Basic Fundamentals of Radioactivity
Source of image of public domain pixabay

Source of image of public domain pixabay
¿ But was exclusive interview of the uranium this property? Marie Curie tackled some experiments with atoms of similar atomic weight. The oxide tórico was producing an ionization that needed a load piezoeléctrica of 53 x 10^-12 amperes to neutralize it, this property was not an exclusive interview of the uranium: the torio also was radioactive. These were not the only important discoveries of Marie Curie. Two minerals of uranium, he explains in his report, <<there are great more assets than the proper uranium, which makes suppose that they can contain an element even more active than the proper uranium>>. For example, the mineral of uranium proceeding from the pechblenda was reaching a record four times major for than it would be necessary to expect from the quantity of uranium that it was containing. It did not seem to be to explain it, unless the pechblenda should contain another radioactive element. But this one would have to be present in minuscule quantities, since otherwise already it would have been detected. Also, they would have to be extremely radioactive, judging by the high ones that were turning out to be the records of radioactivity in his set. Since one had not found any other element that was containing similar levels of radiation, it was probable that this was an element till then strangers.
textual Appointment: I free of Curie and the radioactivity for Paul Strathern, pág: 7. 2015.
To discuss in a general way of the radiations or in the subject-matter of the radioactivity, there is necessary to realize well the following thing, which we live in a naturally radioactive world, which comes from natural and artificial sources where it is inevitable the majority of them is exhibited. And the important thing of all this with the time has achieved and at the same time learned to use the nuclear energy with different intentions: medical, warlike, industrial and for the generation of electrical energy dividing as source of radioactive emission.
As this one is born question of the radioactivity, to come to her we have to know, that the radiation is the transport or the spread of energy in the shape of particles or waves. I mention them also in a dynamic way, that we have to bear the nature of the radioactivity in mind, which it spends inside the atoms, at the same time these are content of three types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons, since the matter is constituted by atoms. The interesting thing since we enter the world of the atoms, it is that it is necessary to know something very important, since it it is one of his conditions where the atom is electrically neutral, which is due to the fact that the nucleus of every atom contains protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of electrons, then let's imagine the following thing that the atoms have the same quantity of protons, which of electrons balancing some with others, which does that the atom is electrically neutral. What does it particularly that the atomic nucleus has thousands of times more mass, that all the electrons of the atom, as for the diameter of the atomic nucleus it is 10.000 times smaller than that of the atom.
Either realizing well little basic knowledge, either we can describe or say in an opportune way that the process of emission is called a decay, radioactive breakup or radioactivity, notice because the beginning mentions on the invincibility of the human spirit, due to the whole scientific context, which had to be observed and determine his source, in this case the radioactivity and the form in this one must be tackled. When we speak about ionization, refer to interaction that happens in an atom or molecule and they liberate an electron, coming up to a point that The radiations ionizantes can go so far as to ionize or break ties in atoms or molecules millions of times before losing all his energy, that's why it is said in the science of the physics of way determinística, the radioactivity is tackled also as a physical phenomenon, which has very particular properties, related to the quantum mechanics, because it is supported according to the following abstraction of the reality, is a process at random or probabilístico, and the physicist only can predict the frequency or the rhythm in which it happens, we realize already well as it is the handling of this phenomenon at level of the science of the physics.
At technological level in the application of the handling of emission of radioactivity, because there uses potentially the electromagnetic radiation which is formed by particles called photons. This type of energy receives different names: visible light, x-rays, gamma beams, ultraviolet light, microwave, theoretically is supported in atomic processes that possess sufficient energy like to ionize atoms or molecules, in such a way that the activity of a material that it contains radionucleidos is the number of breakups, which happen per second in the above mentioned material. From obligatory other one also of the radiations ionizantes, the so-called radiations exist not ionizantes, constituted for example by the infrared radiation, big part of the ultraviolet status (UV), the visible light, the waves of radio, the microwaves, the radiation used in the magnetic resonances.
Close with the following essentials in radiation:
• Radiation α (alpha): in this type of case we have an unstable nucleus it expresses a nucleus of helium; the original nucleus transforms in other, this happens for the following thing, since result of the loss of two protons the atom will change to a different element, which has an atomic number two values down, in such a way that one considers or takes place normally in the heavy elements.
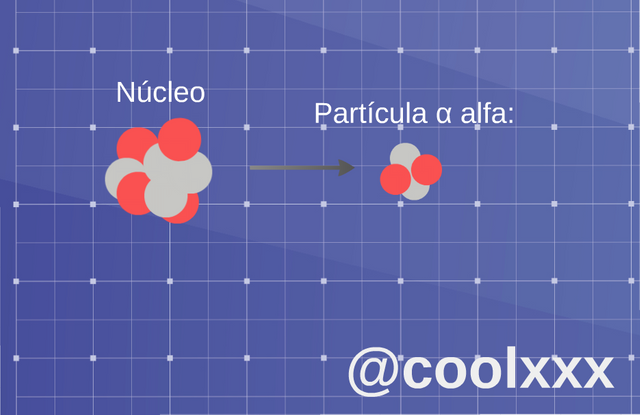
Radiation α (alpha). (Image prepared for @coolxxx)
• Radiation β (beta): when we come to this case two slopes of this radiation exist: if an unstable nucleus expresses an electron of beta less (β-), and if it expresses a positron it is named a beta more (β); also there happens the case, in which original nucleus transforms in other of the following way, the atom turns into an element a number higher or lower in the progressive series.
