Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 6 - Homework Post for @stream4u


WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN?
Blockchain is a novel technology that involves blocks containing transactions connected to one another in a sequential manner.
In details, blockchain is a series of blocks (memory spaces that store transaction data) that are connected together (every block is represented in subsequent blocks and has a representation of previous blocks). Each of these blocks is timestamped and they are all arranged in order, from the earliest.
TYPES OF BLOCKCHAINS
There are four main types of blockchains. They are:
Public blockchains
Private blockchains
Consortium blockchains and
Hybrid blockchains
PUBLIC BLOCKCHAIN
A public blockchain is a blockchain that allows anyone to sign up and become an authorized node in its network. Such a user then gets access to the blockchain data, both past and current. Upon joining the blockchain's network, the user can participate in mining, verification of data, proposals of changes, etc.
This type of blockchain has no central authority but is governed by the users who signed up as nodes on the blockchain's network. These users follow an agreed protocol called a consensus algorithm, in governing the blockchain. They can propose changes and effect them as the code of the blockchain is open source
Multiple users governing the blockchain means validated transactions are very difficult to change.
Advantages of Public Blockchain
Sustainability: The blockchain is run by users who are usually well incentivized with rewards to invest time, efforts and resources. Thus, the blockchain has a very low chance of ceasing to exist as there is bound to be users running the blockchain and enjoying the benefits.
Transparency: The presence of a consensus algorithm through which the blockchain is run creates transparency. This consensus is known publicly and so are the activities of the nodes that apply the consensus. The details of transactions can also be publicly accessed.
Security: Where numerous nodes are competing to be verify transactions as a result of the lucrative rewards that accrue to being the first to do so, it reduces the financial feasibility of trying to be malicious.
Disadvantages of Public Blockchain
Scalability: Scalability is a major challenge for decentralized systems like blockchain. Centralized systems are known to be more scalable generally. Public blockchains experience this scalability issue as the users often find it difficult to agree on scalability enhancing fixes on the blockchain.
Security breach: Though unlikely but still possible. In public blockchains, if a single node or a group of nodes combined can wield up to 51% of the total computing power, they could exerct some dominance over the other nodes in the network and achieve some malicious objectives.
Non-private: The public nature of these blockchains discourages private setups from adopting it as they will be unable to exert control over these blockchains.
Use Cases Of Public Blockchains
Transparency and trust: Organizations that aim to achieve transparency and trust will find public blockchains very invaluable. These blockchains provide a great level of transparency and also have impressive trustworthiness.
Peer-to-peer trustless payment systems: Trustless peer-to-peer payment systems like bitcoin, are built using the public blockchain technology. This is because public blockchains enhances transparency and trust and can also facilitate decentralized transfer of digital assets.
PRIVATE BLOCKCHAIN
Private blockchains are an exact opposite of public blockchains. Not anyone can sign up and become an authorized node, this aspect is restricted to the management of the organization that owns the blockchain. It however, permits peer-to-peer decenralized transfer of information though on a small scale.
Private blockchains' networks are usually not as elaborate as public blockchains as they do have limited participants or users. They operate a close networks and are usually restricted to within the organization that owns the blockchain. They are under the control of the organization.
Advantages Of Private Blockchains
Ease of control: This type of blockchain is controlled by a central entity and as a result, changes and upgrades are quickly implemented.
Private usability: This type of blockchain caters for private organizations who would want to harness the potency of blockchain to improve on or run their operations.
Time efficient: Relatively smaller, private blockchains can process transactions faster. Their small network also mean fewer and faster transactions.
Disadvantages Of Private Blockchain
Lack of trust: There's a lack of trust with private blockchains as the validation is done by the single entity running the blockchain. This has led to some disagreement over the decentralization of private blockchains.
Insecurity: Since the validation is left to a few people, the requirement to achieve a malicious attack is far reduced, increasing the chance of insecurity.
Lack of anonymity: On private blockchain, the benefits of anonymity are non-existent. Every user is known as it is run by amd within an organization.
Use Cases Of Private Blockchains
- Voting: Perhaps one of the more important use case of private blockchain. Organizations can utilize private blockchains to achieve a successful voting process.
HYBRID BLOCKCHAIN
A combo of both private and public blockchains, hybrid blockchains are how organizations can benefits from the advantages of both blockchains. The data on the blockchain is restricted from the public alright, but through special smart contracts, they can be verified.
