Steemit Crypto Academy Homework Post for @stream4u.
Introduction.
I am very excited to be part of professor @stream4u lecture again this week on blockchains.
The courses so far have been very good and explained very well by you our prof.
This week we have been introduced to blockchain and it's types, benefits, distributed ledgers, what blockchain double spending is, advantages and disadvantages of blockchain and we have as well explored the blockchain demo I'm detail.
I would now like to present my answers to the questions given.

Blockchain And It's Types.
Blockchain can be described as a series of blocks or ledger that contains huge data.
Blockchains are responsible for the record of unchangeable or unedited data and record of all transactions.
Blockchains are important because they promote transparency and avoid cheating.
Information stored on blockchains cannot be edited or changed by a single person or an "identified authority" because a single change in a any block means all other blocks have to be edited.
Blockchains are decentralized systems which means that every user has the freedom to carry out activities and nothing is hidden.
An executed activity is recorded on duplicated from that account's ledger and distributed to all other ledgers on several other computers forming a chain of ledgers.
There are four components of a blockchain. These are; nodes, blocks, chains and miners.
- Blocks: Blocks are digital or virtual files that make up a blockchain.
They contained encrypted data of all transactions on a blockchain. A completed block gives room for a new block to get completed.
Blocks have their unique hash and nonce.
A block contains uneditable data, a nonce which is a 32 bit number randomly generated and a hash which unlike the nonce, is a 256 bit number.
- Chains: Blockchains contains a series of blocks that form a chain or link.
Every new block in the blockchain contains a hash for both the new block and the previous block.
A new block must contain the hash of the previous block since it is required because it is what links the new blocks to the previous ones.
When this is achieved, there is a chain of hashes and in turn a chain of blocks formed.
- Miners: Miners are individuals of the blockchain responsible for solving complex mathematical problems with high computing power for creation and validation of blocks.
Miners are usually rewarded with tokens of the blockchain since the mining of blocks are jobs those individuals perform.
- Nodes: These are computers that have been connected or linked in the blockchain to create, mine, approve and validate blocks.
A new node is given all the necessary information the previous node contains in a gossip protocol system.

Types of Blockchain.
Blockchain are of four major types; public, private, consortium and hybrid blockchains with their various advantages and disadvantages.
I would like to talk more about them in the next paragraphs.
- Public Blockchain.
Public blockchain is a type of blockchain technology that is decentralized and open source.
It is open source in the sense that it allows every and user to partake in block mining, validation, etc. This can be done simply by having Internet access with high computing power, the brain and other necessary tools to carry out this function.
Users of the public blockchain can access all past and present records on the blockchain and therefore make suggestions on improvements that can be made to the blockchain.
Public blockchains first came out with the introduction of the first cryptocurrency, BTC. They usually use Proof of Work and Proof of Stake consensus algorithms.
The primary aim of the public blockchain is to mine and exchange cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and Ethereum.
In the table below are advantages and disadvantages of the Public blockchain.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Public blockchains are decentralized | There's no user restriction. |
| Miners are rewarded with blockchain native tokens | Not scalable. |
| Blockchain transparency | Public blockchains use PoW and PoS consensus algorithms which consume a lot of energy. |
| Blockchain is secure | Requires high computing power for mining |
- Private blockchains.
Private blockchains are opposite of public blockchains. In this type of blockchain, there is a single authority which means there's no freedom or decentralization.
Users of the private blockchain are granted permission by the authority to carry out activities. Each user has different permissions depending on what they do.
They are operated on small network mostly used by only organizations.
Private blockchains require the users of identities and so doesn't tolerate anonymity. Distributed ledgers are used but decentralization is not a feature of this blockchain.
Private blockchains can be used for internal voting.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| There's accountability due to authorizations from central or single authorities | Not decentralized |
| They're scalable | Source code is closed |
| Private blockchains are environmentally friendly | No anonymity |
| Not as secure as public blockchains | Not everyone can mine or validate blocks |
- Hybrid blockchains: Hybrid blockchains are types of blockchains that use both private and public blockchains.
In this kind of blockchain, an organization or system has control over what information or data they want public by keeping it in a public blockchain and what information they want private by keeping it in a private blockchain.
This way, transparency can be provided when needed. Security of hybrid blockchains is very good.
