Understanding Blockchain-A Layman's Primer
Why is Blockchain a Chain? An Easy-To-Understand Primer on Blockchain!
“Why is Blockchain called a chain?” “What the hell is a distributed ledger?” These are just a few of the numerous questions, those who are new to the blockchain technology have.

If you're the Blockchain cognoscenti, the information covered herein may hold no value for you. This is just a gentle, non-technical introduction of the blockchain to our Steemit friends who proudly claim, “Yeah, I’m on Steemit! It’s an amazing blockchain-based social media platform that pays you to blog and comment.” But they have no answers to the next question, "So what's a blockchain?"
We believe it’s important to understand the basics, to be able to perceive the advantages or disadvantages of anything.
The ideology Behind Blockchain
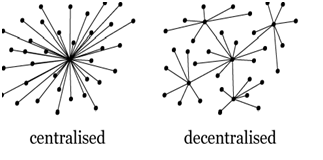
Blockchain is a result of Bitcoin’s need to be Decentralized, which means to be anonymous without a point of central control. Bitcoin was developed using this ideology.
You’ve heard about the Bitcoin Blockchain. But Blockchain is not just Bitcoin or Ethereum or Steem. It is the technology that powers Bitcoin, and today, it is powering a whole lot more than Bitcoin.
‘Satoshi Nakomoto’ is the mysterious pseudonym of the creator who released blockchain as the free Bitcoin software, in 2009. Nobody knows the real identity of the person who created this revolutionary system.
Let me tell you that all blockchain ecosystems may not come with the same mechanisms as Bitcoin. But for the purpose of understanding Blockchain, we will be focusing on bitcoin Blockchain, which is a public blockchain as opposed to a private blockchain that can come with a different set of rules set by those creating the blockchain.
What is a Blockchain?
Blockchain allows a “decentralized “open computer network to create and share valuable data. Because there is no central authority, blockchain is also called a “decentralized ledger.”
A blockchain is a public database of records of all digital events or transactions that have occurred among people.
It is called a Distributed Ledger. Distributed = Shared among people (not centralized). Ledger = Database or a register. It’s nothing but a publicly shared database of events and transactions. Exact copies of this ledger are stored on a large number of computers around the world and NOT on a central server, like your bank does.
Let’s take an example…
A majority of us use online banking for our banking transactions. Once you log in to your bank’s online banking site, you’ll find several options. You can view your account balance and statement details, pay bills, transfer funds, find interest details and even change your personal information. You can also find all the information pertaining to the different savings, checking and deposit accounts.
You’re not the only one accessing this information. Thousands of people holding an account in the bank, can access all their personal banking details.
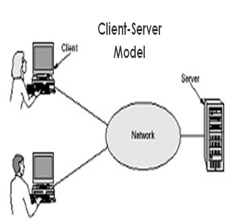
The Client-Server Model
Where do you get all this information from? When you log in to your account, you’re interacting with the bank’s computer system, which maintains a copy of your bank balance, transactions and a whole lot of information about you, in its huge databases.
If you find a mistake in any of the transactions or your account summary, you bring the error to the bank’s notice, asking for a correction. If you wish to transfer funds to your dad’s account, your request is routed through the bank’s server. You don’t access your dad’s account directly and push funds from your account to his. (NOT peer-to-peer)
Most networks, whether its banks, eCommerce sites or companies, use client-server networks, as seen in the image above.
In the client server model, clients (nodes) communicate with other computers on the same network or computers on other networks, through the “server.” The server acts as the mediator. This is very different from the blockchain.
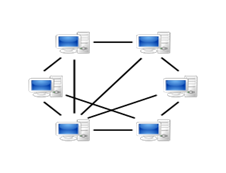
The Blockchain Model
Peer-to-peer is the keyword here. In the above image, you will find no central server. No middleman. All communication takes place one-on-one - peer-to-peer. It is called that, because all the nodes (clients) are peers with equal power, and not all of them are connected to all other nodes. In a peer-to-peer network, some of the nodes or all of them, keep a copy of the database.
A blockchain is like a big box that contains a normal database, software that keeps adding new data and information, validates it based on pre-set rules, and broadcasts all new information to the people across the blockchain network, making sure all peers have the same data and information in their databases.
All the information is verified by consensus (general agreement) of a majority of people within the system. Please make note of the word CONSENSUS, which is an important aspect of blockchain.
Similarly, all new transactions on a blockchain are broadcast to every node in the network. Every block has to be verified for validity and accepted by consensus, before being added to the blockchain.
Once a block has been accepted, the information on the block cannot be erased.
Here are some important elements of a blockchain:
Exists over a peer-to-peer network
All activity over the peer-to-peer network is replicated across thousands of systems in almost real-time
Cryptography and digital signatures are used to verify identity and authenticity
Sets read/write access rights
Has security mechanisms in place, making it hard for anyone to change historical records
It is also easy to find out if someone is tampering with the records
The “Block” and “Chain” in The Blockchain
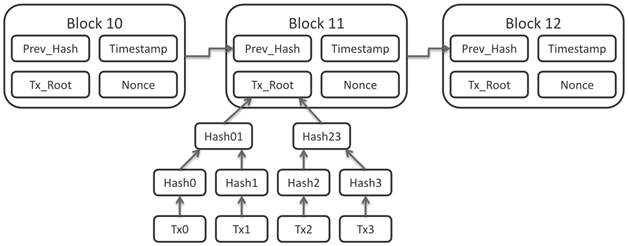
In essence, a blockchain is nothing but a file, where data is logically organized and stored. This file contains everything from databases, text, numbers, tables etc.
Think of the blocks as pages in a book. Just like the interlinked chain of pages make a book, the connected chain of blocks make a blockchain. Each block in the blockchain contains a story (set of transactions), a header with the chapter name or number, and a page number at the end of the page.
Miners mine the blocks. Transactions are added to the blockchain in blocks, block by block, in a linear, chronological order. Each new block is connected to the previous block using a hash from the previous block’s header. Because each block is connected, it is called a chain. This connection makes it easier to verify that the blocks are in correct order.
Take a look at the above diagram of a Blockchain. Do you see the progression from one block to another? When Block 10 turns into Block 11, it carries with it a connection from Block 10, which is the Prev_Hash, a reference to the previous block. The time stamp shows the time of conversion.
Conclusion…
The “Blockchain Technology” is a collection of technologies that can be combined in different ways to create different results. It’s like a bag of Lego. You can take out the bricks you need to create the result you seek.
We haven't had a chance to talk about the most important members of a blockchain, the people who create the blocks - Miners. Mining and the merits of the miners calls for an entire post, which we will soon work on.
Author: @knowledge1

