the
internet. This is made possible using real-time protocol (RTP) (which is an internet transmission
protocol designed for end-to-end real-time, transfer of streaming media), a real-time streaming
protocol (RTSP), or a real-time transport control protocol (RTCP).
Archived Streaming
In this type of streaming, the media file is uploaded online to the database of a media streaming site.
These files could further be multiplied into several versions and these separate files are all chopped
into tiny bits whose usually sizes are several kilobytes. Thus whenever any person on the web
requests for this file with its unique URL, the version requested is downloaded from the database of
the media streaming site to the person's device in a serial succession of this tiny bits. This data is
instantly converted to a comprehensive media file through a plugin in the web browser of the
person's device and this files after being played are discarded. These streams of tiny bits continue to
flow, and the rate of this flow is determined by the network of this user, the video quality requested
and the accessibility of the media streaming site's database. A perfect example of an archive
streaming media site is YouTube.
Token sales have started
Vidcoin(VDC) will be listed on coinmarketcap in a moment
Visit https://vid-stream.org to purchase tokens
Thank me later mucho !
This post recieved an upvote from minnowpond. If you would like to recieve upvotes from minnowpond on all your posts, simply FOLLOW @minnowpond
This post has received a 2.19 % upvote from @booster thanks to: @bluestacks.