In hybrid blockchains, transactions cannot be altered but are only hidden and made public when it is needed by giving access to smart contracts to trigger release of the data. This is done to promote privacy.
Users who are in the hybrid blockchain have full access to the platform but it's anonymous until a transaction is made.
This type of blockchain can be used in governments and medical systems.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| There's privacy | Not 100% decentralized. |
| Fast transactions | Users still need permission sometimes. |
| There's good security | Data can be hidden |
- Consortium blockchain.
Consortium blockchains is similar to hybrid blockchain because it also makes use of the private and public blockchains.
Although it is similar to the hybrid blockchain, consortium blockchain has sever members that work on a decentralized network as compared to in the hybrid blockchain.
The other difference in the consortium blockchain is that nodes from multiple consortium blockchains are required to verify blocks.
An example of where consortium blockchain is applicable is where multiple banks link and have nodes that verify their transactions.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Security is better than in public blockchain systems | Less transparent than public blockchain networks |
| More scalable | Hacks or failure of individual member nodes can be problematic to the system |
| Access to multiple blockchains where nodes can connect to other nodes of different blockchains | Not as decentralized as public blockchain systems. |

The Benefits Of A Blockchain.
Blockchains were introduced with the introduction of cryptocurrencies and have since been very important .
Below are some benefits of the blockchain system.
- Decentralization.
I don't think there's anywhere else than to start at decentralization. Cryptocurrencies were introduced with the aim and ideal to make transactions and trading decentralized with user freedom.
With that, blockchains were created where transactions, block details and a lot more are stored on blocks and ledgers where all nodes are interconnected to facilitate an effective system.
Decentralization of system data means that every blockchain data can be accessed and viewed by users but cannot be edited therefore promoting transparency in transactions.
- Transparency.
Because blockchains technologies are decentralized like explained above, every user can see all that is happening on the blockchain hence gets rid of cheating and promotes transaction transparency.
Due to this, organizations have adopted the use of blockchains like private blockchains so that internal votes and other things can be done with top transparency.
- Cost effective.
Blockchains are cost effective. It is no news that sending fiat currencies using the banking systems have varied fees charged especially when sending internationally where high fees are charged.
Blockchains and cryptocurrencies generally trade at the same rate across the globe which is usually very cheap at a low fees.
Another way blockchains are beneficial is through the removal of intermediaries. We usually pay extra fees when we make transactions through third parties but in transacting with blockchain technologies, there's no need for third parties and hence no extra fees is charged.
- Security.
Another very important benefit of blockchains is security. Everyone would agree that before they venture into opportunities, security is the very first and major factor to consider.
Using blockchains are very safe because they are protected by cryptography. Usually there are private keys that are very long and cannot be saved off head.
We are usually advised to save private keys offline so that they cannot be hacked by online hackers.
Because of the nature of blockchains and cryptography, hacks are sometimes attributed to carelessness of users by clicking of suspicious links or leaving private keys exposed.
- Data cannot be edited or deleted / data is immutable.
Immutability is used to describe in this case, the inability to edit or delete stored data on blockchain ledgers.
Data stored on blockchains have time and date stamps and hence making even a slight change to a block would mean that the dat must be changed on all computers connected to the blockchain.
Because of this, blockchains are transparent, trustworthy and secure.
- Smart contracts.
Over the years after introduction of BTC and blockchains, smart contracts have been the 'next big thing'.
This is because it has reduced the work load of humans and removed the need for third parties.
With smart contracts, orders can be set such that when the conditions of those orders are met, smart contracts trigger the orders and they are filled.
The only problem with this is that, it is human coded and can be liable to hacks.

Blockchain Distributed Ledger.
Blockchain distributed ledgers are what is used by blockchains to record and distribute data. Blockchain distribution ledgers contain recorded information of blocks and linked nodes and is responsible for distributing all the information to all ledgers of the blockchain.
Blocking distributed ledgers distribute the same data without even changing a bit or removing any portion of the data because the each node contains new data and data from previous nodes and are hence stored on the ledgers and transfer as they are.
These data on the distributed ledgers are permanently saved and cannot be erased or edited. These distributed ledgers ensure that there is high transparency in the system by making all transactions public.