It satisfies both private and public blockchain description as it is owned by a central entity, but this central authority has not the power to alter the data on the hybrid blockchain.
Users can join the network, get access to data and also be anonymous but when the enter into a transaction they lose their anonymity to the other the other transacting parties. Interestingly, hybrid blockchains has some of the advantages of both private and public blockchains.
Advantages Of Hybrid Blockchains
Enhanced security: Though public users can join the hybrid blockchain network, there's not the chance of a 51% attack by any malicious node or group of nodes.
Anonymity: Anonymity is possible on the hybrid blockchain. Users have their identity hidden until they engage in a transaction then they lose their identity to the other transacting party.
Disadvantages Of Hybrid Blockchains
Limited transparency: Without smart contracts, the information can still be shielded, meaning it is not readily available like those of public chains that can readily be accessed through blockchain explorer.
Lack of incentive: This blockchain doesn't afford the benefit of participating as a node for rewards. Mostly, there are no incentives offered on hybrid blockchains. Recall that they are also privately owned.
Use Cases Of Hybrid Blockchains
- Medical records: One strong use case of this blockchain is in keeping and accessing medical records. These records are sheilded from the public but a user can access his/her medical records via a smart contract.
CONSORTIUM BLOCKCHAIN
The word consortium implies its original meaning. In this type of blockchain, members of an organization come together to run a blockchain. It has some public properties as any user can join in the network and become a node, only that, these member nodes can only initiate and receive transactions.
Advantages Of Consortium Blockchain
- Scalability: This type of blockchain is quite scalable, especially when compared to the public blockchain. One of the characteristics of public blockchains that reduces scalability is the number of validators or miners or decision makers. With consortium blockchain, this number is quite few, ensuring that agreements on upgrades that will improve the blockchain can quickly be reached and implemented.
Disadvantages
Low transparency: Consortium blockchains have an iota of privacy and this impedes transparency. The fact that not all nodes are able to validate transactions means that verification of transactions on the blockchain to an extent, is not transparent.
Low security: Another problem with privacy is that it also impedes security. One of the controlling nodes could be compromised and in that case, pose a serious security problem. This possibility of having nodes compromised is more than that of public blockchains.
Use Cases Of Consortium Blockchains
- Banking: This type of blockchain is very useful in the banking sector. Here, banks can come together to create a consortium blockchain. Amongst these banks, some will be selected to validate transactions. Customers can sign up and transfer payments but not validate transactions.

BENEFITS OF BLOCKCHAIN
TRUST:
With blockchain technology, the evidence of trust is reinforced. Where you have different miners competing to verify transactions and these verified transactions are visible to all and these transactions are almost unable to be altered.
DECENTRALIZATION:
Blockchain successfully executed the idea of decentralization. With blockchain, it is possible to have the power of control shared away from a central authority. This is because on blockchains, governance, validation and change proposals and implementation can be done by anyone who is an authorized node.
CONTROL:
Blockchain offers control to both organizations (private blockchains) and individual users (public blockchains) in a decentralized system. Users especially on public blockchains have total control over their assets and can't suffer sanctions from any central authority.
ANONYMITY:
Blockchain offers a means of payment where transacting party can transact without revealing their identity. They just need private and public keys to carry out the transactions. This anonymity has been one of the attractive benefits of the blockchain technology. Although details of the transaction is revealed, it does not include the identity of the transacting parties.
SECURITY:
Some blockchains, especially public blockchains make it difficult to carry out a malicious attack as a lot of resources is employed to confirm transactions and these resources are expended in a race to be the first to confirm transactions in a block. To carry out a malicious attack the attacker will need to control 51% of the computing power. This is a very huge difficulty.

BLOCKCHAIN DISTRIBUTED LEDGER
A distributed ledger is a record which is shared among different entities (called nodes) in different locations and is accessible by a lot of people. When these record changes at any node, the whole record at every node also changes. The blockchain distributed ledger enables transaction to be carried out under the watch of the public.
Each node has a copy of all the transactions done on the network and is also entitled to every data shared on the network.
ADVANTAGES OF DISTRIBUTED LEDGER
NO SINGLE POINT OF FAILURE:
With distributed ledger, data compromised at a particular node is only compromised at that node unlike a centralized ledger. In centralized ledger, once the central storage is compromised, malicious attacks can go on.
SECURITY
Where multiple nodes have to verify transactions and employ huge resources to do so, malicious attacks on the network is such a grave task. It not only so much effort but also enormous resources as well, so difficult is it that it has not yet been done on major blockchains like bitcoin.

