Why Businesses Are Investing in Artificial Intelligence in 2026
Why Businesses Are Investing in Artificial Intelligence in 2026
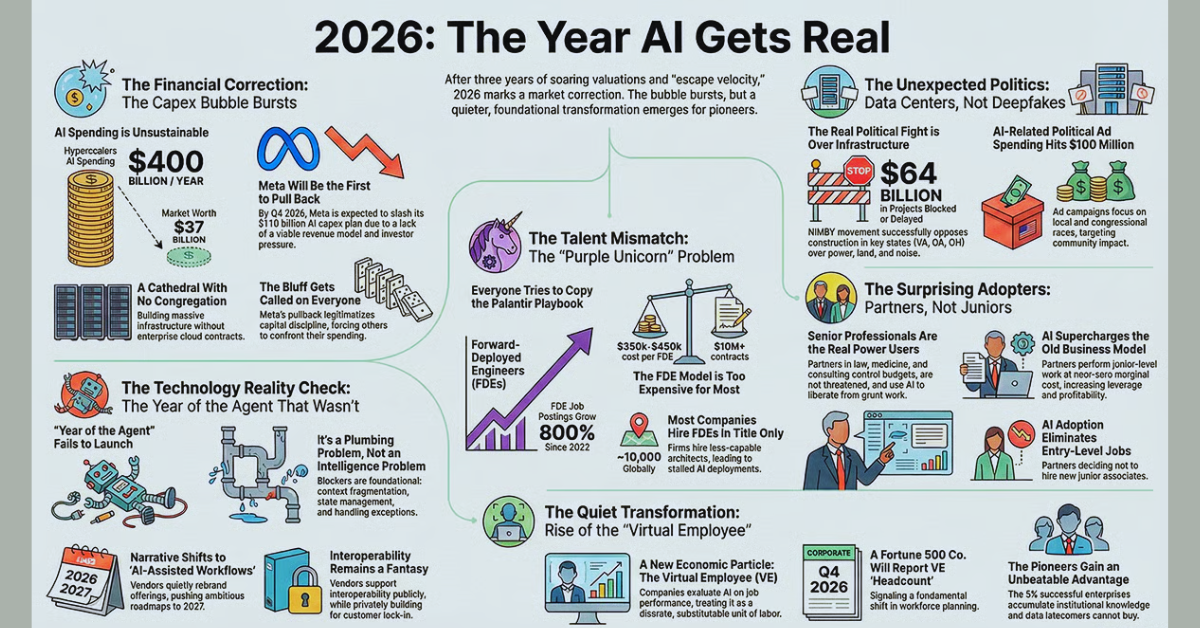
The experimental phase of Artificial Intelligence is officially dead. In 2026, enterprise AI isn't a sandbox for innovation teams—it is the core operational engine of corporate survival. If you are still relying on basic wrapper applications or treating AI as a side project, you are already years behind the curve.
We are currently witnessing a historic capital expenditure super-cycle. Major tech giants like Google, Microsoft, Meta, and Amazon are pouring unprecedented capital into AI infrastructure, with investment projections crossing the $500 billion mark this year alone. But this massive spend isn't just about building bigger data centers; it reflects a fundamental shift in how businesses expect to operate, generate revenue, and outpace competitors.
Here is a deep dive into the technical shifts, market data, and strategic reasons driving the massive surge in AI business investments in 2026.
Quick Overview: The 2026 AI Investment Landscape
- What it is: A shift from experimental, generalized Large Language Models (LLMs) to highly specialized, autonomous AI agents and vertical industry solutions.
- Key Use Cases: Autonomous workflow orchestration, hyper-personalized customer experiences, predictive supply chain modeling, and automated code generation.
- Who it's for: Enterprise leadership (CEOs and CIOs driving top-down adoption) and developers tasked with integrating complex, multi-agent systems.
- Current Status: Moving from pilot programs to full-scale, mission-critical production deployments.
- Notable Drivers: The need for verifiable ROI, the rise of Small Language Models (SLMs) for cost-efficiency, and massive hardware infrastructure build-outs.
1. The Macro View: Following the $500B+ CapEx Surge
To understand the business adoption of AI in 2026, you must look at the infrastructure layer. The hyperscalers—Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud—are engaged in an arms race to secure computing power.
Why are businesses of all sizes riding this wave? Because the unit economics of intelligence have fundamentally changed. In 2023, querying a top-tier model was computationally expensive and slow. Today, thanks to advancements in model optimization, quantization, and specialized silicon (beyond just GPUs to custom TPUs and NPUs), the cost of inference has plummeted.
Businesses are investing heavily now because the infrastructure can finally support thousands of AI transactions per second without destroying profit margins. This allows companies to move AI out of the "chat interface" and directly into their backend databases and APIs.