Blockchain ledgers are decentralized and secured by cryptography. These ledgers have no failure and if in case a user decides to change data on any block, the user must change the data on all other ledgers connected to the system around the globe which is highly impossible.
No single authority is needed for block and data verification.
Properties of blockchain distributed ledger.
Distribution : The distributed ledger makes sure that all available data from block generation to addition of data on nodes, and every permanently recorded data is sent to all users of the blockchain.
Security: Cryptography is the way blockchains ensure security like already stated and is the same way blockchain distributed ledgers are secured. This form of security makes use of hash functions for data encryption and block validation.
Privacy: Blockchain distributed ledgers used in blockchains promotes privacy. Identity of users are hidden unless a user wants to make his or her identity public.
Immutability: Immutability has already been explained as a way of not being able to delete or edit saved data. Distributed ledgers ensures that data that has already been recorded is permanent and cannot be edited or erased.
Transparency: Because blockchain distributed ledgers are immutable, there's high level of transparency because you cannot edit delete or hide information.
Smart contracts: We are in a computer age which seeks to reduce human workload as much as possible. The blockchain distributed ledger is programed to work by triggering when pre set conditions are met.
An example is by setting a market order and it being filled when you price is met. This can happen even when you are asleep and hence reduces your workload.

Blockchain Double Spending And How Bitcoin Handles This Problem.
Double spending is making multiple payments usually 2 transactions with the same currency or asset in order to receive more than you are supposed to receive.
Because the same currency or asset is used, double spending cannot be done with fiat currencies since you can't give out the same dollar bills, cedis, naira or rupees to a trader.
But with cryptocurrencies, there can be double spending when a seller is careless and a buyer is devious.
A buyer is devious in the sense that he or she is aware of this double spending mechanism and takes advantage of the seller's carelessness to dupe him or her.
Double spending occurs in blockchain distribution ledger usually from unverified transactions or unreleased funds.
Double spending usually means that the blockchain is attacked and that the system is manipulated. It can be in the form of controlling more than 51% of the blockchain's computing power.
Example of blockchain double spending is when I want to sell 0.0005 BTC. When I send that BTC and it is received by the buyer but not removed from my account, I can still the same 0.0005 BTC to the same or another buyer and receive double rewards.
Double spending are of 3 main types, race attacks, finney attacks and vector 76 attack.
Race attacks: this form of double spending occurs when a receiver is careless to accept an unconfirmed transaction therefore allow a sender to perform multiple transactions with the same tokens before the transaction is confirmed.
Finney attack: this form of double spending occurs when miners use duplicated details of transactions from more than one block. It also occurs when transactions are unconfirmed.
Vector 76 attack:this form of double spending occurs when hackers send fake crypto assets to people within the blockchain. Hackers use bugs or special programmed software to create these fake crypto assets.

How Bitcoin Solves Blockchain Double Spending.
Bitcoin blockchain has a public distributed ledger that permanently stores transactions. When a user starts a trade, it is first categorized as unconfirmed by the blockchain and not validated and as such is not added to the block.
The approximate generation block time of BTC is 10 minutes meaning BTC blockchain adds anew block every 10 minutes.
Through the use of cryptography, confirmed transactions are added to the distributed ledger and recipients are aware of this.
This way of adding confirmed transactions to blocks and the ledger through cryptographic tools is the method deployed by Bitcoin blockchain to avoid double spending.
Miners are responsible for block verification and so when the transaction is completed and verified by them, it is now changed from unconfirmed to confirmed releasing assets to recipients and is then details added to a new block.
So generally double spending is solved by BTC blockchain by confirming transactions and releasing them to recipients before they are added to the block.
So when there's double attack, the unconfirmed transactions are disregarded and the confirmed transactions are regarded. This way, assets cannot be double spent.

Blockchain Demo And How Block Hashes Work In The Blockchain.
Block Hashes In Blockchains.
Hashing of blocks is the encryption of transaction details using cryptographic technology. Block hashing takes all types of input and delivers output in fixed length.
