Acute Myeloid Leukemia - Know Your Health Series #2
Let's take a detour and get to know what leukemia is.
It sounds strange to hear the word leukemia. Growing up and before entering medical school, I thought of it as a fatal disease that could clear the existence of man off record but the truth is, I got to know that it could be feared tho but there are measures in place to cure this awful canker.
Image Source
What is Leukemia?
Leukemia is a clinical condition which stands for a group of cancer/malignancies associated with the white blood cells. Basically it is the accumulation of uncontrolled proliferated white cells within the bone marrow of man. Still confused? In a layman's language, leukemia means a particular type of blood cells called white blood cells multiply uncontrollably and become many(rise) above its normal level within the bone marrow.
Leukemic patients showcase symptoms related to bone marrow failure (anaemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia) and organ infiltration.
Classifications of Leukemia
There are two broad classifications of leukemia.
- Acute Leukemia
- Chronic Leukemia
These types are further subdivided into myeloid and lymphoid acute/chronic leukemia. I know things are getting complicated as we are moving further but take in a deep breath and let it all sync in lol. It's quite simple. Now let's get to know what acute (myeloid) leukemia represents.
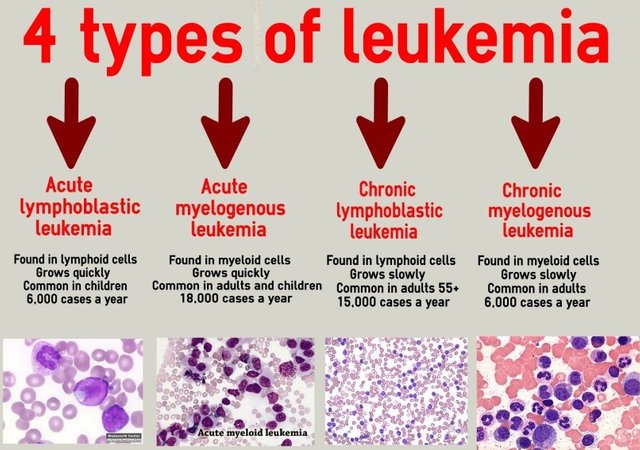
Image source.
Acute Leukemia
Acute leukemia usually occurs suddenly and known to be the most aggressive form of leukemia. In here, the malignant transformation occurs in haemopoietic stem cells (where the blood cells originate from) or early progenitor cells. From a scientific background, I would say that acute leukemia arise from the malignant proliferation and accumulation of blast cells in the bone marrow (BM). Acute leukemia is rapidly fatal if untreated and leads to bone marrow failure due to the accumulation of blastocytes (dominant clinical feature).
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
I made this the main ingredient of this blog because I wanna throw some lights on it and leave the general leukemia for another blog. I read about this topic two semesters back and felt I must share it to help my fellow colleagues who work in a biomedical laboratory come out with more convincing results after diagnosing a leukemic condition.
To set it in action, let's delve into the incidence of AML (acute myeloid leukemia).
Do you know that age group influences the incidence of AML? From authors of various books, AML is the most common form of leukemia in adults and becomes increasingly common with age with a median onset of 65years.
| Age group | Type of acute leukemia prominent |
|---|---|
| Adults >65years | 80% AML; 20% ALL |
| Children <15 years | 80% ALL; 20% AML |
*ALL = ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
*AML= ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
FAB Classification System for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Two main classification systems come in play when subtyping AML into various groups. These classification systems are FAB & WHO systems. In this blog, my emphasis will be on the former and the latter treated later in subsequent blogs.
AML is different from the other forms of cancer which are well known. AML do not form tumors. It is generally widespread throughout the bone marrow and in some cases spread to other organs such as liver and spleen. Knowing the subtypes is very useful in determining a patients outlook and deciding on treatment.
