Work and Energy

WorkOften the word is used I work, as synonymous of effort, but in physics all work involves the achievement of a force and the existence of displacement of the point of application of this force.
Physical work.
The physical work defines as the product to climb of the force applied by the covered distance, his magnitude depends on the applied force have or not the same direction that the movement has the same direction, that the movement in question. This way the force and the movement has the same direction, the magnitude of the work carrying out is the product of both, nevertheless, if the direction of the force does not coincide with that of the movement, the magnitude of the work is minor and results from the product, between the component of the force in the direction of the movement and the covered distance.
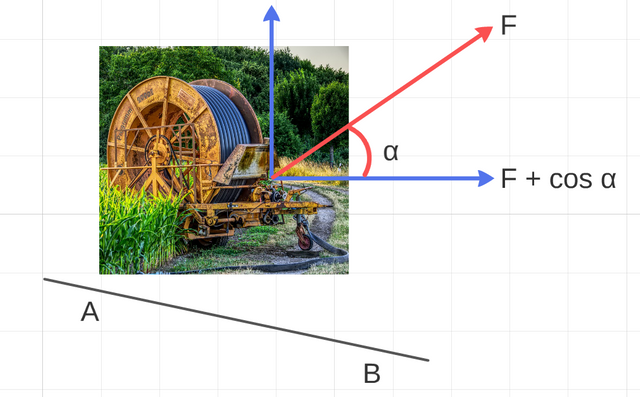
The product of the module of the vector forces for the module of the vector displacement and for the cosine of the angle, that form both. The work will be, also, positive or negative depending on that the force operates in the sense of the movement or sense opposite to this one.(Image prepared for @coolxxx).
The work will be zero (0), in the case that there is no movement and also if the force and the displacement are perpendicular, since cos 90 ° = 0. Joined of work and also of energy in the international system it is a July (joule), a July is the work of displaces one meter in the point application of a force, of a newton, in the same direction and sense.
Energy.
The energy is defined, in general, as the aptitude which a system has, to realize a work. In this respect diverse types of physical energy exist, since it can be the kinetics, the potential, the thermal one.
The kinetic energy.
It is the one that possesses a body in reason of his speed, that is to say, it is equal to the necessary work so that the above mentioned object reaches a certain speed.
The Theory of force of Van der Waals.
This is a theory fisicoquímica, because from molecules and chemical molecular substance, they can achieve to generate attraction or repulsion, that's why this theory raised the following thing; force of molecular stabilization develops, at chemical level also chemical linkage takes place, not covalente, together it develops electronic layers of 2 contiguous atoms, caused an induced force or forces between a permanent dipole and an induced dipole. Considering the following thing, a dipole that is induced in not polar atom, it interacts with a molecule that has a moment dipolar permanently, giving this way a totality of the intermolecular forces.

Johannes Diderik van der Waals (1837—1923)
The potential energy.
It is the one that the bodies have to causes of the position that they occupy with regard to a system of force, the potential energy, which they acquire of the weight or weight it depends on the height, which reaches these on the soil. This way the bodies, which are submitted to the gravitational field created by the ground, change his potential energy when they modify his height with regard to the surface of está, when work does so that it increases it or when trasforman part of his potential energy in kinetics.
The potential gravitational energy measures with regard to a level arbitrary zero, which generally is chosen as the level of the terrestrial surface.
The thermal energy.
It is the one that has a body according to his temperature, and in fact they are alone a form of kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules, which compose it, being so much higher major all that is the temperature, therefore major is also the oscillation of the atoms or molecules.

