The mitocondrias and the cellular respiration // Cycle of Krebs

Source of image of pixabay
The mitocondrias they are orgánulos citoplasmático, with spherical form or of cane, that he is in almost all the cells eucariotas, as the nucleus and the cloroplastos, the mitocondrias are surrounded by two membranes citoplasmática with compositions different from the following way: membrane mitocondrial day pupil and membrane mitocondrial internal, separated for the space intermembranous. The internal membrane delimits a cavity or cellular counterfoil, which occupies most of the mitocondria, unvagina forming combs mitocondriales that increases considerably his membranous surface, in the counterfoil mitocondrial there is ADN, which can double independently of ADN of the cellular nucleus and ribosomas that take part in a protein synthesis intramitocondrial, these facts award the true mitocondrias cellular autonomy.
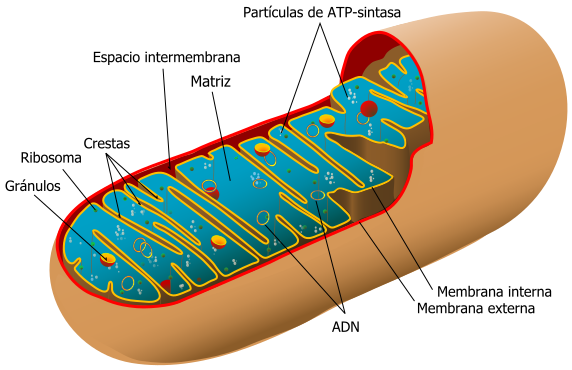
Structure of a mitocondria, source of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: Aibdescalzo.
In the mitocondria it takes place important functions in the counterfoil mitocondrial give themselves the last steps of the oxidation of the polisacáridos and the greasy, separate acids oxidize completely we have that the internal membrane forms the ATP, it takes place during the fotorrespiración and the cellular respiration, and it is consumed by many enzymes in the catalysis of numerous chemical processes, his molecular formula is C10H16N5O13P3. The trifosfato of adenosina (adenosín trifosfato, of English adenosine triphosphate, ATP or TFA) is a fundamental nucleótido in the securing of cellular energy, is formed by a nitrogenous base (adenina) joined the carbon 1 of a sugar of type pentosa, the ribosa, that in his carbon 5 has three groups connected phosphate, is the principal source of energy for the majority of the cellular functions.
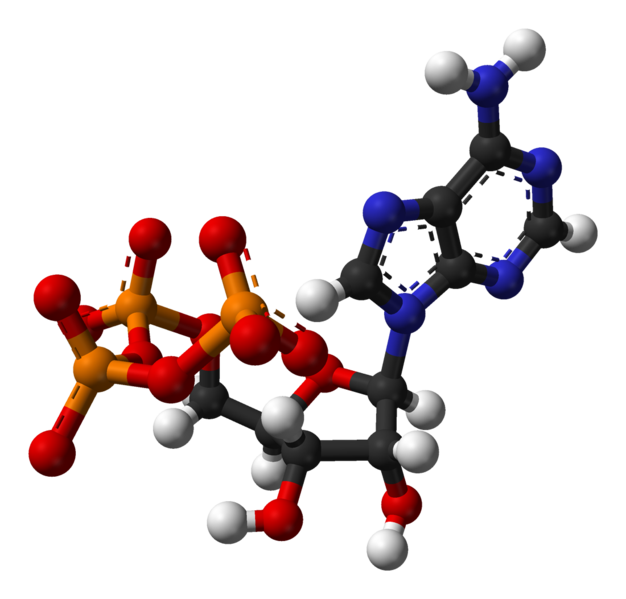
Model of balls and rods of the ATP. source of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: Ben Mills
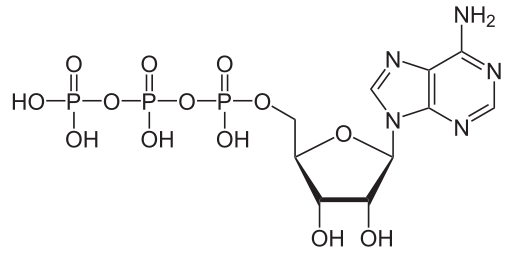
Structure of trifosfato of adenosina (ATP), protonado, source of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: NEUROtiker
to assure the provisions of greasy acids and glucose, the cells you store these compounds in the citosol in the shape of fat and glucógeno, the mitocondrias it uses as fuel majority both the greasy acids and the piruvato, molecule of three carbon that form in the citosol from the glucose. The proteins of the double membrane mitocondrial take charge incorporating the piruvato and the greasy acids into the counterfoil mitocondrial, where one turns by means of the action of several enzymes as the acetil CoA, compound that to the being hidrolizado, liberates big energy.
Also in the counterfoil mitocondrial the acetil CoA, it joins to a series of reactions, which receive the name of the cycle of Krebs or cycle of the citric acid.
By means of the cycle of Krebs, the atoms of carbon of the acetil CoA it turns in CO2, whereas the atoms of hydrogen trasfiere to a called molecule transportadoras, which stay energéticamente activated (NADH AND FADH2). The metabolism oxidativo of glúcidos, lípidos and proteins frequently it splits into three stages, of which the cycle of Krebs supposes the second one, in the first stage, the carbons of these macromolecules lead to acetil-CoA, and it includes the routes catabólicas of amino acids, the beta oxidation of greasy acids and the glucólisis, the third stage is the fosforilación oxidativa, in which the power differential (NADH and FADH2) generated is used for the synthesis of ATP as the theory of the connection quimiosmótico.