DOUBLE SPENDING
Double spending is a type of security breach in digital currency systems where one coin is spent more than once. This is peculiar to digital currencies unlike physical currencies.
This is because digital information can be created by someone who understands how the digital system works whereas physical currencies can hardly be duplicated or created by anyone except the respective issuing bank.
Take for instance,
Mr. A has 0.5 BTC and then sends 0.2 BTC to Mr. B for the purchase of a Car and 0.3 BTC to Mr. C for the purchase of a motorbike.
If Mr. A can out-compute the other nodes in the network, he could do some thing malicious like reverse the 0.2 BTC he sent to Mr. B's wallet and the 0.3 BTC he sent to Mr. C.
Mr. A would then have his 0.5 BTC back and could even spend it again on a house or something else. In that case, Mr. A would have spent his 0.5 BTC twice.
Note: Over-computing occurs when a node or group of nodes control about 51% of the total computing power of the blockchain.
HOW BITCOIN PREVENTS DOUBLE SPENDING
Bitcoin prevents double-spending through:
Confirmation and
Time-stamping
Confirmation:
On the bitcoin blockchain, every transaction is confirmed over and again. Blockchains like bitcoin that uses Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, once a transaction has been confirmed, it cannot be reversed. So double-spending through reversal of transaction has to be by the 51% attack which is very unlikely as it has not yet been done.
Time-stamping
Transactions are confirmed and time-stamped as well. Once they are time-stamped, a duplicate of the transaction coming later becomes invalid. This is because the time-stamped is what is used to join the various blocks in a chain.
A time stamp indicates the existence of a transaction at the particular on the stamp and contains the timestamp of the previous block. When a similar transaction happens later, it is easy to detect it and nullify it as it will be cross-checked through the PoW mechanism.
On bitcoin the Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism enables the verification of transactions and crosschecking them to identity invalid ones.

BLOCKCHAIN HASH
A hash is a string of data that has a fixed length and represents another string of data. It is generated to always have a certain number of characters no matter the data thatbit used to generate it. The hash of a particular data will always be the same for that particular data.
However, if the data changes, even if it's a little, the characters in the hash changes but the length of the hash remains unchanged. A hash cannot be reverse engineered. This, it helps conceal transactions details, though the transaction can be deciphered because a hash is always exactly the same for a given data.
Usually, a block on the blockchain is hashed to produce a hash that will represent every other data in the block. Each transaction in a block is hashed and the resulting hashes are hashed. The hashing of resultant hashes continue in a cascade pattern until a final hash emerges. This is called the root hash.
The root hash is added to the block header which also contains the hash of the previous block, the timestamp the hashing difficulty, the blockchain version number (for bitcoin), the hashing difficulty, and a nonce.
The block header is then hashed repeatedly, with the nonce being changed at different trials just to get a hash that will meet the mining difficulty. When this is reached, the block header and the block is hashed.
Once any change occurs in the data that generated the hash, even the slightest, the hash is altered.
Take for instance, an empty data string, with no input entered,
The hash is - e3b0c44298fc1c149afbf4c8996fb92427ae41e4649b934ca495991b7852b855
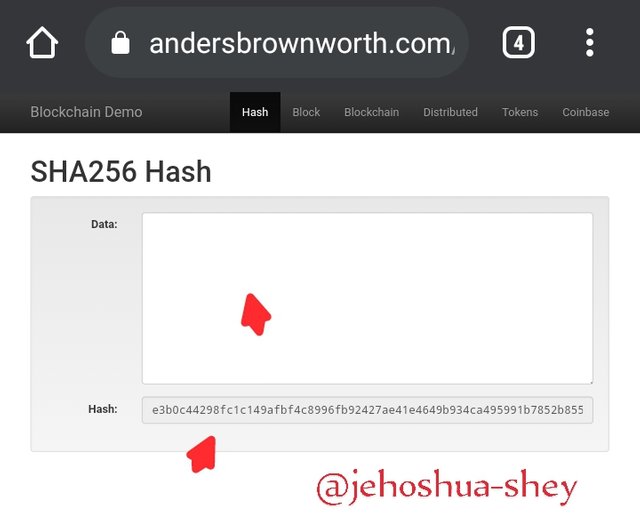
An empty string return a hash
Now we change the data from empty and write down the following words 'Hash has fixed length'
Then the hash changes to -
aff1d43ab84e58d03131e91b4449d26687ad10f5fa1efa6cbd5d2b1b50e9a396

The hash is changed when the data in the string is changed
CHANGES IN BLOCK HASHES IN BLOCKCHAIN
In blockchain technology, each of the block has a hash that represents every data in the block.
