Crypto Academy | Season 3 | Week 6 - Homework Port for @stream4u --- Lets Open The Blockchain.
Hello everyone, i am glad to be participating in this week's homework task, but before i dive in to it, i want to specially appreciate @stream4u for this interesting and detailed lecture. So lets start up with the homework task.
1. What is Blockchain?
Alot of traders find the blockchain to be kind of complicated but then, its concept is quite simple. Blockchain is considered to be a type of database, but before we can have a better understanding of the blockchain, we need to know what the database is.
A database is known as a collection of well organized and structured information or data that is stored in a computer system electronically in a table format so it can be easily accessed or managed. It can accommodate relatively large amount of data and also more than one user can access this information at once.
Now, Blockchain is kind of similar to a database. It is a decentralized digital ledger of transactions that records information, it is structured in chucks otherwise called blocks which are chained together, that is, if this blocks gets filled at a point, it is chained to the previous filled one with help of a hash which forms a chain of data called blockchain.
Now lets look at the main components of this blockchain ecosystem below.
Nodes: The nodes are applications that are connected to a computer that enables the blockchain to generate and validate a block. So when a transaction is carried out the nodes gets the information from the block once its connected making the network a decentralized one.
Blocks: Blocks are files that stores encrypted information so that once its stored, it cant be changed or tampered with. So once a node is connected, it get a copy of the information in the block, hence making the network a decentralized one.
Chain: Chain occurs when a filled block is linked to a previous block by a hash. This helps the blockchain to be well organized and structured too. The chain ensures that information is stored accordingly making the accessibility of the information easy.
Miners: these are the participants that carry out transactions in the blockchain network through mining of crypto and this is carried out by using a highly energy consuming computer to solve mathematical problems.
What are the types of Blockchains?
There are four major types of blockchain networks and we will be understanding in details what these blockchains are.
1. Public Blockchain
The Public Blockchain technology is where the cryptocurrencies like the Bitcoin started from. A user does not need permission to join and carry out a transaction. This blockchain helps to reduce the risk that comes with centralization like less security and transparency, in otherwords, anyone can access the blockchain in a decentralized manner as long as the user has an internet connection. However, transactions are verified through some consensus methods like Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work.
Moreso, the nodes in the blockchain enables transactions to be validated, but then the public blockchain can end up being non-functional if the required peers are not present. This blockchain can be used by the government during a voting process and companies can use the blockchain during fundraising to pose transparency and trust. Examples of public blockchains are Litecoins, Bitcoin or Ethereum blockchain.
Advantages
- There are no third party required for the public blockchain to work.
- The number of nodes participating on the blockchain does not pose any security risk on the blockchain.
- Everyone can easily access the public blockchain.
- The users of the public blockchain trust each other because the system is decentralized.
- There is transparency on the network during the verification process and other activities in the network.
Disadvantages.
- The transaction process is quite slow, it takes some time for a transaction to be completed.
- Scalability: As more nodes are been added to to the network, it becomes clumsy and can not scale making the network very slow.
- Using Proof-of-Work as the consensus method can consume more energy on the network.
2. Private Blockchain
This blockchain is just the opposite of the public blockchain, it works in a restrictive space and requires permission to join because it is controlled by a third party. It is more like a centralized network because only one authority is in control. The blockchain is mainly used by organizations and only allows the participants that are permitted to join the network. Though the blockchain provides security, transparency and trust to the participants but then the third party is incharge of the authorization and other settings in the network.
Moreso, the private blockchain can be used by organizations to manage their supply chain, track and verify their asset and carry out an internal voting process. Examples are Multichaim, Corda, Hyperledger Fabric etc.
Advantages
- Transactions carried out on this network is very fast, it takes less time because there are only few participants on the private blockchain.
- Scalability: the private blockchain is very scalable in the sense that only few nodes are required to validate transactions.
Disadvantages
- The private blockchain is been controlled by an entity making it a centralized network.
- There are no trust among participants as only the centralized nodes authorize the network.
- There is the risk of security that is, once a node is comprised, everything is lost.
3. Consortium Blockchain.
This is also known as Federated blockchains which is used as an creative way of solving an organization's problem both the private and public aspects. The consortium blockchain uses the present nodes during a consensus procedure and it's not open for everyone to join. It has a decentralized nature in the sense that it is authorized by more than one entity or organization.
