Glycogen
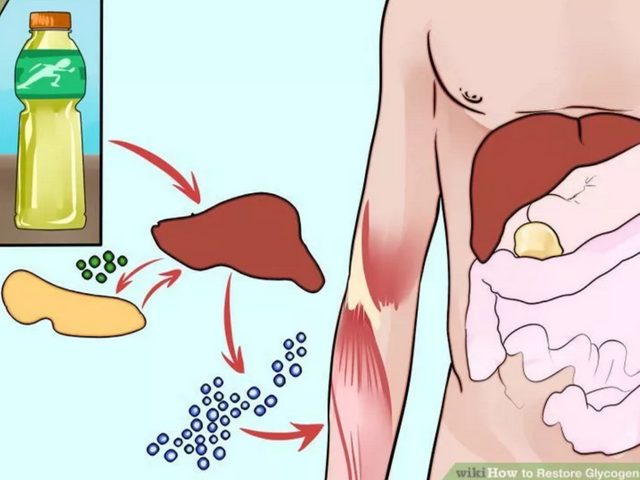
Glycogen is a branched chain of glucose which serves as an energy source for animals.
It can be stored in the liver and muscle. The liver contains 100 g to 120 g and from here the other organs can use it, but the muscles also contain about 500 grams (1-2% of muscle mass).
Why is there glycogen when we already have fat tissue as an energy source?
The fatty acid needs oxygen for the conversion of fat into energy, while glycogen provides energy to the body in an anaerobic mode.

What does this mean for you?
When doing activities of certain intensity, the body consumes energy depending on the intensity of the activity. We divides activities in three categories:
- < 10 seconds –PHOSPHAGEN system: Creatine phosphate is consumed at high speed and gives a tremendous amount of energy, also without oxygen. (Example sprinting, maximum lifts)
- 10 seconds - 3 minutes - GLYCOLYTIC system: Glycogen is consumedwithout the help of oxygen and gives the body glucose, which the body converts into ATP and uses to be able to continue a particular activity. The by-products are hydrogen ions and lactates that alter muscle pH and contribute to the appearance of fatigue. (Example weight training, 800 Metres run)
- > 3 minutes - AEROBIC system: The oxidation of carbohydrates and fats (in extreme cases protein).It usesblood glucose and glycogen, although fatty acids may be used to restore ATP. Fat has the greatest energy potential (9kcal / g) and therefore the body wants to keep it at all costs. (Example marathon, running, cycling ...)

Summary
Training that depends mainly on glycogen gives you a period of time after training in which the intake of carbohydrates focuses on replenishing spent glycogen stores (you can eat high glucose foods to an hour after training).
Thank you for reading.
Brief and informative. Thank you :)
That was the intention!
Thank you for your votes furion, always on time ;)
Well done, thanks for the info! You sure get my upvote, namaste :)