The thermal energy (Image prepared for @coolxxx).
Radiant energy.
It is the only form of energy, which can exist in absence of matter and is constituted by an undulatory movement of the magnetic and electrical fields. It takes place for the fall of the atoms from levels superior to low others and for the emission of the excess of energy in the shape of radiation, which different types, are the electromagnetic spectrums.
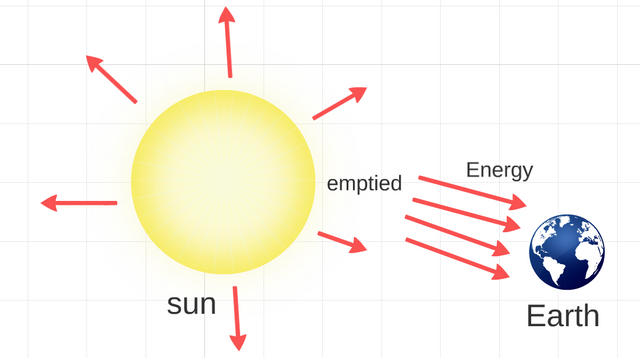
Radiant energy.(Image prepared for @coolxxx).
The sonorous energy.
It is very interesting, since it is constituted by the wave displacement of pressure, in a material way as it could be the air, the water, a metal. Since it is a question of vibrations of the molecules of the way in question, he can consider also, like a form of kinetic energy.
Conservation of the energy.
Between the diverse existing types of energy processes of conversion happen, from one to other one and when a body they modify the energy as consequence of the so-called beginning of conservation.
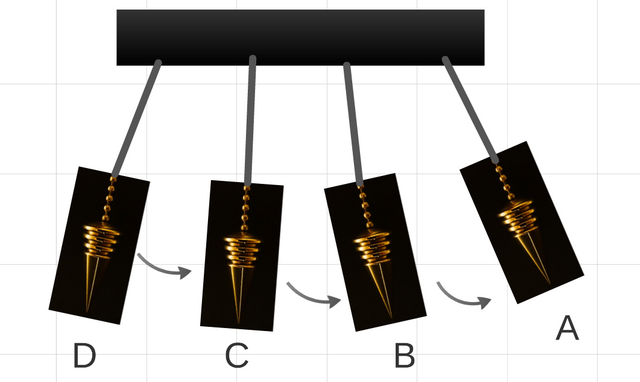
A graphic simple demonstration of this beginning is the pendulum, where the energy is changing from kinetics to potential, into the absence of friction, the sum of both constant and is named a mechanical energy. (Image prepared for @coolxxx).
A trasformación of the energy of big technological importance, is the one that turns the difference, between the mass of the resultant products in energy of nuclear origin. In the above mentioned reactions, a small quantity of mass leads to big quantity of energy, although, finally along any reaction the entire mass, and they have not changed the energy, that is to say, there is fulfilled the so-called beginning of conservation of mass and the energy.
In accordance with the relation of Einstein, E=mc ², where E is the energy, m the mass, c the speed of the light in the gap, the energy, which takes place from the mass, is the value of está multiplied by the square dela speed of the light in the gap, since it is the theory dela relativity, it demonstrates that it fulfills equivalence between the mass and the energy.
The broadcast of energy happens often by means of undulatory movements, that is to say across the waves, since they are perturbations, which departing from an origin, trasportan the energy with his advances. Also the waves present several characteristics that define her, the largeness, speed, frequency, and length, since the wave represents the distance that was measuring between two successive comb of the perturbation, because also it transmits a kinetic and potential energy, which goes to depend on his speed.
Potency.
Considering that the achievement of the work mentioned according to the time.
The physical magnitude defines this parameter it is the potency (p), that expresses the quantity of work that can do in a certain unit of time, and it increases for the same work, when it diminishes the time in which it realizes this one. The most used close one of potency is that of the international system (IF), and it is the watt (W); the watt is the potency of a machine, which realizes the work of a July (J), in a second (s), the potency of one watt, it is very small and normal to express the potency of the industrial machines the Kw is used (1000w).
Source of energy.
It is called a source of energy, those resources of the nature from which the man can obtain energy.

Not renewable energy. (Image prepared for @coolxxx).
Not renewable energy, they are those that become exhausted as they are used, as: the coal, oil, and the renewable energy, they are those which quantity, it can be considered that unlimited, that is to say, for much that should be used practically they do not become exhausted, as: the sun, the wind, the sea and the rivers.

Renewable energy. (Image prepared for @coolxxx).
Bibliographical reference.
Tipler, P. (1999) Physics for the science and the technology (Publishing house Reverté, S.A., Barcelona) vol. 1
Sears, F. et to. (2004) University Physics (Pearson Educación. Mexico) vol. 1
Burke, J. R. and S. M. Lea. (1998) Physics: the nature of the things (International Thomson Eds., Mexico) vol. 1
Resnick, R et. to. (2002) Physics (Cecsa, Mexico) vol. 1
Street, C. (2001) Superstrings and other things: to guide to physics (IOP publishing, Bristol and Philadelphia).
Magazines: Scientific American, Investigation and Science, The Recherche, Scientific World, Science et the Vie, American Journal of Physics
Physics Today, Databases: The Sciences, Springer Journal, Science Direct, Coastal Engineering, Engineering Structures
Serway. Physics. Publishing house McGraw-Hill (1992)
Tipler P. A. Physics. Publishing house Reverté (1994).
Alonso M. and Finn E. Physics. Publishing house Addison-Wesley Interamericana (1995).
Several authors. The physical Ist. The first four-month period of Industrial Engineering. I study 1998-99. Dpto. Applied physics the Ist, E. T. Ist century. Industrialists and of Telecommunication (Bilbao).
Several authors. The physical IInd. The second four-month period of Industrial Engineering. I study 1998-99. Dpto. Applied physics the Ist, E. T. Ist century. Industrialists and of Telecommunication (Bilbao).
Eisberg, Lerner. Physics. Essentials and Applications. Publishing house McGraw-Hill (1983).
Gettys, Keller, Skove. Classic and Modern physics. Publishing house McGraw-Hill (1991).
Burbano S., Burbano E., Grace C. General physics. Publishing house Tebar (2004)
Goldemberg. General and experimental physics. Inter-American publishing house (1972).
Sears, Zemansky, Young. University physics. Publishing Educational Inter-American Fund (1986).
Melissinos A . C ., Lobkowicz F. Physics for Scientist and Engineers. W. B. Saunders * Co (1975).