Moreso, the consortium blockchain make use of a validator node to validate transactions and initiate or receive transactions. So the network provides transparency, efficiency and privacy but not controlled by just one party. Use cases of the blockchain is in food tracking, sharing research data and results and lastly in the banking payment system. Examples are Marco Polo, IBM Food Trust etc.
Advantages
- The consortium blockchain have scalability and also security.
- The participants have their control access.
- The network is more efficient than the public blockchain.
- There is better customizability and control of resources in the blockchain.
- The network works with a well organized governance structure.
Disadvantages
- Transparency is not completely guaranteed.
- The identity of a user is not completely concealed in the network just like in other blockchain
- The functionality of the network can be affected by the Regulations and censorship.
- A member's integrity can compromise the security of the network.
4. Hybrid Blockchain
The Hybrid blockchain sounds like the consortium blockchain, it has the properties of private and public blockchain and organizations make use of this blockchain if they wouldnt want to use just the private blockchain or just the public blockchain. Examples are Dragronchain, XinFin's Hybrid blockchain.
However, the use cases of the Hybrid blockchain is in the Real estate companies, they use the blockchain to run their system, also used in highly regulated markets like financial markets and lastly, in the retail business where they use the Hybrid network to work on their procedure.
Advantages
- the network provides privacy even when linked to the public network.
- the Hybrid network can withstand up to 50% of cyber attack.
- It works in a closed ecosystem, that is, it really doesnt make all the transactions public.
- The network is open to changes in the rules when the need arises.
- it provides a better scalability than the public network.
Disadvantages
- The network is not totally transparent.
- There is difficulty when the network has to upgrade.
- The network does not provide incentives for partaking in the network.
2. What are the benefits of Blockchain?
Advanced Security
The blockchain uses an advanced security to secure the transactions that are been recorded in a way that those transactions are encrypted and properly connected to the previous transactions through the hashing method.
Highly Efficient and Speed.
The blockchain is highly efficient and fast in the sense that it does not consume too much time in storing transactions and at the same time removes errors by automating the transactions made by the user in a highly efficient way.
Transparency
The blockchain has shown a high level of transparency by being a decentralized network, it uses the consensus method to provide validation and once the validation takes place, each nodes holds a copy of the transaction recorded.
Less costs
The blockchain network enables organizations to reduce cost of paying a third party. The blockchain also doesn't need much interaction when validating a transaction so this also reduce cost.
Instant Traceability.
The blockchain allows user to trace a transaction, like if a company is having fraud issues, they can get proof from the blockchain that can help expose the issues.
3. Explain Blockchain Distributed Ledger.
A blockchain distributed ledger is a decentralized database that distributes transactions that has been stored in the network to the nodes. It can be managed by multiple participants. The distributed ledger does not require the authority of a third party as it is not a centralized network.
The distributed ledger consist of an encoded and distributed database that stores transactions with a unique cryptographic signature called hash. It makes sure that the connected nodes are updated whenever there is a new data stored in the blocks. This helps to secure the network in a way that a new block is created if a node mines a block and it becomes validated making the system distribute a copy of the transaction to the nodes.
The Properties of a Distibuted Ledger.
Secure
This is very important in a way that the records that are been stored in the ledger are individually encrypted and this secures the record so it can not be hacked.
Time-Stamped
The transactions that are been recorded in the block are usually managed in a way that they appear to run in a timestamp order.
Distributed
The transactions are distributed in ledgers to all the participant so as to pose transparency in the network.
Anonymous
The blockchain does not display the identity of its participants.
Immutable
Transactions that are been recorded and stored in the block can not be changed or tampered with.
4. What is Blockchain Double Spending?
Blockchain Double-Spending is an issue that affects the cryptocurrency. This occurs when a cryptocurrency is used to make payment twice simultaneously. This is usually common with Bitcoin because it is a decentralized currency so hacker tend to target the digital information associated with Bitcoin so as to manipulate it and because it runs a peer-to-peer method of exchange where there is no third party, hackers tends to target the network.
Moreso, double spending tends to be impossible with physical currencies as they cant be replicated easily. For instance, if a person goes to the mall to get an item that is worth $30 and the person pays in cash, once the mall cashier registers the money, the person can not re-spend that cash except the person steals the money physically, but if that person was to pay in cryptocurrency, after making that first payment, the person can still use that same $30 in another mall through some manipulative act.