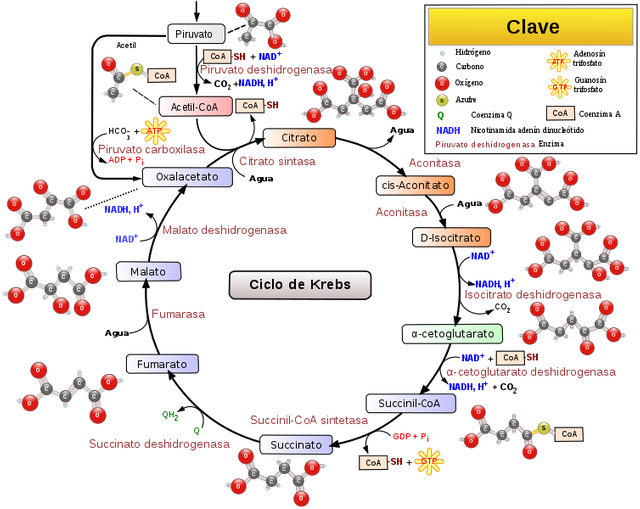
Didactic scheme of the cycle of the citric acid, source of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: Narayanese, WikiUserPedia, YassineMrabet, TotoBaggins
Is necessary to think that the NADH and FADH2, they migrate to the membrane mitocondrial internal and by means of a process integrated by several reactions that happen sequentially, trasfieren to the molecular oxygen O2, the electrons that they had incorporated during the cycle of Krebs, the energy liberated by this one reactions is made use to impel the formation of ATP, called process fosforilación oxidativa. The acetil-CoA (Acetil Coenzima A) is the principal precursor of the cycle, the citric acid (6 carbons) or citrate is obtained in every cycle by condensation of an acetil-CoA (2 carbons) with a molecule of oxaloacetato (4 carbons), the citrate produces in every cycle a molecule of oxaloacetato and two CO2, from what the clear balance of the cycle is:
Acetil-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O → CoA-SH + 3 (NADH + H+) + FADH2 + GTP + 2 CO2
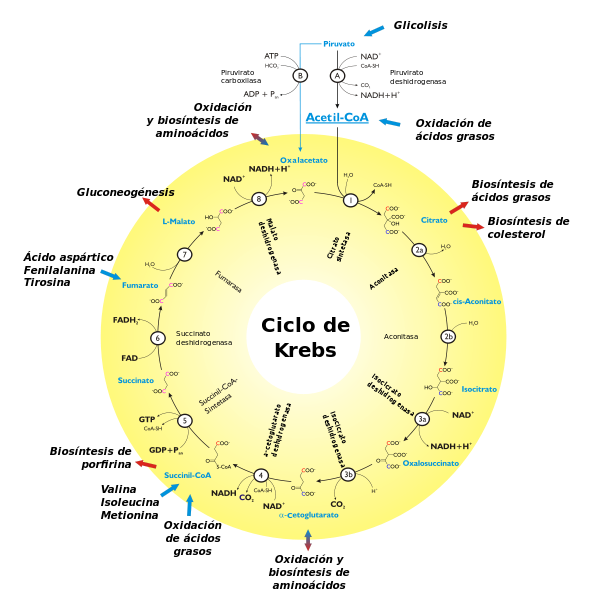
Cycle of Krebs in the mitocondrial counterfoil, source of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: derivative work: r@ge (talk)
Two carbons of the acetil-CoA are oxidized to CO2, and the energy that it had piled up is liberated in the shape of chemical energy: GTP and to be able differential (electrons of potential high place): NADH and FADH2. NADH and FADH2 are coenzymes (molecules that join enzymes), capable of accumulating the energy in the shape of differential to be able for his conversion in chemical energy in the fosforilación oxidativa. Many of the enzymes of the cycle of Krebs are regulated by negative feedback (feedback), by union alostérica of the ATP, which is a product of the route and an indicator of the energy level of the cell. Between these enzymes, standard includes the complex of the piruvato deshidrogenasa that there synthesizes the acetil-CoA necessary for the first reaction of the cycle from piruvato (by means of an irreversible reaction), proceeding from the glucólisis or from the catabolismo of amino acids gluncogénicos (that is to say, 20 amino acids excepting lisina and leucina).
Also the enzymes citrate sintasa, isocitrato deshidrogenasa and α-cetoglutarato deshidrogenasa, that catalizan the first three reactions of the cycle of Krebs, they are inhibited for high concentrations of ATP. This regulation brakes this cycle degradativo when the energy level of the cell is good.
Someone enzymes are regulated also negatively when the level of differential of the cell was able is high. The mechanism that is realized is a competitive inhibition for product (for NADH) of the enzymes that NAD as substratum uses. This way the piruvato deshidrogenasa complexes and citrate are regulated, between others, sintasa.
The FADH2 of the succinato deshidrogenasa (the complex IInd of the chain conveyor of electrons), on not having been able to get rid of the enzyme, must oxidize again in situ. The FADH2 transfers his two hydrogens to the ubiquinona (coenzyme Q), which diminishes to ubiquinol (QH2) and leaves the enzyme. The processes catabólicos that they have in the place inside the mitocondria, from the cycle of Krebs up to the fosforilación oxidativa, receive the name of cellular respiration or catabolismo oxidativo. It is represented by the gaseous exchanges at level of the alive cells where the absorption of oxygen happens, expelling of anhídrico carbonic and for the employment of the oxygen as energy fuel.
Bibliographical Source
Cellular And Molecular Biology - Page 297 for Jimenez - 2003.
Biochemistry: text and atlas - Page 210. for Jan Koolman, Klaus-Heinrich Röhm - 2005
Stevens and Lowe. Histology humanizes StudentConsult - Page 21 for James S. Lowe, Peter G. Anderson - 2015.
Functional Wheater's Histologia: - Page 22 for Barbara Young, John W. Heath - 2000.