To perform operations on block has. we first visit blockchain demo
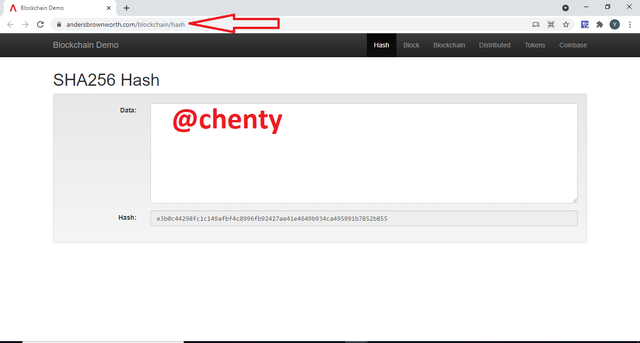
Hash.
In regards to the hash, when we input any data into it, we are given a corresponding hash value of fixed length.
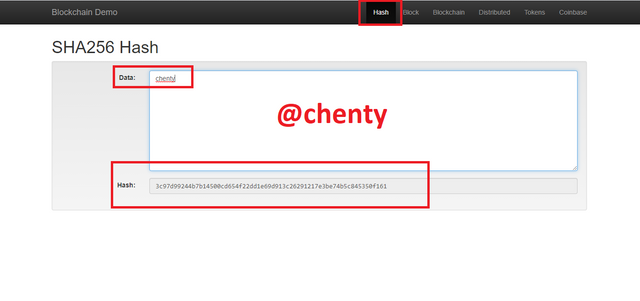
Even a single change in the data gives a new hash value but still of the same fixed length.
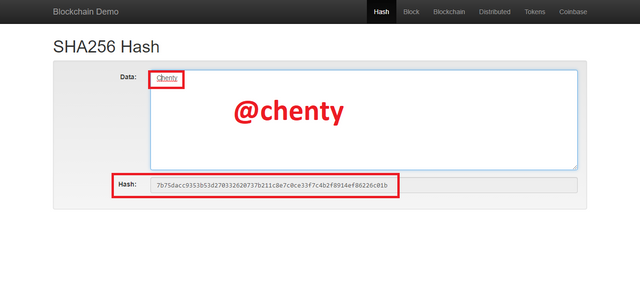
An example is in this case where I used chenty and Chenty which produced two different hashes.
Block.
In the block section of blockchain demo, there is block number, nonce, data and hash.
I would be exploring each of them.
When we click on the block button at the top of the screen, block page is opened. Block number starts from 1 and so it is observed here with no data.
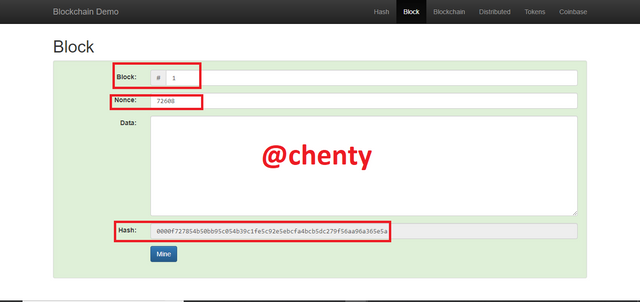
The Nonce value like explained by prof is used to validate the block. This nonce value should start with 0000 and if it doesn't then block is not valid.
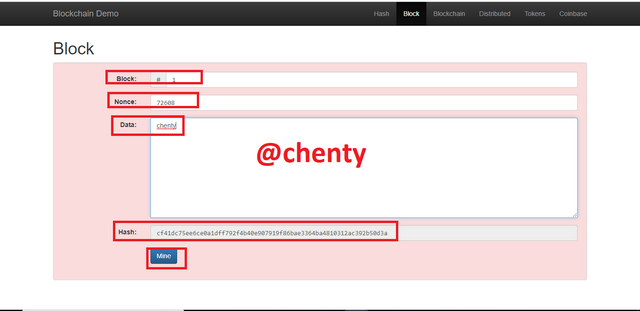
So I entered a data ( chenty ) and the box changed from green to red showing that the block was invalid.
The value of the hash didn't also start with 0000. The hash value was cf41dc75ee6ce0a1dff792f4b40e907919f86bae3364ba4810312ac392b50d3a
To validate this block with data chenty, I would have to change the nonce value individually until there is a match which is difficult to do. The easier and faster way is to use computational power so I clicked on mine and the right nonce value was obtained to validate the block.