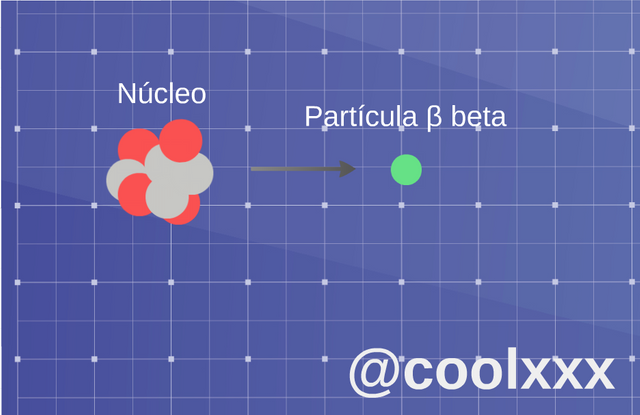
Radiation β (beta). (Image prepared for @coolxxx)
• Radiation (gamma): in this opportunity we have that now they are usually photons of very high energy, expressed by unstable nuclei or other processes and his nucleus only loses energy, in the shape of electromagnetic, radiation like it they are the x-rays or the microwaves.
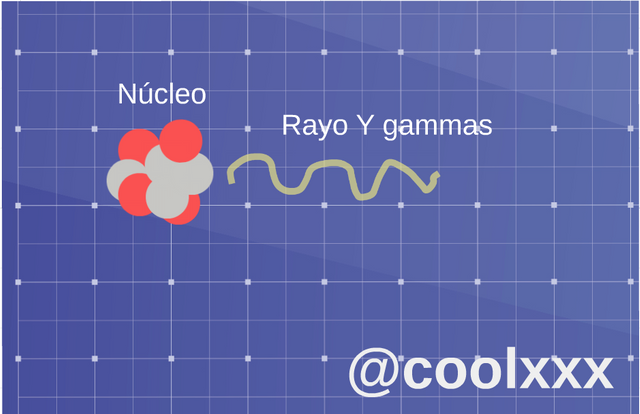
Radiation (gamma). (Image prepared for @coolxxx)
These different types of radiation react with the matter in different ways and someone of them are more penetrating than different.
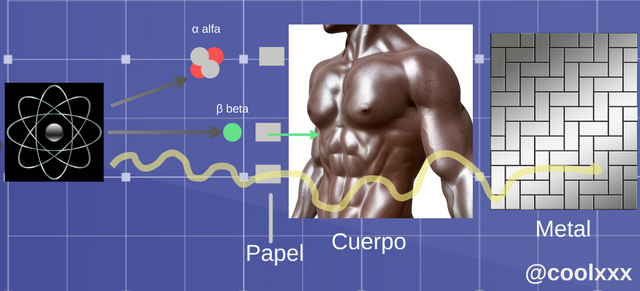
Penetration of the different types of radiation (Image elaborated and edited for @coolxxx)
Conclusion.
It is important to know and to spread that the radioactivity comes from natural and artificial sources, chemical level has diverse technological applications, in the medicine, electrical energy also because all the atoms of the same chemical element, it has the same quantity of protons. This is known as the atomic number of the element and it is named by the letter Z, also on the one hand we know that quite what surrounds us is a matter, which is composed by atoms.
consulted Bibliography:
Will weave, A., ' Nuclear energy: production of radisótopos and electricity ', Science and Development 23, p. 59, 1978
Folsing, U., Women Nobel Prize, Chapter 1. Madrid: Publishing alliance, 1992.
Muñoz Páez, A., Marie Curie, the radioactivity and the elements. Barcelona: Collection Big Ideas of the Science, RBA, 2013.
Quinn, S., Marie Curie, to life. London: Mandarin Paperbacks, 1995.
Radvanyi, P., They Curie. You give birth: Editions Belin, 2005.
Laugh, R., Marie Curie. Barcelona: Publishing Salvat, 1987.
Strathen, P., Curie and the radioactivity. Madrid: XXIst century Publishers, 1999.
Sánchez Ron, J. M., Marie Curie and his time. Barcelona: Ed. Critique, 2000.
Radioactivity and environment for León Garzón Ruipérez 1979.
The radioactivity Silvia Bulbulian. 2001.
Curie and the radioactivity for Paul Strathern. 2015.