Now, the block hash in a block on a blockchain is the hash that is used to confirm the block. It is made up of every details in the block. When the details in a block changes, the block hash changes. For a block hash to be valid, it must meet a certain target criteria.
Let's take an example below:
The block data we'll use is:
Block number,
Nonce, and
Data
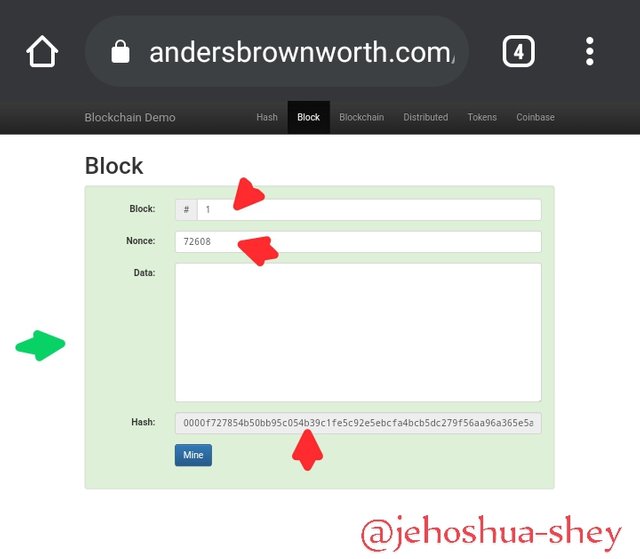
The target criteria is that the hash starts from '0000' (four zeros).
From the image below, with an empty data string, and a pre-input nonce and block number, we see that the target hash has been met. Notice the green colour background.
But on changing the data, the confirmation is jeopardized and the background color turns red. A close look at the hash, will reveal that it doesn't meet the target hash as the hash doesn't start with 'four zeros'
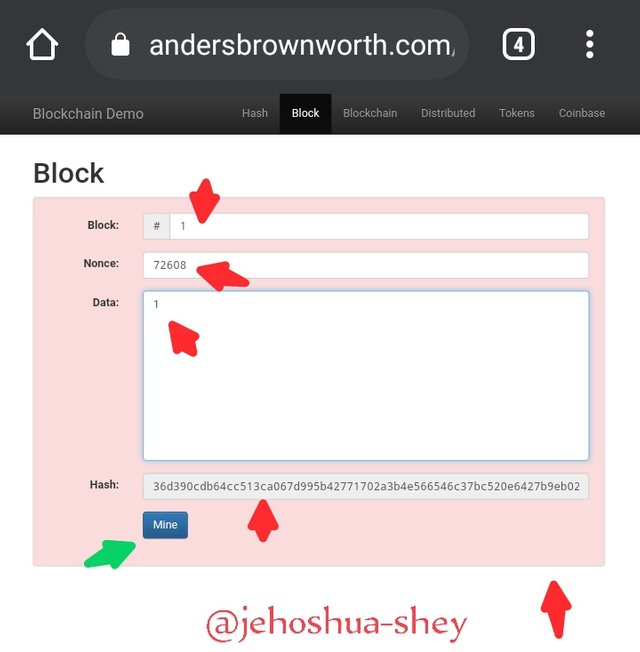
Thus, when the information in a block is changed, the hash automatically changes and the block will have to be re-mined to confirm the change.
