CONTAMINANTS IN THE AIR WE BREATHE-HOW WE SURVIVE

Image Source
Air is very essential to life but polluted/contaminated air can be detrimental to one's health. The exposure to polluted air could result in health complications such as asthma, bronchitis, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, emphysema and even lung cancer.
COMPOSITION OF AIR
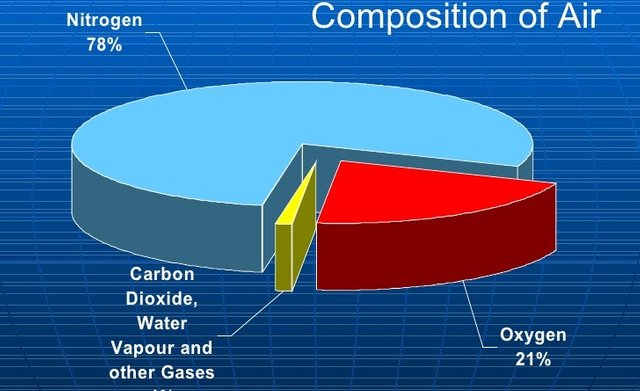
Image Source
The air we breathe is a mixture of gases which include Oxygen, Nitrogen, Argon, Carbon dioxide and other trace gases. Air also contain a variable amount of water vapour.
AIR POLLUTION
Air pollution is the state in which the air is contaminated by foreign substances called pollutants.
Air pollution arises when harmful/hazardous or excessive quantities of substances, including gases, biological molecules etc, are released into earth's atmosphere. These harmful substances can be solid particles, liquid droplets, or gases. Substances released into the atmosphere by human activities include:
- Carbon dioxides
- Sulfur oxides
- Nitrogen oxides
- Carbon monoxide
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC)
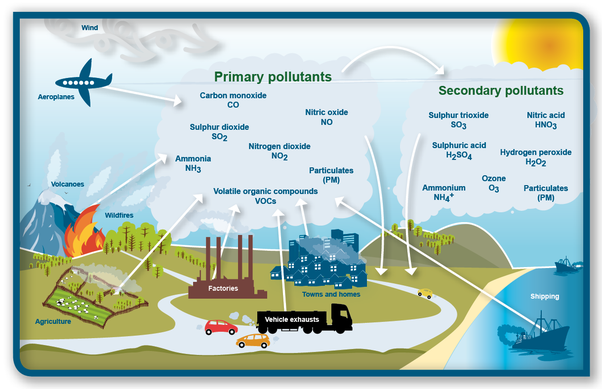
Image Source - Particulates
- Toxic metals such as lead, mercury
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Ammonia etc...
However, despite the harmful substances in the air we breathe, our body still finds a way to survive. Sometimes these harmful substances get excreted, other times they dont (this is where the problem lies).
When it comes to air pollution, the major route of exposure is inhalation. Once a chemical enters the body, it often gets absorbed into the bloodstream and can circulate throughout the body. This circulation is termed Distribution.
After a chemical gets absorved into the bloodstream, it has several different fates; sometimes this chemical can be expelled from the body through urine or feces. In other situations it is not so; it may be stored in various parts of the body, e.g fats, bones, and remain there for a long time. Another fate of this distributed chemical/compound is its interaction with certain other compounds in the body and its conversion into one or more other chemicals (a process known as Metabolism). In some cases, metabolism may lead to products (metabolites) that are easier to excrete from the body, in other cases the metabolites prove to be more harmful than the original chemical.
The toxicity of a substance depends on the following factors:
Dosage/Dosage-Time relationship
Exposure route
Species
Form and chemical activity
Life stage of the exposed individual (infant, young adult or elderly adult)
Metabolism
Distribution
Excretion
Health of the individual
Nutrition status of the individual
Presence of other chemicals (e.g drugs).
EXCRETION OF INHALED COMPOUNDS
The Liver serves a major function when it comes to the elimination/expulsion of harmful substances from the body. Other organs with the role of elimination/expulsion are the Kidneys, Intestinal tract, and the Skin. The liver detoxifies these harmful substances and converts them to a form that can be easily excreted. The cell organelle majorly concerned with the detoxification process that takes place in the liver is the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). The amount of SER in the liver increases considerably in response to an overload of toxins/toxicants in the body.
Detoxification reactions occur throughout the body, these reactions follow three phases with the aim of converting the toxicant into an inert, water-soluble form for easy excretion.
PHASE 1 Reactions, catalysed by a group of enzymes known as the Cytochrome P450 family CYPs or Mixed Function Oxidase enzymes MFO, convert the toxicant into a chemical form that can be metabolised by the phase 2 enzymes.
.png)
Image Source
PHASE 2 reactions attach the toxicant to other water-soluble substances in order to increase its solubility. Enzymes involved in phase 2 reactions include:
UDP-glucoronyltransferases
Glutathione-s-transferases
Sulfotransferases.
PHASE 3 reactions involve the transport of the transformed toxicants in or out of cells. Here, proteins known as TRANSPORT PROTEINS work to shuttle/transport the toxicants from different parts of the body into bile or urine for excretion.
Products of liver detoxification can sometimes be transported into the bloodstream for processing by the kidneys and eventually get excreted from the body as urine.
TIPS TO PROTECT YOURSELF FROM AIR POLLUTION EXPOSURE
.jpg)
Image Source
To be realistic, we can't totally (100%) avoid inhaling polluted air because the air we breathe, on a daily basis, gets polluted/contaminated by various substances but there are few tips listed below that can help us reduce our exposure to polluted air, they include:
- Avoid indoor smoking and generally avoid places where people smoke a lot.
- Use electric-lawn care equipment rather than gasoline.
- Always avoid exercising near high-traffick areas e.g. bus stations/parks.
- Cook in a well ventilated kitchen, if you use a gas stove.
- Use a dehumidifier and/or air conditioner to reduce moisture.
- Minimize use of air freshener.
- Keep trash covered properly and dispose them regularly.
- Dust surfaces and vacuum frequently.
- Place air-purifying plants indoors such as Ivy, Aloe vera, Spider plant as they help purify indoor air and minimise indoor pollution.
- Ventilate your kitchen properly (make sure there is a chimney in the kitchen).
- If convenient, wear a face mask when going outdoors. According to Ed Avol, a professor of clinical preventive medicine, face masks are often ineffective unless they conform to the contours of your face.
- Drink more green tea as it is high in antioxidants which can reduce damage caused by exposure to toxicants.
The best is to reduce CO2 emissions.
That could work also.
Nice post @von96 this is very educative
Thanks, I appreciate.