Types of double spending
There are three types of double spending that go on in the blockchain and they are:
1. Race Attacks: in this type of double spending, transactions are been sent by the hacker in quick succession, at the end only one transaction is been confirmed by the blockchain. The hacker tends to use the unconfirmed transaction to purchase an item and quickly invalidate it before it is been confirmed. This mainly affect companies that accepts unconfirmed transactions.
2. Finney Attacks: this type of attack is done by miners and it is done by pre-mining a transaction into a block using two wallets, so that the first wallet is used to make payment to the second transaction which is then broadcasted as the pre-mined block that also contains the first transaction. This also affect companies that accept unconfirmef transactions.
3. 51% attack: this is when a group or an individual is incharge of or in control of more than 50% of the hashing power used by the network for the purpose of altering the blockchain. So cryptocurrencies with relatively less hashing power normally face this kind of attack. This type of attack is very expensive to pull off, so hackers tend to go for cryptos that they can gain profit from.
How Bitcoin handles this problem.
Bitcoin make use of both the security features of the blockchain and the blockchain distributed ledger (in which miners have to verify their transactions first before they can be added to the blockchain) to handle this problem. When two transactions are been initiated using same amount of bitcoin, the nodes are notified (as they both go in to the unconfirmed pool) so the blockchain helps to do that.
However, when the two transactions are been received in to the blockchain as unconfirmed, the first one gets confirmed and verified in to a block meaning that the nodes agrees with the first transaction but then the second transaction did not get confirmed and verified, so the blockchain sees it as invalid and discards it.
5. Practical + Theory, Visit Blockchain Demo and check section Blockchain, then explain in detail how Blocks Hashes Work in Blockchain, what will happen when any middle of the block gets changed, try to give screenshot for each possible details.
Block hashing is a way of ensuring security to the messages that are been transmitted to a particular recipient. It encrypts the transaction and stores them in a block. Now i am going to be explaining in detail, how it works using the Blockchain Demo and some screenshots for better illustration.
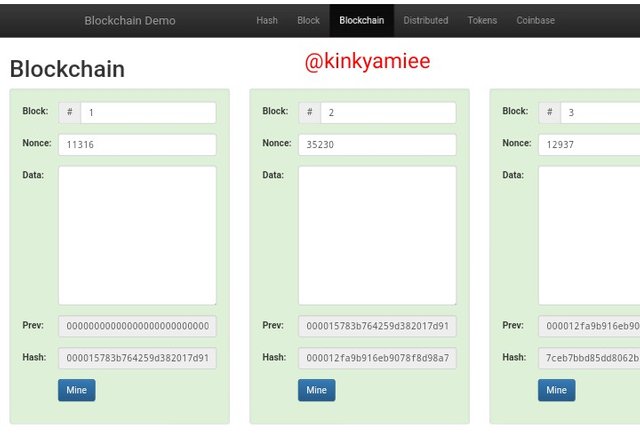
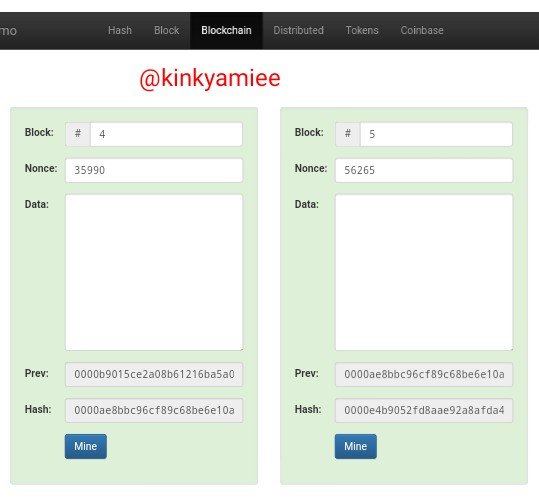
So from the screenshot about, we can see that the blockchain is structured in to 5 blocks and each of these blocks have some special features which are the Blocks(it is identified by its number), Nouce, Data, Prev and Hash.