On this note, we'll re-mine the block by altering the nonce since we've altered the data in the block. To do this, we simply click 'Mine'
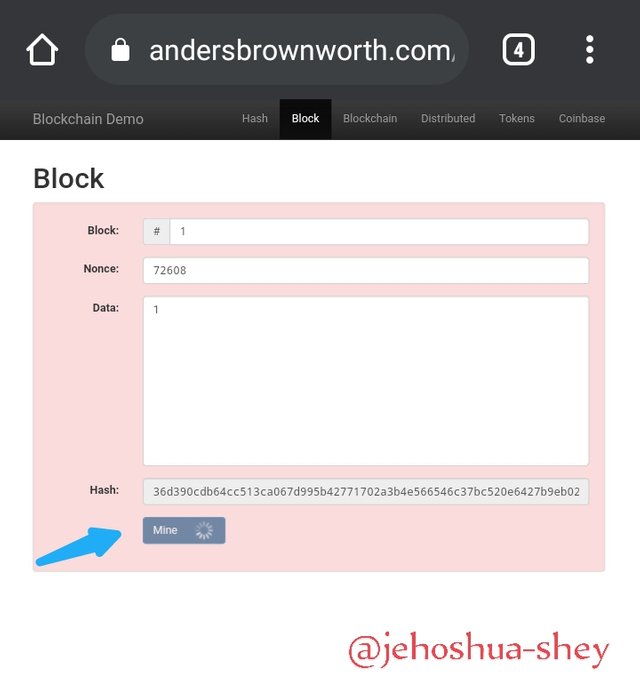
Then, after sometime, a nonce is iterated or guessed that when combined with the block number and the block data, gives a hash that meets the target hash (i.e a hash that begins with '0000' or 'four zeros')
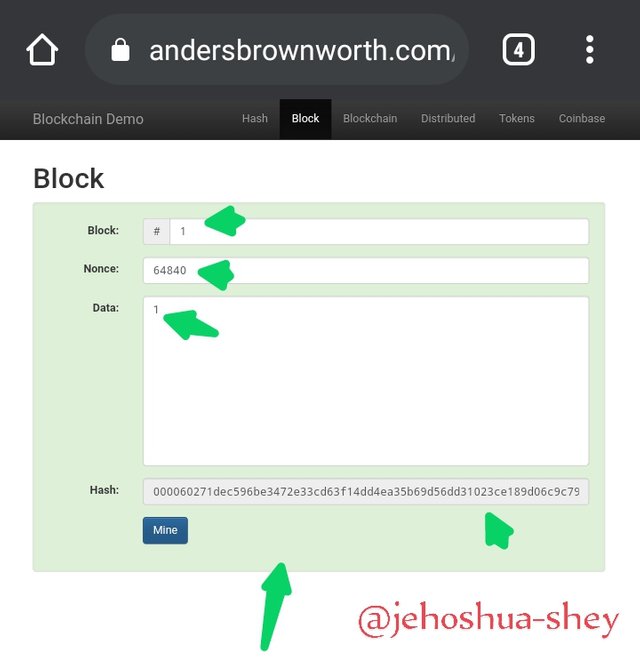
The background color changes again, from red back to green, indicating a confirmation.
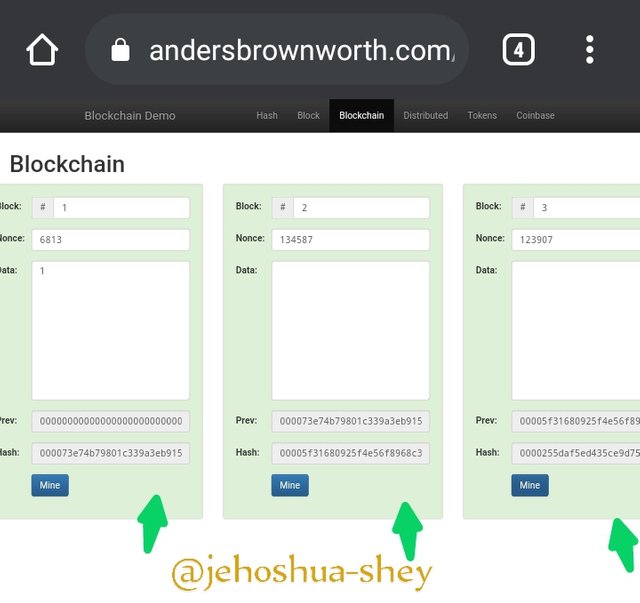
Changing the data in a block has an effect on the blockchain in general. Lets see how this affects the blockchaim with another example.