The Shift in Investment Focus (2024 vs. 2026)
| Feature | 2024 AI Landscape | 2026 AI Landscape |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Interface | Chatbots & Copilots | Autonomous Background Agents |
| Model Preference | Massive General LLMs | Domain-Specific SLMs & RAG |
| ROI Measurement | Productivity / Time Saved | Direct Revenue Generation / OpEx Reduction |
| Leadership | IT & Innovation Teams | CEO & Board of Directors |
2. From Copilots to Autonomous AI Agents
The biggest technical leap driving business investment in 2026 is the transition from reactive AI to agentic AI.
Previously, an AI required a human prompt to generate an output. Today, businesses are investing in multi-agent frameworks. These systems utilize a primary "orchestrator" model that breaks down a high-level business goal into smaller tasks, delegates them to specialized sub-agents, executes code, verifies the output, and self-corrects—all without human intervention.
Developer Insight: Developers are no longer just building API calls to an LLM; they are building complex state machines. Utilizing frameworks that support long-term memory, secure tool use (giving AI access to internal CRMs, ERPs, and secure databases), and multi-agent reasoning is where the bulk of engineering capital is flowing.
Businesses invest in this because autonomous agents scale human labor. A team of AI agents can monitor network security, triage customer support tickets, and optimize logistics routing 24/7, fundamentally altering a company's operational capacity.
3. Verifiable ROI and the Push for Vertical AI
Investors and boards have lost patience with "hype." In 2026, AI initiatives must prove a tangible Return on Investment (ROI). This demand has led to the explosion of Vertical AI—models fine-tuned on highly specific, proprietary industry data.
A generic AI model might know how to write a Python script, but it doesn't know the specific compliance regulations of a regional healthcare provider. Businesses are investing millions in data engineering pipelines to clean their proprietary data and feed it into Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems.
By combining the reasoning capabilities of foundational models with their own secure, internal data, companies are creating insurmountable competitive moats.
Key Areas of Proven ROI:
- Software Development: AI-assisted coding is now standard. Development teams are reporting 30-40% faster sprint completions, allowing businesses to ship features faster.
- Financial Modeling: Real-time risk assessment and algorithmic trading models are processing unstructured data (news, social sentiment, global events) at speeds humans cannot match.
- Manufacturing & Logistics: Computer vision combined with predictive analytics is reducing machine downtime by accurately predicting component failures weeks in advance.
4. Building vs. Buying: Implementation Strategies
As the technology matures, businesses face a critical decision: Do they build custom AI solutions in-house, or do they buy off-the-shelf SaaS products?
While many opt for integrated enterprise software for basic tasks, companies looking for a true competitive advantage are choosing to build. However, the talent shortage for experienced AI engineers remains a massive bottleneck. You cannot simply pivot a traditional web developer into an AI systems architect overnight.
Because of this complexity, many companies now rely on professional AI development services to build custom intelligent systems. Partnering with specialized teams allows enterprises to rapidly deploy RAG architectures, fine-tune models securely, and integrate agentic workflows without the overhead of hiring an entirely new internal AI division.
5. Navigating the Challenges and Limitations
Despite the massive investments, the 2026 AI landscape is not without friction. Businesses must navigate several critical challenges to ensure their investments don't become costly liabilities.
- The Hallucination Problem: While drastically reduced, models still confidently invent facts. For businesses in highly regulated sectors (legal, healthcare, finance), a 1% hallucination rate is still unacceptable. Investments are heavily skewed toward "guardrail" technologies and advanced output verification loops.
- Data Privacy and Security: Feeding proprietary company data into an LLM remains a severe security risk if not handled correctly. The focus has shifted to deploying open-weight models locally or on private cloud instances to ensure data never leaves the corporate perimeter.
- Compute Bottlenecks: Despite the $500B CapEx buildout, securing dedicated GPU compute for massive data processing remains expensive and highly competitive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why are companies investing so heavily in AI in 2026?
Companies are investing heavily to secure long-term operational efficiency and competitive advantage. The focus has shifted from experimental features to core business functions, with AI automating complex workflows, reducing operational costs, and driving new revenue streams through hyper-personalization.
What is the difference between General AI and Vertical AI?
General AI (like a standard ChatGPT interface) handles broad, diverse tasks. Vertical AI is highly specialized for a specific industry (e.g., a model trained exclusively on medical imaging or financial compliance laws), offering far greater accuracy and practical value for enterprise use cases.
How do AI agents differ from traditional AI chatbots?
Chatbots require continuous human prompting and operate reactively. AI agents are autonomous; they can be given a high-level goal, break it down into steps, interact with external software (like a CRM or database), self-correct errors, and complete the task without human supervision.
What is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) and why does it matter?
RAG is a framework that connects an AI model to a company's private, real-time database. Instead of relying only on the data it was trained on, the AI "reads" your secure internal documents before answering. It prevents hallucinations and ensures the AI provides accurate, company-specific answers.
What are the biggest risks of enterprise AI adoption?
The primary risks include data security breaches (if private data is fed to public models), the high costs of continuous compute infrastructure, algorithmic bias, and the challenge of seamlessly integrating new AI architectures with legacy IT systems.
