Refrigeration: Working Principles and Cycle (Actual and Vapourized)
|
INTRODUCTION
The Process of removing heat from a low-temperature reservoir and transferring the heat to a high-temperature reservoir is known as Refrigeration
Basically, Refrigerators work by the means of passing cool refrigerant gas around food items (kept inside the fridge) for house refrigeration and the cool refrigerant absorbs the heat from the food and then loses that heat to the relatively cooler surroundings outside.
Refrigeration has been saving the life in a way that it can soothe your patched throat as a chilled glass of water can do.
In the ancient days, people have different techniques for Cooling water but there is no way they could keep their food fresh for days or even weeks.
.png)
The above diagram shows the cycle of a refrigeration system and the 4 major components that do the cooling. In a refrigeration system, there is a chemical refrigerant(Freon) which is a chemical compound and can easily change state from liquid to vapour and also from vapour to liquid.
In addition to the refrigerant, an air conditioning system requires a minimum of four components, the compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator.
- The Compressor:
 compressor image from Wikimedia commons under CCO license
compressor image from Wikimedia commons under CCO license
The compressor works exactly as the heart of the body, the job if the heart is to pump blood through the body at a particular flow rate and pressure; likewise, the compressor in a refrigeration system the compressor pumps the refrigerant through the refrigeration system at a particular pressure and flow rate.
The refrigerant enters the compressor as the vapour. The compressor sucks in the refrigerant from the suction side or the low-pressure side. Vapour is compressed in the compressor as it is being pumped through it and when vapour is been compressed both the pressure and temperature of that vapour increases so the vapour leaving the compressor is very hot.
- The Condenser:
The high-temperature refrigerant that is coming from the compressor is passed into the condenser. As the vapour refrigerant moves through the condenser, it has been cooled by an air from a fan passes over the condenser. As the vapour cools it condenses it changes state from vapour to liquid as we see on the outer part (condensing unit) of the air-conditioners or at the back of a fridge. You can be practical about it by placing your hand over this unit and feel the warm air being blown out. In the condensing unit, high-temperature vapour refrigerant is entering into it, as the heat energy in the vapour is removed by blowing air across the condenser coil, the vapour changes to a liquid.
- The Expansion Valve
The expansion valve controls the flow of the liquid refrigerant from the condensing unit to the next the evaporator. The expansion valve is a dividing point between the low pressure and high-pressure sides of the system. As this high-pressure liquid refrigerant is passing through the expansion valve and into the evaporator the pressure drops.
- The Evaporator:
After the refrigerant leaves the expansion valve it enters the evaporator. The evaporator has a fan also that is blowing across it. Refrigerant entering the evaporator at very low pressure begins to boil and then change state again back to vapour from the liquid. During this process of changing state heat energy is been removed from the passing air over to the evaporator and it is been absorbed by the refrigerant i.e heat that was in air initially is been transferred into refrigerant.
So the cycle proves when heat is been removed from the air blowing over the evaporator, the air leaving the refrigeration system is cold, this is the cold air that keeps the room or office cold or the food in the fridge fresh because the heat that is in the air absorbed is gone into the refrigerant depending on the adjustment of the temperature from the thermostat.
And finally there is heat from the food in the freezer or the heat from the room is in the refrigerant and what does the system needs it for?
The heated refrigerant in a vapour state is been sucked backed into the compressor, the heats that are been absorbed by the refrigerator in the evaporator from the environment or inside the fridge is released and removed.
°°°The process of the refrigerant changing states from vapour to liquid ( releasing heat through the condenser) and from liquid to vapour(absorbing heat in the evaporator) is how a refrigeration system workssource
Working principle of the Refrigeration system
Simplifying all this process is saying that the removal of heat from one region and putting it in another region. When a low-temperature liquid close to an object you want to cool, the heat from that object is been transferred to the liquid and also take away the heat in the process.
Gasses heat up when compressed and it cools down when it is expanded. Example is the bicycle pump...... It feels warm when it is used to pump air inside a tire and when it is sprayed it is cool.
Actual Refrigeration Cycle
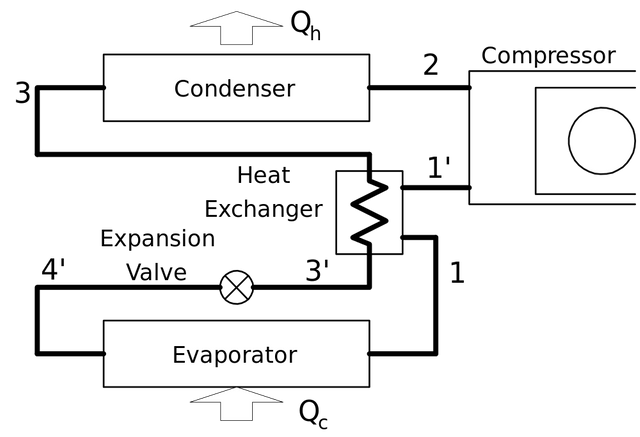 The schematic diagram of the refrigerator: img from Wikimedia under CCO license
The schematic diagram of the refrigerator: img from Wikimedia under CCO license
First, the cycle is an ideal cycle.