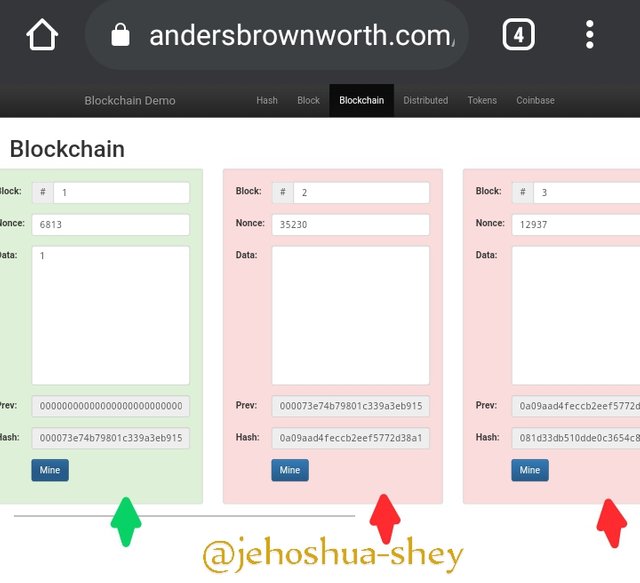
In this example, we have 3 blocks in the blockchain - the genesis block and next two blocks.
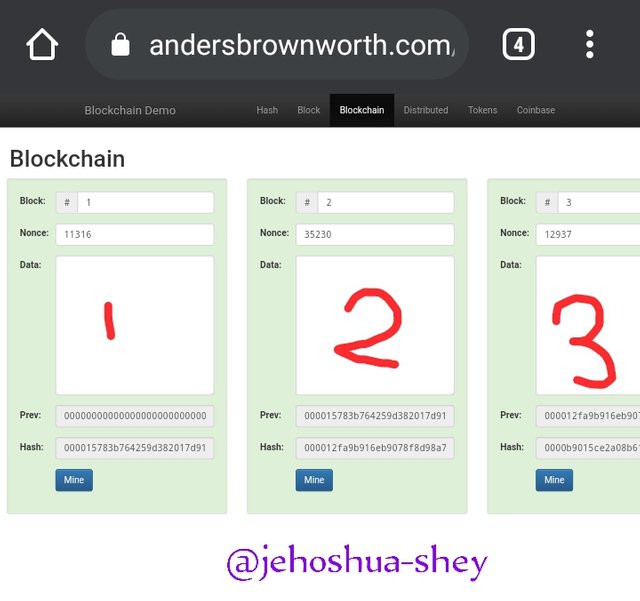
Note the following data.
Block 1:
Block No.:
Nonce: 11316
Data:
Prev. Hash: 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Block Hash: 000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf
Block 2:
Block No.: 2
Nonce: 35230
Data:
Prev. Hash: 000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf
Hash: 000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19
Block 3:
Block No.: 3
Nonce: 12937
Prev. Hash: 000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19
Hash: 0000b9015ce2a08b61216ba5a0778545bf4ddd7ceb7bbd85dd8062b29a9140bf
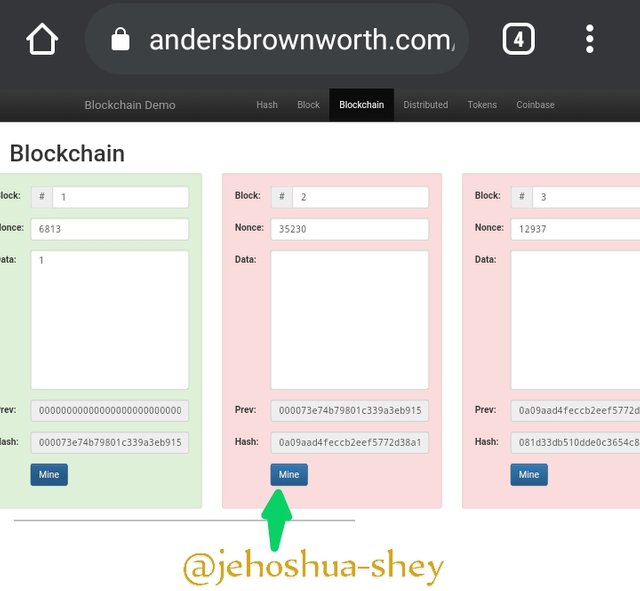
Now, let's make a change to the first block by adding to the data the number - '1'
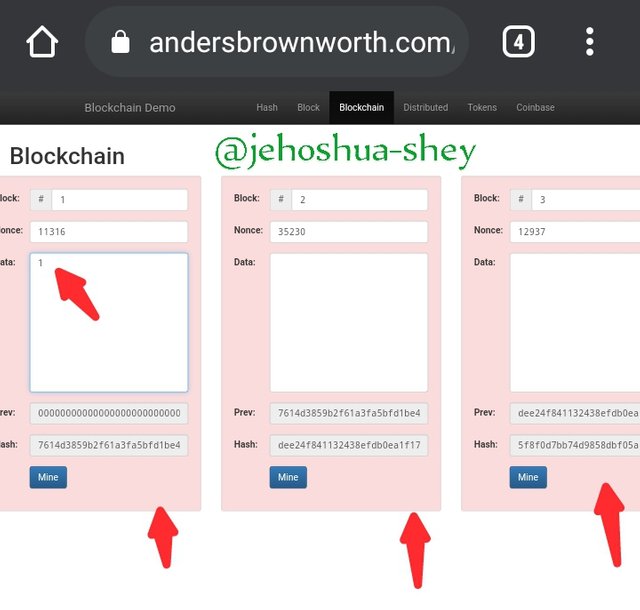
From the image above, you notice that all the other blocks after the first block were affected and will all have to be re-mined. This is clearly indicated by a change in color from green to red.