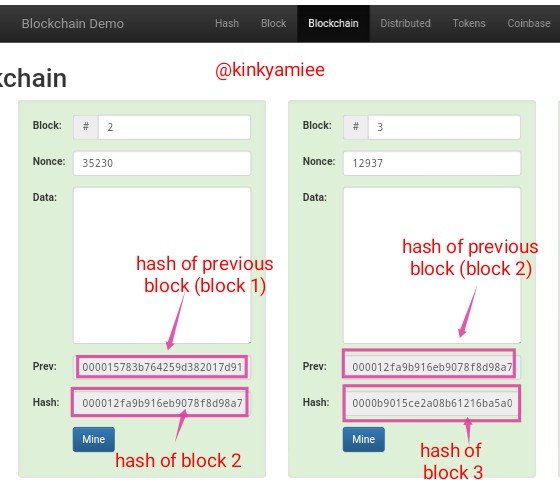
Now, From the screenshot above, we can see that Block 2 has its Previous hash as 000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf** which is the hash for Block one and to show the linking of both blocks, if we check out block one, we will see same hash there, so this hash links block one and block two with the hash for block 2 which is 000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19 together.
For block 3, we see the Previous hash as 000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19 which is the hash of block 2 and same is applicable to block 4 and 5, they are all linked.
What happens to the hash when data is Added to a Block?
So we can see from the above screenshots that no data has been stored in the blocks, so i am going be showing us what happens when a new data is stored in the block.
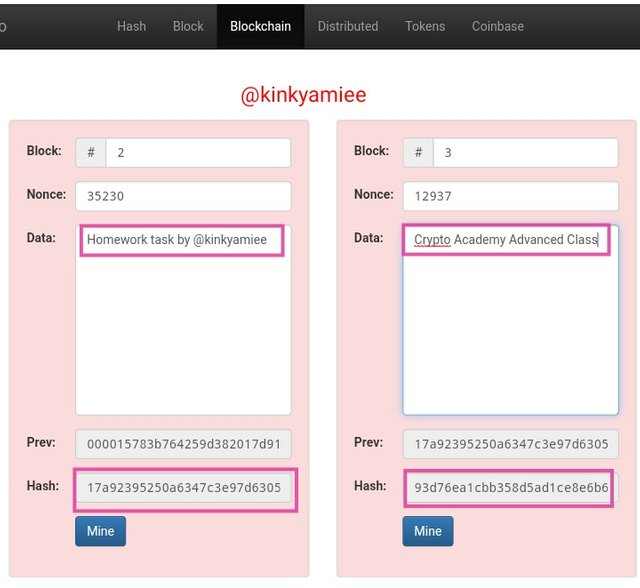
From the screenshot above, we can see that i have just added two separate data in to Block 2 and 3 and that has changed the hash for block 2 and block 3, so once a new data is added, the nodes are been updated, in otherwords, the new changes are distributed to the nodes.
The Mining Process of the Block?.
Mining in cryptocurrency is the process by which transactions are verified using high energy consuming computers to solve mathematical problems and adding them in to the blockchain. To be able to carry out a successful mining process on the blockchain, the nouce has to be correct and valid, so i will be checking for the right nouce value that will be validated by the block.
Now, going on to Mine Block 2, we noticed that the Nouce Value is 35230 and the hash is 17a92395250a6347c3e97d6305d4c9739cb3e03aa452e8f69159233f1dd64427, which when Mined, it came out to be invalid.
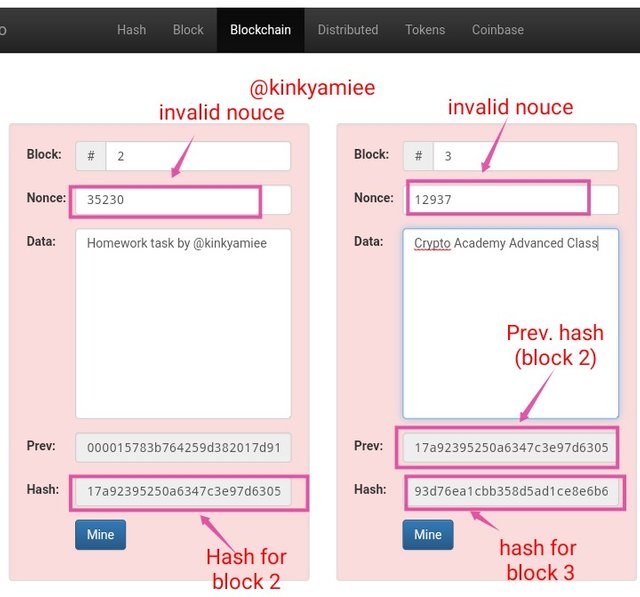
So i continued by changing the Nouce Value to 35300 and the hash was changed to fe643e33700d61287a75e3057619fb46988ae2780aa214c2d44564cdc74e03e9 which was also invalid.