In an ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle, the refrigerant enters the compressor as a saturated vapour and is cooled to the saturated liquid state in the condensersource.
The chemical compound (Refrigerant) at a low pressure and temperature is sucked in through the suction side of the compressor. In between the suction side of the compressor and the evaporator is an accumulator that collects liquid refrigerant that is released off the evaporator and to prevent incomplete evaporation from getting back to the compressor. The next step is in the condenser where the vaporized refrigerant is condensed into a liquid form at high pressure but low temperature. The liquid refrigerant at high pressure formed in the condenser flows through a filter into the expansion device. The high-temperature refrigerant which is flowing from the expansion device passes through the expansion valve and cools down some of its heat to the cold suction line. An increase in the heat absorbing quality of the liquid refrigerant then occurs which increases the heat of vapour entering the compressor.
The regulation of the flow of liquid refrigerant and change of state is done by the expansion valve and in the evaporator, liquid refrigerants evaporate by absorbing heat from the space and then the cycle is repeated over and over again.
The Vapor Compressed Cycle of the Refrigeration Cycle
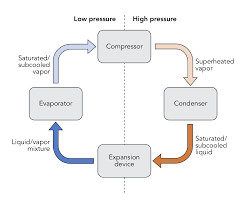 The vapour compression cycle: img from Wikimedia under CCO license
The vapour compression cycle: img from Wikimedia under CCO license
The refrigeration cycle is an ideal gas vapour cycle in which a maximum number of assumptions or conditions are neglected. The basic stages of the refrigeration cycle are Compression, Condensation, Expansion and vaporization.
The vaporized refrigerant that is at low pressure and temperature is been sucked into the compressor where it becomes compressed isentropically and when the temperature and pressure are been increased.
The vapour after leaving the compressor to the condenser where the vapour changes state to high-pressure liquid and from there it moves to the expansion valve where it is been reduced to a lower temperature and pressure. Then the refrigerant goes back through the expansion valve where and into the evaporator which extracts heat from the insulated space and vaporizes to low pressure vapour.
CONCLUSION
As the cool refrigerant gas flows through the chiller cabinet or the room or office, it absorbs the heat inside and vapourizes and then the refrigerant that should now a gas flows into the compressor, where it is sucked inside and compresses the molecules together to make it into a hot, high pressure gas.
The refrigeration cycle has so many applications and can also be inverted to produce a heat engine in the principle that the principle of cooling will now be for heating which can be used in a microwave, hair dryer and more.
References
.gif)
The refrigeration has done a lot in the lives of everyone. One way or the other. Through medicine, storage, transport, comfort, and many more.
This is brilliant studying what brings about refrigeration although i did something similar few weeks ago. This is nice.
Thanks for stopping by
Much appreciated..... I read your work about refrigeration... I liked it but I noticed you touched so many areas and little explanation of them
But it was an inspiration for this tho
Yeah.. I am glad i was able to inspire you.
Nice technical post. I like the red wine but it doesn't belong in the frige.
Congratulations @mittymartz! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
To support your work, I also upvoted your post!
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPGood read.
Are you planning to join @originalworks this weekend and write about FarmaTrust ? Your previous post about Crowd Machine has been really easy to read. I think you should join this contest again :)
Also I've made my first contest ever. Would you mind checking it out and sharing your feedback? And perhaps also commenting as Im interested what is your view on discussed issue:
https://steemit.com/blockchain/@crypto.piotr/mini-contest-how-ai-supported-by-growing-blockchain-technology-can-change-the-world
I would really appreciate if you could share some of your experience with me :)
Cheers, Piotr
And obviously upvoted and followed :)
Yea am participating
Great. Good luck. Gonna go and read your post now :)
I cannot find our post about FarmaTrust .... but I've found some poems :)
are you an artist?
Hey, good post but I'd just like to point out that you put cc0 under your image licensing, when the first one I checked was in fact CC4.0.
It's still Ok to be used but would be better to keep things clarified ^__^
Thanks for the correction
I would work in it
Nicely written article sir.
Thanks bruv
Interesting topic.
Thank you!