This change is because the hash of the first block was changed as a result of the change in the 'data'. The hasb of the first block was also used in getting the hash of the second block, so a change meant that the hash of the second block must also change. This in turn affects the hash of the third block.
Evidently, when the data in a block is altered, there is a ripple effect on the blockchain as the hash of the block is first altered, which alters the hashes of subsequent blocks which are generated with the hashes of the previous blocks.
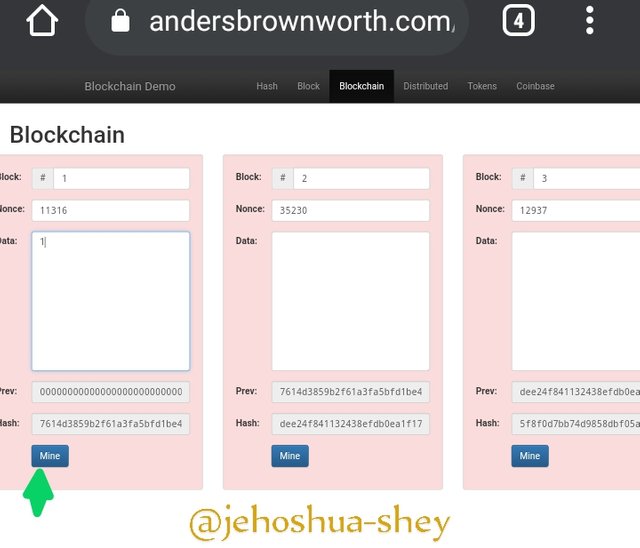
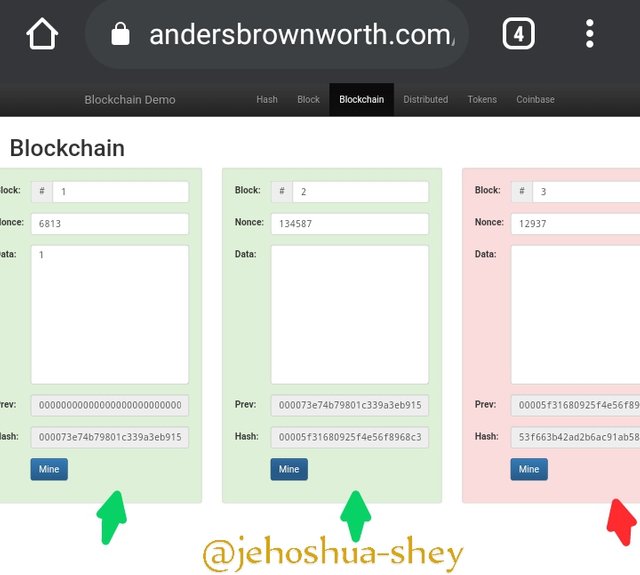
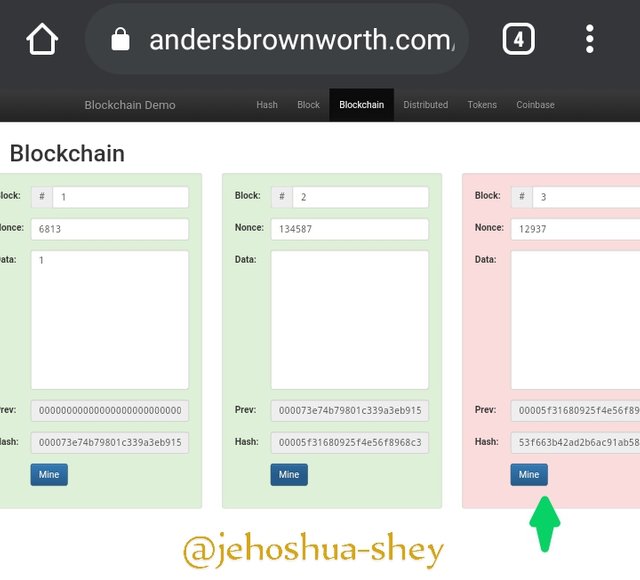
FIXING THE ALTERATION
Now, if by any means a block data is altered, also altering subsequent blocks, each altered or affected block has to be re-mined one after the other.