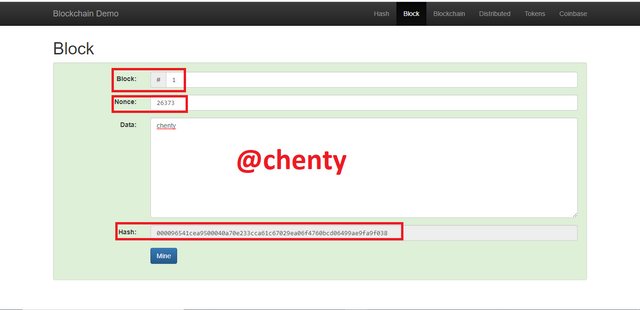
The new nonce value is 26373 and the hash data is 000096541cea9500040a70e233cca61c67029ea06f4760bcd06499ae9fa9f038
Blockchain.
In the blockchain section of blockchain demo, there are 5 blocks numbered from 1 to 5 with their induvial node number hash and previous hash.
There's block number 1 which has nonce value ( 11316 )and previous hash of 000000.
In block 2, there is nonce value (35230), previous node value (000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf ) and a hash value (000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19 ). Hash value starts from 0000 which shows validity of block.
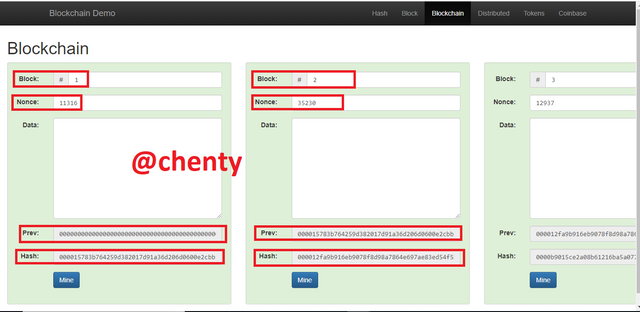
The same steps is used to check validity for 4 and 5.
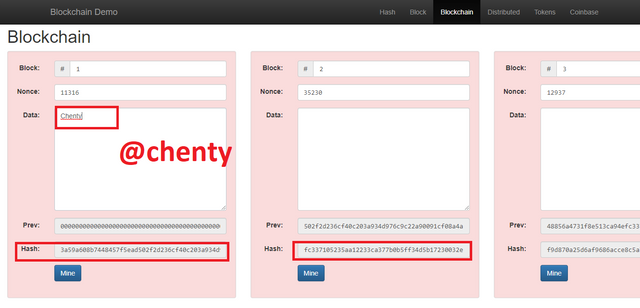
If data input is put in any of the boxes, we realize that all the boxes turn red showing invalidity of the blockchain.
I put Chenty into block 1 and all boxes turned red.
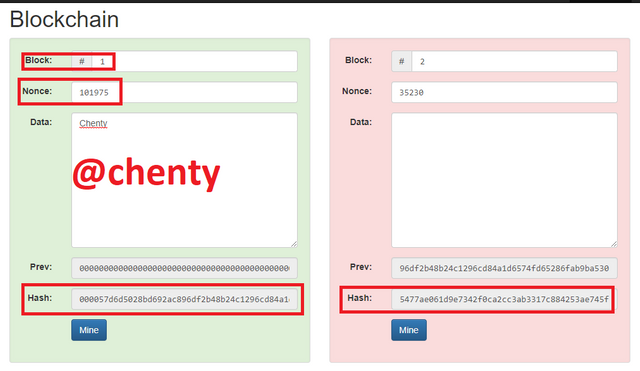
To validate this new block, it is necessary to re mine so I clicked on mine of block 1 and block was mined and validated.
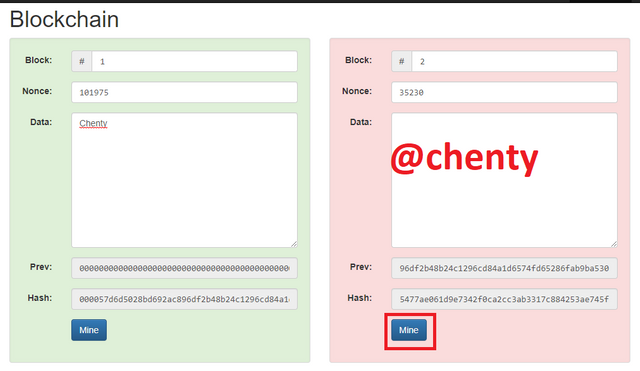
It is observed that only block 1 is valid leaving the other 4 blocks which means they should also get re mined.
