Uremia
Uremia is a clinical syndrome associated with fluid, electrolyte, and hormone imbalances and metabolic abnormalities, which develop in parallel with deterioration of renal function. The term uremia, which literally means urine in the blood, was first used by Piorry to describe the clinical condition associated with renal failure.
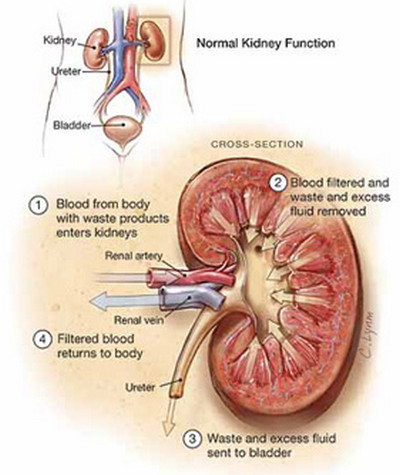
It occurs when urea and other waste products build up in the body because the kidneys are unable to eliminate them. These substances can become poisonous (toxic) to the body if they reach high levels.
Uremia may cause you to have some of the following symptoms:
extreme tiredness or fatigue
cramping in your legs
little or no appetite
headache
nausea
vomiting
trouble concentrating
The chief cause of uremia is damage to the kidneys, which has a variety of causes. Diseases that can affect kidney function include Bright disease (glomerulonephritis), chronic hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Blockages of the flow of urine due to urinary stones or, in males, enlarged prostate glands can also cause uremia
Treating Uremia
Uremia treatment requires hospitalization to properly care for the underlying health condition, targeting the kidney filtration function. This may be done with intravenous fluids, blood transfusions, fluid therapy, medication treatment, and hemodialysis. It is important to eliminate the potentially harmful amounts of nitrogen waste and promote normal blood circulation.
Surgery
Renal replacement therapy can be accomplished by hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or renal transplantation. Referral to an appropriate surgeon (ie, vascular, general, transplant) is made after the modality for renal replacement therapy has been determined.
medications employed in the management of uremia are indicated for associated metabolic and electrolyte abnormalities, such as anemia, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperparathyroidism, and iron deficiency. Agents used include erythropoietin (EPO) for anemia, iron, phosphate binders, calcitriol for parathyroid hormone (PTH) suppression and hypocalcemia, water-soluble vitamins (eg, folate, vitamin C).

Thanks for sharing this beautiful information.
health medical