Fat Protocols in decentralized technologies
Fat Protocols
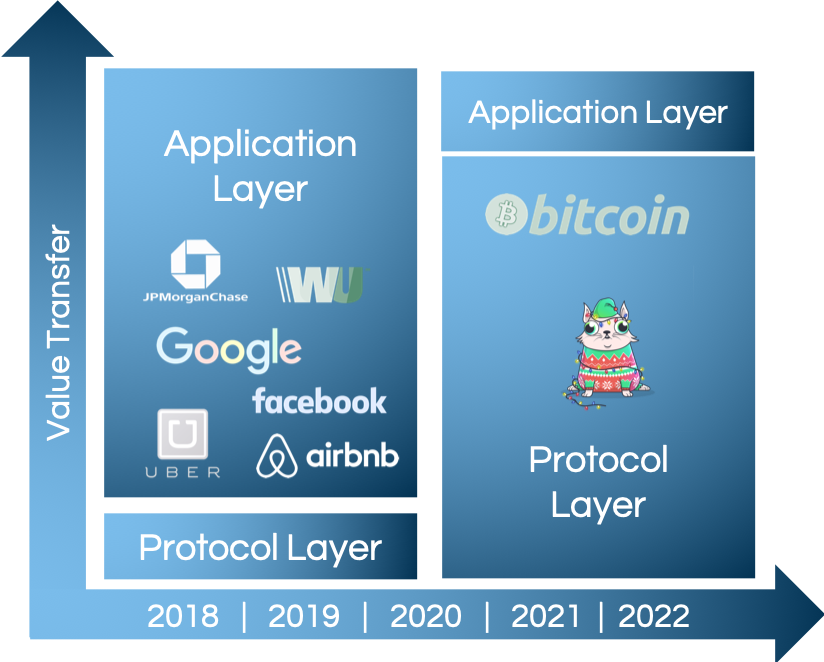
Here's one way to think about the differences between the Internet and the Blockchain. The previous generation of shared protocols (TCP/IP, HTTP, SMTP, etc.) produced immeasurable amounts of value, but most of it got captured and re-aggregated on top at the applications layer, largely in the form of data (think Google, Facebook and so on). The Internet stack, in terms of how value is distributed, is composed of "thin" protocols and "fat" applications. As the market developed, we learned that investing in applications produced high returns whereas investing directly in protocol technologies generally produced low returns.
This relationship between protocols and applications is reversed in the blockchain application stack. Value concentrates at the shared protocol layer and only a fraction of that value is distributed along at the applications layer. It's a stack with "fat" protocols and "thin" applications.We see this very clearly in the two dominant blockchain networks, Bitcoin and Ethereum. The Bitcoin network has a $10B market cap yet the largest companies built on top are worth a few hundred million at best, and most are probably overvalued by “business fundamentals” standards. Similarly, Ethereum has a $1B market cap even before the emergence of a real breakout application on top and only a year after its public release. There are two things about most blockchain-based protocols that cause this to happen: the first is the shared data layer, and the second is the introduction cryptographic “access” token with some speculative value.
When a token appreciates in value, it draws the attention of early speculators, developers and entrepreneurs. They become stakeholders in the protocol itself and are financially invested in its success. Then some of these early adopters, perhaps financed in part by the profits of getting in at the start, build products and services around the protocol, recognizing that its success would further increase the value of their tokens. Then some of these become successful and bring in new users to the network and perhaps VCs and other kinds of investors. This further increases the value of the tokens, which draws more attention from more entrepreneurs, which leads to more applications, and so on. There are two things I want to point out about this feedback loop. First is how much of the initial growth is driven by speculation. Because most tokens are programmed to be scarce, as interest in the protocol grows so does the price per token and thus the market cap of the network. Sometimes interest grows a lot faster than the supply of tokens and it leads to bubble-style appreciation.
Source
Plagiarism is the copying & pasting of others work without giving credit to the original author or artist. Plagiarized posts are considered spam.
Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
More information and tips on sharing content.
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #disputes on Discord
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://medium.com/newtown-partners/crypto-network-effects-are-driving-thin-protocols-a4108e94b1a
yes this the another content
Hello @kiranrpa! This is a friendly reminder that you have 3000 Partiko Points unclaimed in your Partiko account!
Partiko is a fast and beautiful mobile app for Steem, and it’s the most popular Steem mobile app out there! Download Partiko using the link below and login using SteemConnect to claim your 3000 Partiko points! You can easily convert them into Steem token!
https://partiko.app/referral/partiko
Congratulations @kiranrpa! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!