Sidechains - Crypto Academy / S4W8 - Homework post for pelon53
1.- Explain in detail the Sidechains with the use of ZK-Rollups.
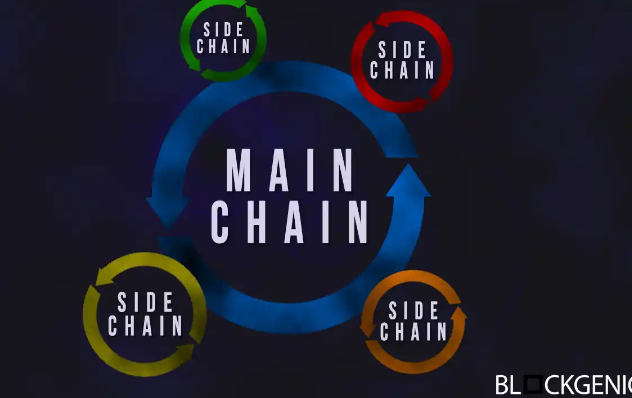
Sidechains are alternative and separate blockchains that run parallel to the main Blockchain. They have different miners from the main chain and these miners are called "validators". They have a separate consensus algorithm as well as a separate transfer bridge used in transferring funds to and from the main Blockchain.
In order to deposit funds in the Sidechain, they will send their assets to a mainnet smart contract where the assets would be locked. If they wish to withdraw the assets to the main chain (Ethereum), they will initiate an exit in the Sidechain, then wait for it to be included in the history on the Sidechain. Then they will provide a proof for that exit.
Sidechains are also proven to be generally effective, as all EVM contracts are capable of being ported to run directly on the sidechain. This enable ETH-like interoperability of contracts on each sidechain, and also on application-level logic.
There is a layer 2 construction that puts layer 2 blocks on Ethereum chain to promote scalability. This construction is known as Plasma, which operate in form of a sidechain.
With plasma, a lot of sidechain transactions can be processed offline and only a single hash of the block produced from these transactions would be added to the main blockchain.
There are some weaknesses of this method as it requires an exit game to be played before users can withdraw their funds. It also required a large volume of data to be maintained to aid validation. Users also needed to stay online for a long time in order not to lose their rewards.
In order to fix these flaws, a more user friendly layer 2 construction was developed to improve scalability. This is known as ZK-Rollups.
ZK-Rollups
ZK-Rollups is a zero-knowledge Sidechain of Ethereum blockchain that exist to solve some scalability problems of the blockchain. It is a layer 2 chain that reduces the resources used for computation and also reduces the storage when validation is being done. ZK-Rollups combines a lot of transfer in one transaction for verification by the smart contract. This goes a long way in improving the speed of operation and scalability.
The users of the ZK-Rollup sidechain are of two classes. First, the transactors and then the relayers. While the transactors are responsible for creating and broadcasting transfers, the relayers put together hundreds of transfers for the smart contract to verify. They create a SNARK proof hash, which facilitates transparency by comparing the snapshot of the wallet before and after transfers are made.
There are some DApps that use the ZK-Rollups scheme. Users of these DApps enjoy a lower transaction charge. However, running a zero-knowledge proof is deep and requires a great volume of computing power.
Merits Of Using ZK-Rollups
There are some advantages associated with the usage of ZK-Rollup. Some of them are mentioned below.
- The transaction fees charged each time a user makes a transfer are reduced.
- There is no requirement for an FG (fraud game) verification, which often delay withdrawals as it is the case of Optimistic Roll-up.
- The data contained in individual transactions are lesser.
- Plasma was faced with some limitations in the area of scalability. ZK-Rollups is found to be faster than both plasma and optimistic roll-up.
- ZK-Rollups promote decentralization by computing blocks in a parallel computing model format.
Demerits Of ZK-Rollups
- They require data optimization because that is the only way efficiency would be enhanced. This is because 'zero knowledge' are generally difficult to compute.
- A certain degree of ZK-Rollups security is unverified, this leaves a doubt in the minds of users.
- At the initial or start up level, ZK-Rollups allow centralization which is unhealthy for blockchains.
- They operate quantum computation, which makes the chain a bit prone to hack.
Zksynk is a good example of a platform that uses ZK-Rollup.
2.- Explain the Liquid Network side chain
Liquid Network
The Liquid Network is a sidechain of the Bitcoin Blockchain which allows faster transactions as well as the creation of new digital assets. It is a concept developed by Strong Federation, which was first introduced in 2017 by blockstream.
This Strong Federation are mutually-incentivized protocol that act between a sidechain and the main or anchor chain. The liquid sidechain operators are held accountable for the sidechain security. There is a body which exist to keep a record of block heights and secure the Bitcoin of the federation. They are known as functionaries.
Operations of Liquid Network
Bitcoin are sent to a certain address where the functionaries mentioned earlier will lock it to ensure that the coin is not in use somewhere else. That is the coins are locked to eliminate multiple usage. Liquid Bitcoin will be generated and issued to the user for use in the Liquid Network. Note that the Bitcoin of Liquid is known as Liquid Bitcoin, with the ticker, L-BTC.
LBTC is pegged at 1:1 with Bitcoin, meaning that L-BTC and BTC have the same value. The L-BTC would be ready for use after 102 confirmations have been made on the main Bitcoin blockchain. If a user wants to change the L-BTC back to BTC, they will also follow the process, but this time, they will only have to wait for two confirmations from liquid, after which BTC would be sent back to the BTC wallet of the parent chain. This process is referred to as peg-out.
Features of Liquid Network
There are basically two most important and most pronounced features of the network. They are;
- Creation of new digital assets: Liquid has a feature that allow users to create new crypto assets such as altcoins, digitized Fiats, collectibles, etc. This is a great feature as these assets can be developed and sent to a place where they can be verified.
- Private Transactions (PT): This is a feature where transaction details are only shared to parties involved without being exposed to external people. The amount transacted could be masked (hid) from others to promote privacy.
3.- Describe the steps to connect the Metamask wallet and the Polygon network wallet. Show screenshots.
To do this, I am going to show how to add the polygon network wallet to metamask wallet through the metamask mobile application. Below are the steps involved.
Step 1: Launch the metamask wallet and you will see the options icon on the top of the page.

