WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT YOUR BLOOD CELL
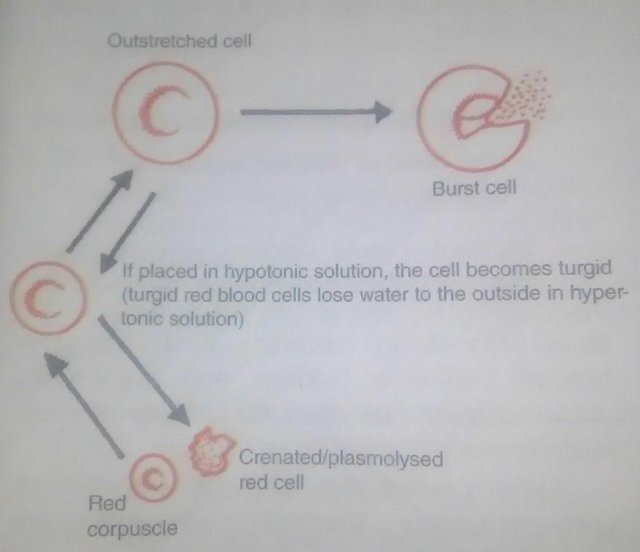
Haemolysis is the breaking open of red blood cells and the release of their contents ( haemoglobin ) into surrounding fluid. If some red corpuscles are placed in a salt solution, which is of lower concentration to the red corpuscles (hypnotic solution), water will enter the corpuscles which will in turn swell and become turgid. Later, the corpuscles will burst and the haemoglobin in them will escape. On the other hand, if some red corpuscles are placed in a salt solution, which is isotonic, the corpuscles will not gain or lose water by osmosis.
If some red corpuscles are put in a hypertonic or stronger salt solution, water leaves the cells by osmosis (exosmosis), and consequently, the cells shrink and wrinkle. The cells become plasmolysed. This condition is decribed as 'Crenation'. If haemolysis is not checked, it can lead to death just like total plasmolysis. Hence, to survive, animal and plant cells must be in isotonic media or be able to maintain an osmotic balance in their cells.
If a cell is placed in an isotonic solution (e.g., water) there would be a continuous inflow of water up to a point that the cell is fully stretched. At this point, the cell is said to be turgid. Turgidity is the state in which the pressure exerted by cell contents outward is equal to the resistance of the inwards.