In the 1970s, a group of French, American, and British leukemia experts divided AML into subtypes, M0 through M7, based on the type of cell the leukemia develops from and how mature the cells are. This was based largely on how the leukemia cells looked under the microscope after routine staining.Document source
Under FAB, patients' samples (mostly bone marrow aspirate or occasionally peripheral blood before /during organ infiltration of the blastocytes) are stained on a glass slide and viewed microscopically. With peripheral blood smear, it is believed that after the blast cells have attained a higher level in the BM, some migrate into circulation (they do not stay in the blood forever though) and start to infiltrate organs.
The table below is a summary of the various subtypes of acute myelogenous leukemia and their diagnostic features.
| Type of AML | Diagnostic Feature |
|---|---|
| M° (Undifferentiated AML) | Predominantly immature blast cells observed |
| M1 (AML with minimal maturation) | Predominantly immature blastocytes with a little differentiated cells observed in the blood film |
| M2 (AML with maturity) | Predominantly myelocytes in blood film |
| M3 (Acute Promyelocytic leukemia) | Mostly hypergranular promyelocytes are observed |
| M4 (Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia) | Predominantly monocytes /myelocytes present |
| M5a ( Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia) | More monoblasts present than monocytes |
| M5b (Acute Monocytic Leukemia) | More monocytes than monoblasts present |
| M6 (Acute Erythroid Leukemia) | Presence of nucleated/Immature red blood cells |
| M7 (Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia) | Presence of immature forms of megakaryocytes (precursors of platelets) |
Images of the Subtypes of AML from a blood stained film
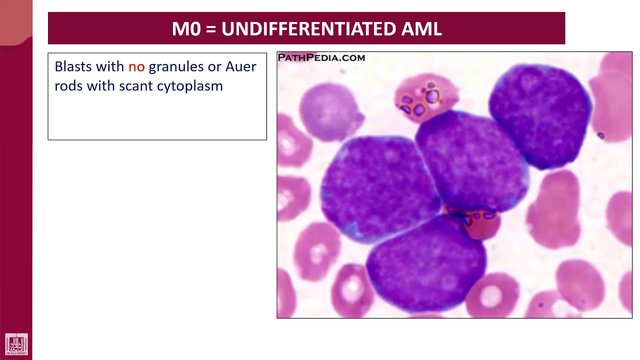
Source
To know a blast cell, the cytoplasm must not contain granules. Granules are present from the promyelocytic stage upwards.
.jpg)
Source
For more images on the various types of AML, click here
Differential Diagnosis
AML could result in:
- Pancytopenia
- Neutropenia
- Anaemia
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy (M3)
- B cell lymphoma etc.
A very important criteria of AML is ensuring that the underlying diseases are as a result of the malignancy and not other contributing factors. For instance, pancytopenia can result from vitamin deficiency or autoimmune diseases and not AML per say. If care is not taken, a patient might suffer and die from misdiagnosis. Pancytopenia due to acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a life-threatening emergency that must be aggressively treated immediately.
Thanks for your input, many people do not understand what to do at the time of this diagnosis, many people do not know what is that disease; With your publication, it motivates me to continue researching to expand knowledge and transmit it to the community where we live, the place where we work, the link where we study, that is, we must spread the information.
Excuse my English, I'm Venezuelan and I must use a translator
Don't worry about your English bro 😂. I am just happy your loved my publication and that you are going to help people learn about their health. Stay awesome
I always find it difficult to keep memorizing the types of AML. Nice to have some recapitulation.
Wonderful Health related article
Posted using Partiko Android
@hafiz34, i appreciate you kind comment. You can always passby my blog to learn more.
Great information. Thanks
You're mostly welcome @wanasoloben
To listen to the audio version of this article click on the play image.

Brought to you by @tts. If you find it useful please consider upvoting this reply.
Congratulations,
you just received a 14.79% upvote from @steemhq - Community Bot!
Wanna join and receive free upvotes yourself?
Vote for
steemhq.witnesson Steemit or directly on SteemConnect and join the Community Witness.This service was brought to you by SteemHQ.com