An Introduction to Cryptoeconomics
Cyber•Fund is introducing a series of publications that provide an overview of some of the best speaker topics we’ve hosted at our meetups. During our first summer meetup session, Dmitry Starodubtsev spoke about the basics of investing in the blockchain sector. This was a great introduction to “crypto economics” that can provide the novice with a better understanding.
The Blockchain Genesis
Blockchain began with an 8-page publication specifically meant for the cryptographic community. In November 2008 Satoshi Nakamoto shared this publication and his new hash development; blockchain was not yet a coined term. By January 3, 2009, the bitcoin net was officially launched. Over the course of 3 or 4 years dot-commers and leading tech entrepreneurs began to support the idea, with many large investment companies taking part in order to understand blockchain’s potential. The net investment in blockchain currently stands at roughly 2 billion USD. The new technology was covered by leading news outlets and media companies, with the number of blockchain studies increasing to roughly 2,000 at this point in time.
The Three-level Template Break Model
The first level of this model is money, which has accompanied mankind since the existence of debt. Roughly 25,000 years ago tokens such as precious artefacts appeared. 5,000 years ago the gold revolution took place, and mankind began to use the precious commodity for evaluation. 500 years ago fiat first appeared as money issued by the state. Fiat money could barely compete with gold other than the aspect of portability. With any new change money becomes increasingly portable, and thus it is vital to note that portability is an extremely important feature along with rarity, divisibility, reliability and interchangeability. As for crypto money, it succeeds all the parameters of fiat money other than popularity. It is only a matter of time before fiat money becomes more popular.
Bitcoin and Why We Need It
Money, goods and a payment system all used to exist separately. Bitcoin is the first tool that allows the combined, stored-value of a payment tool and measure of value. The three pillars of bitcoin are: fairness, freedom and innovations.
Fairness
The common individual does not understand how economics work. Often we are told about inflation, but it is important to understand what this general increase or fall in the purchasing value of money looks like. Inflation is caused by two main factors: a dilution of the money supply when an additional quantity of money is issued and the competitive performance of the economy. As for fiat money no one can guarantee the State does not use the money printing press to suit their own needs, thus diluting the money supply. Satoshi Nakamoto initially set up the maximum amount of bitcoins issued as 21 billion, and no one knows how to increase this amount by a single bitcoin.
Freedom
Tourists are well aware of the multitude of issues that bank cards present: blocked cards, non-working ATMs, etc. Blockchain allows the user to do unique things in this context. In order to open an account, you make a simple calculation in your application. The transaction fees are roughly 20 times less than in the fiat ecosystem, especially when it comes to large amounts. The banking system involves long waiting times, and unsecured protocols require banking institutions to verify the holder’s identity.
Innovations
It is incredible to think about the fact that we live in the 21st century, yet solve issues via messengers and use paper money. Money is just one of millions of blockchain applications, and we live in a paradigm when any fundamental stuff is a simple app.
Bitcoin’s Rising Price
A network exists when several people can communicate and interact. In the 1970s Metcalfe’s Law was formulated when Metcalfe sold moderns, but nobody had a clue why computers should be connected to one another. The law states that “the network utility is quadratically proportional to the number of peers in this network." Utility comes when much higher numbers of peers can communicate with each other. Cryptocurrencies are also networks that have the same features. If the number of bitcoin users reached 1 billion, its’ price would have risen 50 times due to the network effect. Furthermore, blockchain registration entry in the world’s most reliable database can be extremely valuable. For 300 satoshi (10^−8 bitcoins), 1 byte of data can be entered in the most reliable database.
How Long the Price Will Rise
No-way-back technologies such as electricity, the Internet and refrigerators' development all look like an S-curve until the saturation comes. Blockchain will continue to develop the same way until everyone begins to use it on a daily basis. Furthermore, there are 7 billion people around the globe, with 4 billion who use the Internet. Roughly 20 billion devices are connected to the Internet, which is 5 times more than the total number of Internet users. When considering each connected device as a single network peer, the market appears more saturated and interesting.
Risks
Loss
In the blockchain world money is key; there is no other way to identify you as the owner except for entering the key.
Theft
Not many people are computer literate, which means they do not understand how computers work and vice versa. If you are not computer literate, you may lose your funds one day if you clicked a wrong place or entered incorrect information.
Regulatory
The government may forbid the use of cryptocurrencies at anytime.
Misunderstanding
Everyone is capable of understanding various kinds of information to different extents and therefore, everyone makes different decisions.
Property
Blockchain technology elucidates a new angle with regard to the concept of property and introduces the idea of digital property. Most individuals think that a registry is only reliable if maintained by the State, but in reality anyone can maintain a registry as long as it is kept handy, fast-responding, reliable and effective. If this registry sits well with everyone, no State is needed to register and transfer the property. Digital property has some advantages over real property in a common sense: no taxes and restrictions, small fees, transparency (open source code), it can be programmed and exist in and of itself without an assignment to any particular device and no third parties control the items of digital property.