So I clicked on mine for block 2 and block 2 was validated as well.
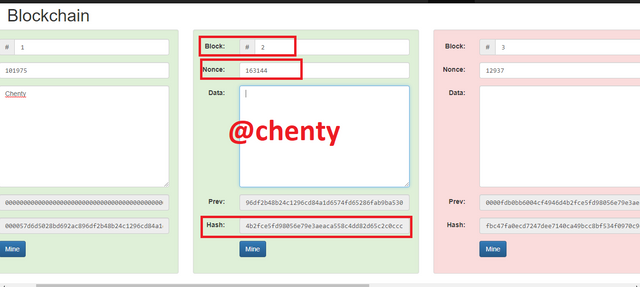
It is important to again note that only block 2 is validated which means that no data in the blockchain can be edited or else the whole system is disturbed.
This shows that an edit to even one data of a block requires a re-mine of all the other blocks.

Race Attack In Blockchain.
Race attacks is a type of double spending which occurs when dishonest users send the same amount of crypto tokens to multiple users at once.
These kind of attacks can only be successful when recipients of the crypto tokens do not wait for confirmation of transaction from the system but releases funds to the sender.
Because the user has sent the same tokens more than once, the system does not validate the transaction that has not been confirmed and therefore renders the unconfirmed transaction invalidated.
The dishonest user who has done double spending now has more funds than what he should have obtained.
So to avoid race attacks it is required to always wait for the system to confirm transactions before you accept the transaction.

Limitations Of Blockchain. .
With all the importance and benefits blockchains have come with, there are some limitations as well. Below are some disadvantages of blockchain.
- Scalability.
One very negative aspect or disadvantage of blockchains has been scalability since its introduction. Blockchains are decentralized and open source and hence it has no user limit. All users with high computing power can partake in mining of blocks and hence makes the network very busy and can affect the performance of the blockchain. This makes blockchains scalable and can reduce the speed of transactions.
- High cost of mining.
Mining of blocks are open to all but to only participants with high processing power and good mathematical skills. Mining of blocks consume a lot of energy and are not environmentally friendly. It is therefore very expensive to engage in mining of blocks.
- Hacks.
Although blockchains are secured with cryptography, they are still pen to hacks or scams. An example is on the steemit platform where hackers have developed bugs and disguised it as giving out free tokens when you click on certain links. When you click on those links, you stand the chance of giving up your keys and losing your assets.
Also, smart contracts used are open to hacks because thy have been created by humans and are not perfect.
- Irreversibility.
Another problem with blockchains is that confirmed transactions cannot be reversed. This means that when you wrongfully send tokens to a wrong address but the account is valid, your transaction goes through and there's no way of getting funds back unless from the good will of recipients.
- High fees on some blockchains.
Blockchains provide fast transactions at somewhat low fees but this is not the case for every blockchain. In blockchains like Ethereum blockchain, fees are very high and grouped into high, higher and highest transaction speeds.

Conclusion.
I must say a very big thank to professor @stream4u for this very informative lecture on let's open the blockchain.
Blockchains are the basis on which cryptocurrencies have been created and are of 4 types; public, private, hybrid and consortium blockchains.
The blockchain has several advantages like immutability, decentralization, security, anonymity, etc and limitations like smart contract hacks, irreversibility of funds, scalability and high cost of mining blocks.
Blockchain systems are vulnerable to what is known as blockchain double spending which the bitcoin system seems to have solve. But still we are advised to always ensure that transactions are confirmed before we accept.
Double spending are of types which include race attacks, vector 76 attack, Finney attack, etc.
Race attack occurs when users accept transactions without waiting for its confirmation.
I also learnt through practice that nonce is responsible for verification of blocks and is to be mined when there is an input data to get a correct hash. A valid hash is characterized by 0000 at the beginning of the hash.
I also learnt through practice that when there is a change to even a portion of one block, all the blocks need to be remined.
Thank you.
Hi @chenty
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 10/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thank you for your review prof. I did learn something new😃