RACE ATTACK, FINNEY ATTACK, AND VECTOR76 ATTACK
Race attack:
This attack is a double spending attempt where an attacker sends two payments transactions with the same coin balance. This can be successful if the receiving party doesn't wait for confirmation before dispensing the item supposedly paid for.
Waiting for even one confirmation can nullify this attack as the false transaction is usually rejected during the confirmation process of the block.
Finney attack:
This attack is an advanced form of double spending attempt in that it requires a miner. In a Finney attack, a miner sends a transaction through a block he controls or created but doesn't broadcast the block. After the items would have been delivered, the miner does another transaction to himself and broadcasts it before the first transaction.
The miner could send the coins to himself first then send the coins to the seller, putting the second transaction in a pre-mined block. He broadcasts the first transaction himself but the other one doesn't get confirmed though the rejection may take some time.
Waiting for at least 6 block confirmations can negate a Finney attack.
Vector76:
Vector76 combines both Finney and Race attacks in one grand double spending scheme. It also involves a miner and can execute double spending by reversing a transaction even after one block confirmation.
Here the miner creates two nodes, one he connects to peers and another to an exchange node. Then he sends two transactions, one of high value and another of low value.
The one of high-value he sends to the exchange node. When the exchange confirms it, he then sends the one of low value to the peers for confirmation. This second transaction gets more confirmations and the first later gets rejected though it was confirmed earlier by the exchange node.
Waiting for at least 6 confirmation is advised and also, connecting nodes to well connected peers.

DISADVANTAGES OF BLOCKCHAIN
SCALABILITY:
This is one of the most pressing disadvantage in blockchain technology. It is the inability of blockchain to increase its capacity as the usage of the blockchain increases. Most blockchain have this problem of scalability with transaction speed being a major drawback.
SECURITY:
Transaction over the blockchain could be well verified but then, there's a security issue for those not acquainted with the operation of blockchain, these could easily fall prey to scams and dubious schemes and there is no cenral authority to investigate and track the perpetrators.
ANONYMITY:
Anonymity is a problem because through it a lot of crimes can be facilitated. Criminals can launder money through blockchains, steal money over blockchain and sponsor crimes through blockchain untraced. This creates a serious problem for policing in the crypto world, a deficiency that has seen crimes thrive in the crypto space.
ENERGY CONSUMPTION
Mining done on blockchains require lots of energy. Bitcoin requires more energy than some countries in the world today. This energy requirement has out off some investors and has raised a concern in some countries. This concern has led to various unfavorable regulations being placed on some blockchains eg. bitcoin.
EXPENSES
Participating in a blockchain's activity is usually very expensive. Mining for instance, which involves lots of energy and money can't be afforded by people with low budgets. This is a very serious deterrent in blockchain participation.
DECENTRALIZATION
In normal finance, when someone has been discovered to be a fraud, such a person can be suspended from using the financial service and their assets seized, but it's not so with blockchain. Even if a criminal is caught, they may not release their keys and so the funds can't be recovered. Moreover, if the criminal is released, they can still carry on with their criminal activities without any ban whatsoever.

CONCLUSION
Blockchain is a very interesting innovation, perhaps, the eight wonder of the modern world. It has very unique features like hashes and immutability and seems to be very secured. Though a facilitator of decentralization, blockchain still achieves very commendable levels of genuine confirmation on transactions done over the blockchain.
The blockchain has flaws though as it is usually limited in the area of scalability. Security and expenses also militate against the use of blockchains.
Hashes also ensures that an attack on the blockchain network is majorly theory. Once a blockchain has been confirmed, it is all but immutable since changing any data in a previous block will require the re-mining of subsequent chains which is time and energy consuming.
Thanks for reading.
Cc:
@stream4u
Hi @jehoshua-shey
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 10/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thank you so much for your lecture and remarks prof @sapwood. Indeed, I learnt something new.