Hey ,
Very interesting read, Thanks you for sharing it!
Blockchain tech. will lead the way in the financial fields of the future.





http://www.FlippyCoin.com is the #1 Cryptocurrency Exchange!
oh
While it may not be a scam in your opinion, it could be considered spam. Spam is not appreciated by the community and could be flagged or may result in action from the cheetah bot..
Some things that can be considered spam:
informative but now take the next step and apply to bitcoin versus ethereum. May help us all especially as the cryptocurrency market is in a fall!
What a fantastic article. For those who aren't up to-date on the concept of Blockchain, this is a very concise and well-written article. I was actually speaking to a friend of mine yesterday who wanted to know more about it, its a shame I didn't have this to hand! Gone and shared this with my followers. Look forward to reading your article on mining!
I've noticed that most people on the blockchain still have several unanswered questions. I'm glad you find it informative. :)
Great article! I look forward to the next article on the topic of miners and their importance to the industry. And on that subject I hear some currencies like DASH and NEO cannot be mined because they use a feature called "virtual mining" (which I hear is done by AI in a cloud and does not require any human input).. can you elaborate on this ? And if this is so, where does it leave the future of mining and those who make a living off of it?
Thanks for reading the post in its entirety and for your suggestion of adding the topic, AI in a cloud to the post on mining. Will certainly consider it.
Upvoted and RESTEEMED!
Thanks for the upvote and resteeming. Take a look at our other posts, where we delve deeper into the blockchain.
thanks @adsactly, you have sharing the useful post for people.
keep steem on !!
i will be wait for your next post :)
i cann't your language, but i now this post is importain for steemian.
now i will to translate your post to google tranlate to know what it means @adsactly.
thanks for sharing
great topic thanks
Please follow also my Steemit Account: https://steemit.com/@drewgista04
Lets Help Everyone by simple means of Following Upvoting Commenting and Re-steeming Everyone's Post.
Join FB Group Also for Support exchange https://www.facebook.com/groups/127151934588379/
I'm fairly new but, that's a wonderfully, simple way for everyone to help each other. I've found so many interesting and useful articles, just from exploring around on Steem. I'll join you and pass your idea along! Thx!
very good..
nice post..
Very informative blog. Keep it up.