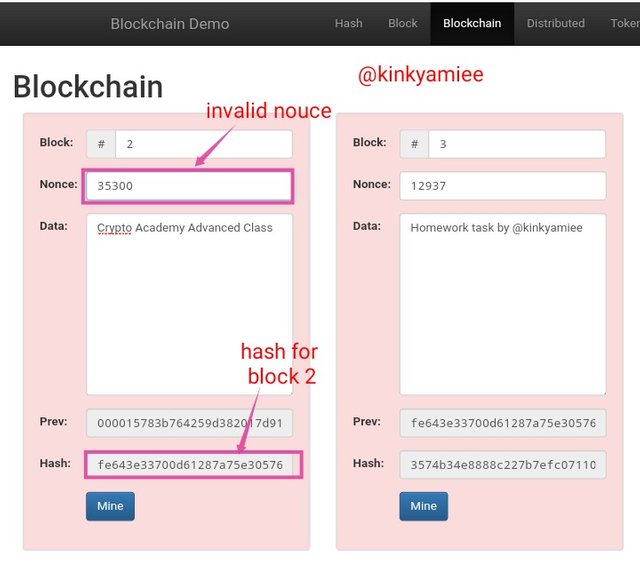
After trying that, i continued until i got the correct Nouce value by clicking on the Mine Button. Once i did that, the new Nouce value became 43978 which produced a hash value of 000094851f7f45ba105b2d288ca2dfc7d028c9ad4060cdc8bc556beae4379d6c and it became valid.
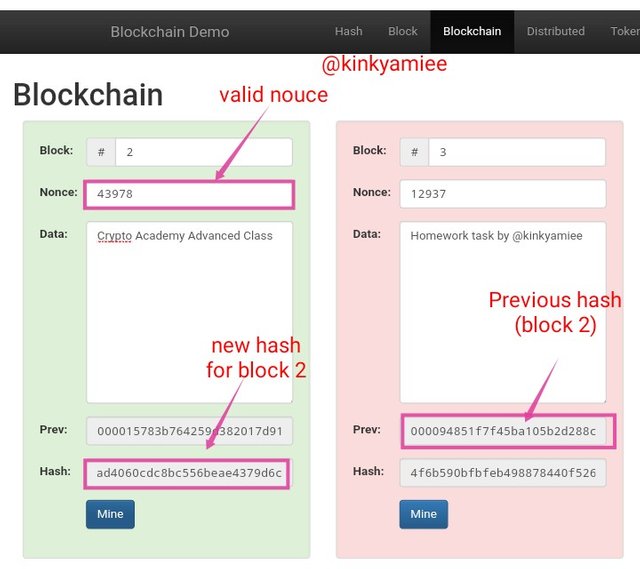
Now, we can see the hash for block 2 appeared on the Previous hash section of block 3 showing that the blocks are been linked up. So when i clicked on Mine again for block 3, a new nouce value was produced which is 337 with hash as 0000f8967abd4ca22e18e6726216b315960fc10e94e3680d73fe588792302b86 which was valid.
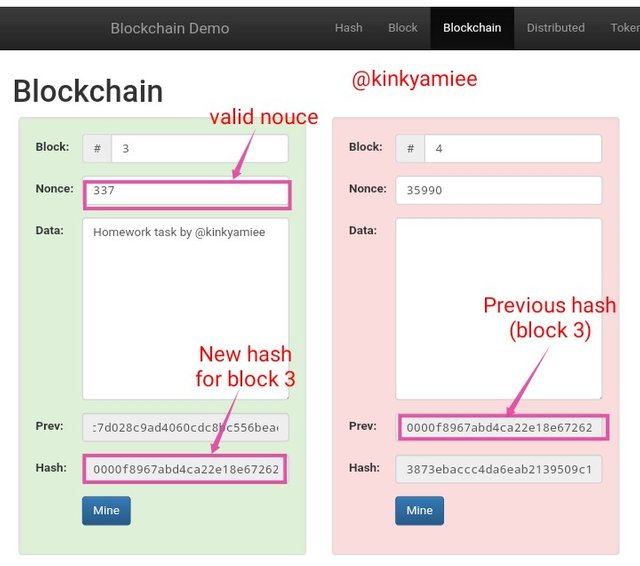
On the next block, we see that the hash for block 3 is now on the Previous hash of block 4, meaning the blocks are linked to the blockchain.
