SCIENTIFIC FACTS ABOUT GSM BASE STATIONS AND COMMON MISCONCEPTIONS OF ITS HEALTH EFFECTS
Some Facts About GSM Network Base Stations

It has been a tremendous increase in the use of mobile communication services over the last few years. To provide better and adequate communication services to the substantial growing users, there is need to also increase the number of base station sites. The increment in numbers of clustered base station especially within dwellings and urban areas has begun to raise public concerns about possible health implications of these communication systems.
3G mobile phone networks require more base stations than 2G mobile phone networks because 3G operates at a higher frequency where radio waves do not travel as far. The higher data rate services provided by 3G also requires more base stations and the coverage area decreases as the traffic increases. Many 3G base stations will be able to share with existing 2G base stations, however, some 3G only base stations will be required. Source
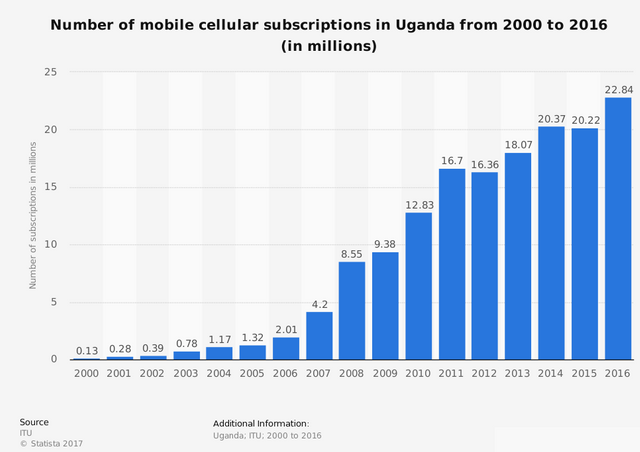
The graph to the right shows the statistics of cellular phone subscribers from the year 2000 to 2016 in Uganda. The tremendous increase in the number of subscribers (0.13 - 22.84 Million) within the year 2000 to 2016 will definitely increase the number of network base stations and equipment so that adequate services provision could be achieved.
A research work conducted by Statistic Brain Research Institute shows that the number of cell phone towers in the US increases from 900 towers in 1985 to 215,000 towers in 2017. The research work also reveals the number of cell tower worker deaths per 100,000 workers to be 183.6 per year. The work does not reveal the actual cause of the estimated number of deaths.
In some area here in Nigeria, people are abandoning their various houses, they claimed that the base stations are becoming numerous and besides, they are too close to their homes. They also claimed that radiation from the towers could pose serious health challenges as a result of geotaxis effects, which could cause DNA mutation and damage to chromosomes.
Perhaps they are right!
During an interview section I put up with some of the occupants of the area, some guys asked a pertinent question that "why base station equipment is not always placed in industrial areas or areas remote from habitation". Let me attend to this question before we proceed further.
Cellular phones are designed to switch from one sub-division of communication network known as a cell to the next available cell as the user moves from one location to another. Therefore, these cells need to be built very close to each other which explains the why base stations are clustered together.
There are numerous reasons why base station equipment is not always placed in areas remote from habitation.
In a practical point of view, considering high numbers of users, there is a limit to the geographic area that a base station can effectively serve. In this instance. Therefore, the base stations need to be erected closer together to provide increased capacity and coverage. Due to their proximity to one another, each base station operates at very low power levels to avoid interfering with others nearby.
As a result, a properly designed network will optimize coverage and capacity, thereby operating at only the lowest power levels necessary to provide good communications.
Also, if the equipment is placed too far from the users, it will not only gives poor communication quality but also causes the phones to increase their output power to sustain the connection, thus decreasing battery life and talk time.

Base station site
Hope this little explanation above lowers your curiosity to know reasons why base stations are clustered together within our habitations
Before we consider possible reasons to justify if network base stations and our cellular system pose radiation hazard on health or not, let get familiar with the mode of operations of a cellular system and base stations. This will help us to draw a reasonable conclusion together.
Here we go!
Cellular system
A cellular system is a radio network designed to ensure that our mobile phones maintain network links with base stations even when users are on a motion. This is achieved by dividing communication networks into geographic areas called cells, each cell is served by a base station. As mobile phone user moves from one place to the next with the phone, is handed-over by one cell is capable to hand over call identity, location, and radio frequency to another cell without interrupting a call.
Mobile phones and base stations exchange radio signals during communication.For proper communication, the mobile phones maintain the link with the network as users move from one cell to another. Since base stations are erected close to each other, they are closely regulated to prevent interference with other radio systems such as radio and television broadcasting stations. Tthe level of these signals is carefully optimized for the network to perform satisfactorily.
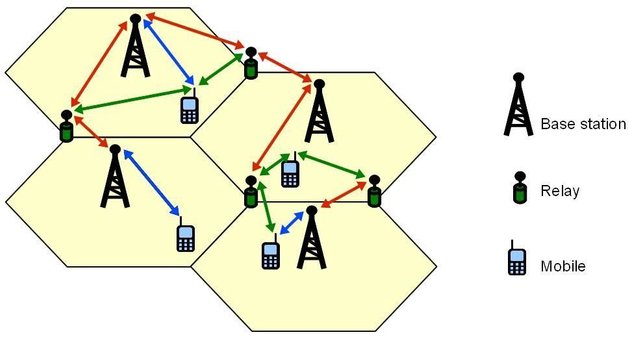
How does a cellular system work?
When the nearest base station in the network to which it subscribes a is available and your mobile phone is switch on, it automatically responds to specific control signals from nearby base stations thereby initiates a connection between the base station and the phone. After the phone is connected, it then remains dormant, but it occasionally updating with the network, until the user wishes to make a call or a call is received. This switching pattern in mobile phones is employed to ensure reduction of the transmitted power to the barest minimum to achieve good call quality.
A cell phone is essentially a two-way radio, consisting of both the radio transmitter and the radio receiver.
The average power output while using a mobile phone can vary between the minimum level of about 0.001 watts up to the maximum level which is less than 1 watt. This feature is designed to prolong battery life and possible talk time.
A mobile communication network is able to pass calls from one base station to another when a user is moving while talking on the phone. This process is called a ‘handover’, literally means where the network hands over the call from one base station to another, without the caller being aware of the change.
Source
A base station comprises of several different components such as, a tower or mast which provides the necessary height to give better coverage, a shelter for equipment, a transceiver, and antennas which is installed on the tower or mast. The antennas are selected depending on the frequency of operation, but typically, it is about 15-30 cm in width and up to a few metres in length.
These antennas are designed to emit Radio Frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy also known radio waves in beams that are quite broad in width but typically very narrow in height, thereby, cause the RF energy at ground level directly below the antenna is very low. These antennas are typically elevated to assure that public exposures remain within the established level.
In the next episode, we will clear all doubts and common misconception that radiation emissions are stronger directly under antennas and its possible health implications.
Thanks for your time!
Thanks for sharing this great information
Thanks @etimbukndem for reading the post
Good topic @oluwabori, i will personally like you to research more on the health hazard of it to the nearest neighbours. Regards
Thanks @noble-noah, I'm working on the health hazard of the GSM base station radiation, where we will conclude if it is hazardous or not. Expect the post soon.