The Big Bang Theory Project
So I have done a project for science... Let me know what you guys think...*
[The Big Bang Theory]
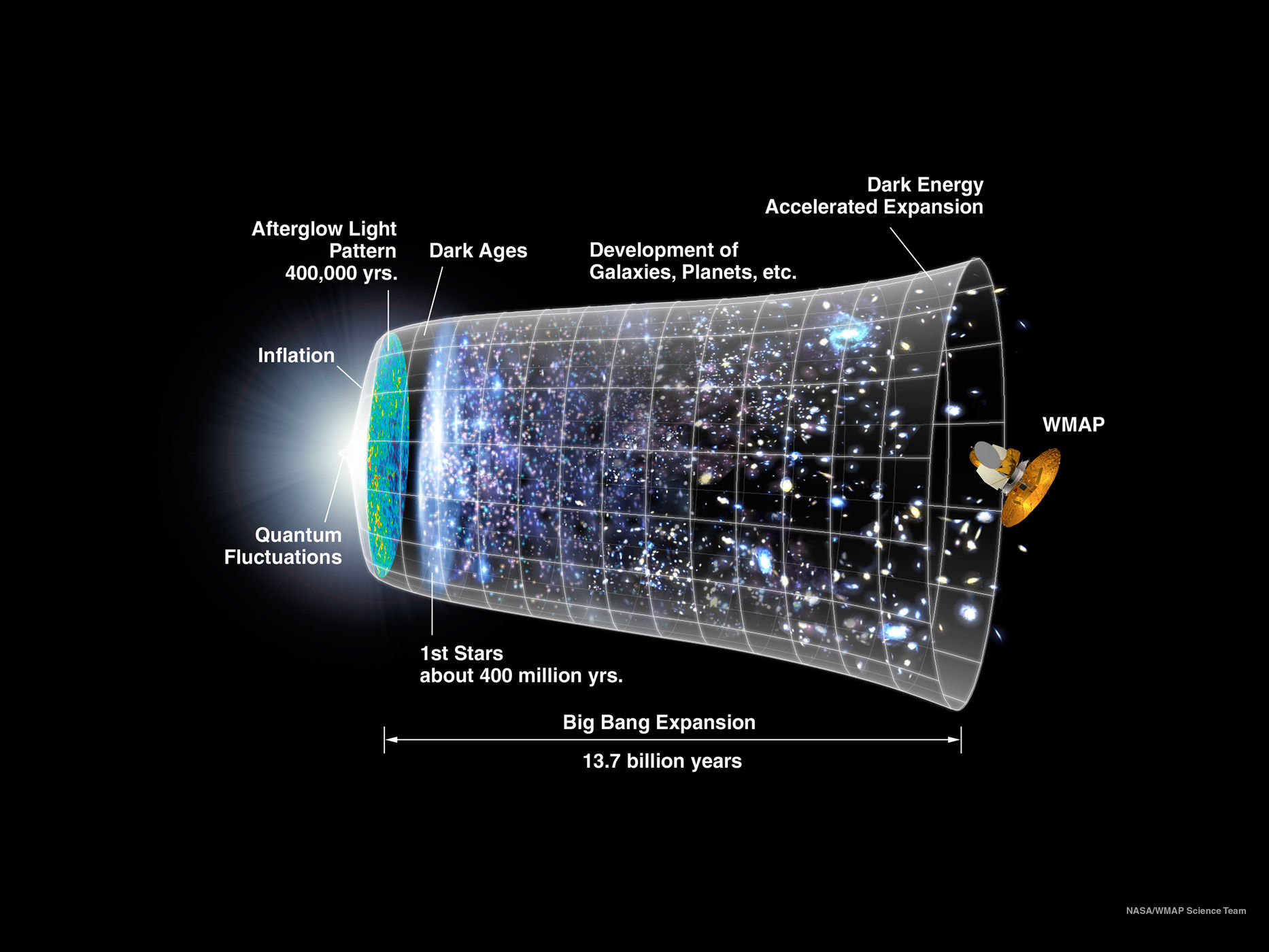
The universe was born with the Big Bang as an unimaginably hot, dense point. When the universe was 10-34 (hundredth of a billionth of a trillionth of a trillionth) a second old, there was an incredible burst of expansion known as inflation. This explosion created the basic atoms that make up our lightest gases from which the stars are formed. The universe doubled in size at least 90 times, going from subatomic-sized to golf-ball-sized almost instantaneously. According to the open universe theory, the universe will either collapse or continue it’s expansion. According to the closed universe theory, the universe will gravitationally collapse at a point in the later future. They call this collapse the big crunch.
The phrase "Big Bang Theory" has been popular among astrophysicists for decades, but actually hit the mainstream in 2007 when the comedy series came out. The show is about several researchers, including an astrophysicist.
[The first second, and the birth of light]

According to NASA, in the first seconds after the universe began, the surrounding temperature was about 10 billion degrees Fahrenheit. The cosmos contained a vast array of fundamental particles such as neutrons, electrons and protons. It decayed or combined as the universe got cooler.
NASA stated that “The free electrons would have caused light (protons) to scatter the way sunlight scatters from the water droplets in clouds”, that is why the early soup would have been impossible to look at. Over time the free electrons met up with nuclei and created neutral atoms. This allowed light to shine through about 380,000 years after the Big Bang.
The “afterglow” of the Big Bang- more properly known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB). It was first predicted in 1948 by Ralph Alpher and other scientists, but was only found by accident about 20 years later.
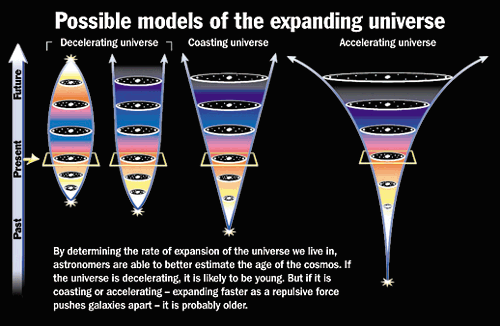
[Determining the age of the universe]
[Gravitational waves controversy]
While astronomers could see the universe’s beginning, they’ve also been searching for proof of it’s rapid inflation. Theory says that after the universe was born, in it’s first second, our cosmos ballooned faster than the speed of light.

[Faster inflation, multiverses & charting the start]

Not only is the universe expanding, it’s also getting faster as it inflates. It means that with time, nobody would be able to spot galaxies from Earth, or any other vantage point in our galaxy.
In March 2014 Avi Loeb said, ‘We will see distant galaxies moving away from us, but their speed is increasing with time.’
So if we wait long enough, eventually, a distant galaxy will reach the speed of light. It means that even light won’t be able to bridge the gap that’s being opened between the galaxy and us. There is no way for extraterrestrials on the galaxy to communicate with us, or send any signals that will reach us.
[Bibliography]
www.space.com



Please add the gedwriting tag.
Okay mam :)