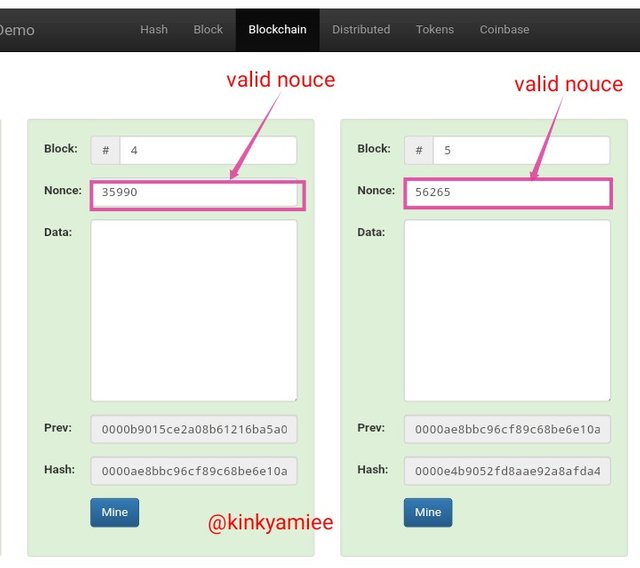
However, we can see that the new data that was added affected the rest of the blocks, changing the hash and nouce value. This just shows how data is been linked in the blockchain and secured at the same time.
6. What Is Race Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Finney Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Vector76 Attack in blockchain?
Finney Attack in Blockchain.
The Finney attack was named after the first Bitcoin transaction recipient called Hal Finney. This hack is a type of double spending attack that happens when a merchant accepts an invalid or unconfirmed transaction on the network. This hack is commonly done by miners in which they control the content of their blocks and hash.
So in this attack, the miner who is the attacker mines a block that has his transaction going on from address one to address two but does not release it to the system. The miners then uses the same coins that was used in the second transaction and releases it in the pre-mined block which is the merchant's block (address Three). However, the second transaction gets rejected by other miners but then its takes some time to do so.
Now for a merchant to avoid this kind of fraudulent attack, they have to make use of the traditional financial system where every payments and transactions can be accounted for and ensure that funds are not double spent.
7. Limitations/Disadvantages of Blockchain.
Scalability
The blockchain is not scalable in the sense that the network starts becoming slower as more nodes are been added to the network. That is, participant adding up nodes has to wait for some time for their transaction to be verified.
Not Secured
The blockchain is not completely secure in the sense that there are some few attacks that are still performed on the blockchain like the 51% attack, finney attack etc
Cost of transaction
The cost of carrying out a mining process is very huge, though it use to be tagged "nearly free" but now the cost of energy consumption is high.
Data is Immutable
The data that is been stored in the blockchain can not be changed or reversed that is, in this kind of situation if a participant makes a mistake while inputting an address and confirms it, it cant be changed.
Inefficiency
The blockchain can be inefficient in data storage and this can be a huge problem on the network as the blockchain size increases with more transactions and nodes.
Conclusion.
The blockchain technology is recognized as a decentralized network that records transactions and it consist of the blocks that stores these transactions and uses the distributef ledger technology to distributes these transaction details to all the nodes connecting to each other. The blockchain has shown some level of transparency due to it decentralized nature but are not completely secured.
Moreso, the mining process is been carried out in the blockchain where high energy consuming computers are used to solve mathematical problems, validate and confirm the transactions by calculating the correct nouce value and hash.
Finally, the blockchain technology has shown some level of competent as most merchant and company adopt the network rather than employing the centralized network.
Thank you for reading.
.jpeg)
Hi @kinkyamiee
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 7/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thank you very much @stream4u but pls i would like you to throw more light on what you meant by "what if any middle of the block was changed".
Because i know i answered the questions, if you read the screenshots properly, you will get the points i made. The only thing here was i didnt use block one and block two to explain, rather i used block 2 and block 3.
This screenshot answers for "how the block hash works"
This screenshot answers "what if the middle of the block is changed."
So pls, if you read properly, you will get the clear explaination because the score you gave for this work is quite low. Thank you Prof. @stream4u as i await your reaponse.