Ovarian Cysts
A story was told of a poor girl whose mother watched her die because she thought she was with child. How couldn't she be? She has all the signs and symptoms. To the ignorant mother, her daughter has brought shame upon her and her family by getting herself pregnant and she doesn't want anything to do with her. Amidst pain and tears, the daughter tried to make her mother understand that whatever was wrong with her was life threatening and she needed urgent medical attention but the mother care less until the poor girl lost her life and autopsy revealed that she has ovarian cyst which had ruptured causing her to have internal bleeding and hence her death.
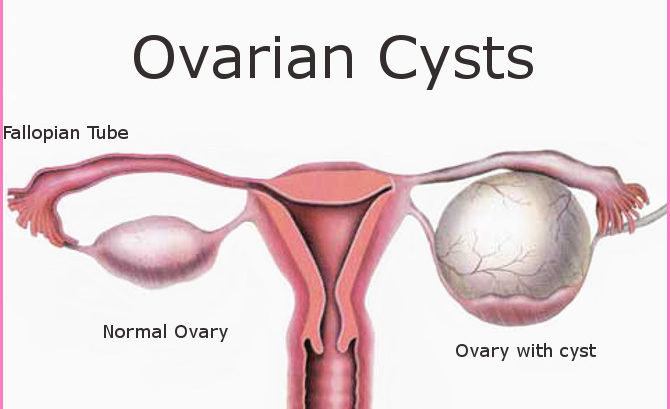
What are ovarian cysts?
According to Wikipedia, an ovarian cyst is a fluid sac within the ovary or on it's surface.
Small cysts are developed by most women of reproductive age monthly. Every woman's body contains two ovaries. The ovaries in the woman's body have the shape and size of an almond or a Walnut. The ovaries are located on each side of the uterus (womb). The ovaries are the major source of female hormones oestrogen and progesterone which controls the development of some features of the female body such as the breast, body shape, body hair etc. The hormones also regulate menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Ovarian cysts are developed on the ovary as a result of the menstrual cycle. Many women will develop at least one cyst during their lifetime. Majority of the cysts casue no harm to the body neither does it cause any discomfort. Although, these cysts can rupture or cause twisting of the ovary and thereby causing severe pain. Postmenopausal women have lower risk of developing ovarian cyst as they no longer ovulate or produce a significant amount of ovarian hormone.
TYPES OF OVARIAN CYSTS
- Follicular Cysts: This is formed when the follicle containing an egg produced during ovulation refused to break open. When this happens, the fluid inside the follicle form a cyst on the ovary.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: Corpus Luteum Cysts is formed when the opening of the follicle seals and additional fluid is developed inside the sac.
- Dermoid Cysts: Sack-like growths on the ovaries that contain hair, fat and other tissues.
- Cystadenoma: These are non cancerous growth on the outersurface if the ovaries.
- Endometriosis: This cyst occurs when the internal tissue of the uterus develops outside the uterus and attaches itself to the ovaries resulting in a cyst.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: This condition as the prefix "poly" which implies that it is a condition in which the ovaries contain a large number of small cysts. This causes the ovaries to enlarge and can lead to infertility if left untreated.
CAUSES OF OVARIAN CYSTS.
- History of previous ovarian cyst.
- Hypothyroidism
- Infertility treatment with gonadotropin medication.
- Early menstruation (11years or younger)
- Tamoxifin therapy for breast cancer.
- Obesity
- Irregular menstrual cycle.
SYMPTOMS
Most cysts do not show any symptoms and disappears on their own. Most time, large ovarian cysts are the ones with symptoms such as:
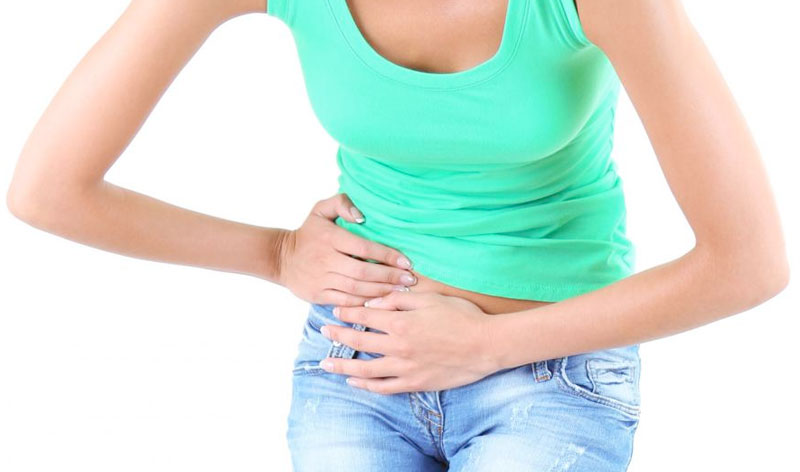
- Severe pain/sharp or dull pain in the lower abdomen. 2. Increased abdominal girth. 3. Bloating or indigestion. 4. Urge to have bowel movement or difficult/painful bowel movements. 5. Pain during intercourse. 6. Breast tenderness. 7. Excess thirst or urination. 8. Unexplained shoulder pain combined with abdominal pain. 9. Persistent fever.
DIAGNOSIS OF OVARIAN CYSTS.
Ovarian cyst can be diagnosed by carrying out the following:-
A. Vaginal pelvic ultrasound
B. Endovaginal ultrasound
C. Laparoscopy
D. Serun CA-125 assay
E. Hormone levels tests.
F. Culdocentesis
MEDICATION:
Hormonal birth control is used to prevent further cysts by suppressing ovulation and ovarian hormone production. Pain reliefs are also used to reduce pelvic pain.
TREATMENT
Treatment of ovarian cyst depends upon the cause of the cyst and varies from observation to monitoring to surgical treatment. Because majority of cysts disappears after a few weeks or months, doctors may not immediately recommend a treatment. Instead, a repeat ultrasound is carried out in few weeks or months. If no changes, additional tests will be recommended to determine the other causes of the symptoms. Ovarian cyst can be shrinked or removed via surgery.
NOTE: Consult a doctor when you feel a sudden severe abdominal or pelvic pain with fever or vomiting. Changes in menstrual cycle, loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss; visit your gynecologist.
REFERENCES:
https://www.healthline.com/health/ovarian-cysts
https://www.livescience.com/54135-ovarian-cysts.html
https://iytmed.com/cysts-on-ovaries/
Written by @zizymena, edited and posted by @camzy
Images source: GOOGLE



An ovarian cyst must be very painful for the woman suffering it, such a delicate problem but at least you mentioned the majority of them are not dangerous.
Very informative. Especially because they become more frequent and more frequent in the female population and need to think about their reproductive health. Thank you for sharing the information!