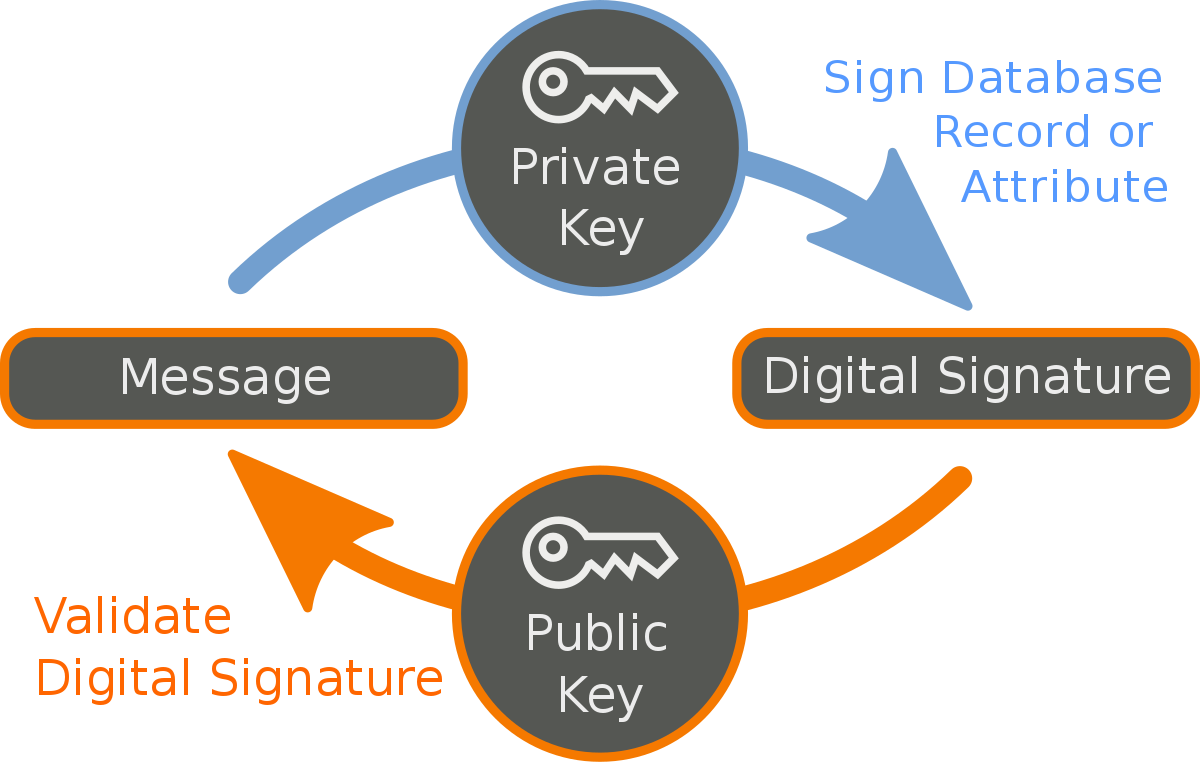
The Digital Signature
This process begins when you make a secret number that becomes your password key. Then you generate a public key out of that using an algorithm. No one should know your private key, but the public key can be sent to anyone because deriving a private key out of a public key is not possible (and rather economically non viable). The public key is an account identifier on which people transfer items of property. When you derive a public key out a private key, you can tell it to anyone. Digital signature generates a unique identification number for each transaction, which is always unique and makes it easy to verify whether you are the private key owner. Digital signature does not require any third party to prove the ownership of the signature, unlike the so called “digital crypto signature” seen on some governmental websites. Blockchain technology allows each individual the ability to maintain property without middlemen. Truly understanding how the digital signature functions will prevent you from ever being swindled.
It is also important to note that Blockchain has many different meanings and you should understand exactly what you are saying when you talk about it. Blockchain can mean a technology; roughly 35 various blockchain technologies currently exist. It is also a database with equal peers and no central manager. Blockchain is a trust protocol that allows the transfer of items of digital property from A to B with no mediation or necessity for A to know B. It can also be a piece of independently working code, or a P2P network where the peers communicate with each other.
The Most Interesting Things in Blockchain
Smart Contracts
A piece of code you transfer money to, where it is predetermined what these values will go through and the contract controls the fulfillment of the provisions.
Standalone devices
Robots can act on their own.
Programmable corporations
These are represented as code, hire people for operations they cannot yet do and programmed via economical incentive systems.
Mining
The concept of mining started when Satoshi devised the Proof-of-Work protocol based on the SHA-256 standard. Today there are lots of algorithms that allow you to prove something has happened, and likewise you can be rewarded for this. Mining is when the network can automatically verify a job has been completed and issue a reward. The world is transitioning to a point where any user’s action can be programmed, verified and the network subsequently issues a reward. Sathoshi ingeniously created this system that verifies, motivates and pays a reward. Blockchain, in short, is one of the world’s technologies that creates a living, virtual-reality.
For more information please contact: pr@cyberfund.io