Step 2: Click on the options icon (the three dashes as shown in the screenshot) to see the options.
Step 3: Click on settings and the settings page will be displayed. To connect wallets, we will be working on the 'network' option.
Step 4: Click on "add network" to start the configuration.

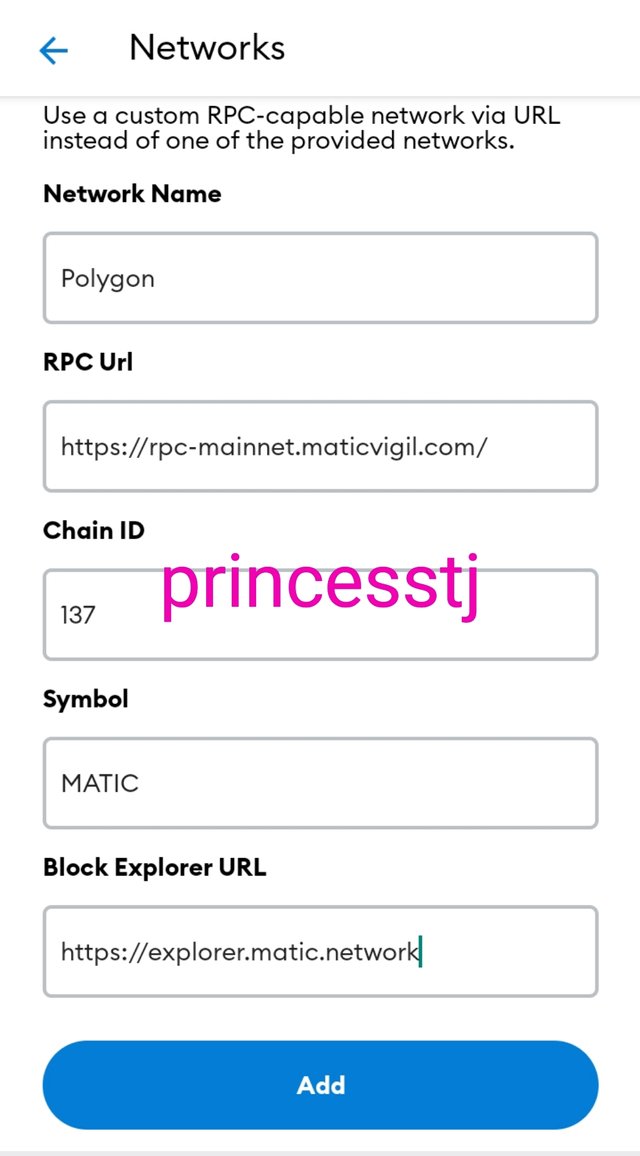
Step 5: Fill in the required information pertaining to the Polygon network as shown below. I have filled in my own and after that, I clicked on 'add' to add the polygon wallet to metamask.
Step 6: The wallet has been added successfully, as it can be seen in the screenshot below.

Step 7: Go back to settings, click on network and you will see the polygon wallet there. The polygon token, MATIC will also be included in the list of tokens.
4.- According to the polygonscan block explorer, when will the block 25,000,000 be generated? Show screenshot. Explore the 12,000,000 block, at that time, what was the price of the Matic? Show screenshots.
In order to get the time estimate for block 25000000, I opened the Polyscan website using the link. When the page opened, I typed 25000000 into the search engine and searched. The estimated time for block 25,000,000 as shown is 120 days, 8 hours, 50 minutes, 9 seconds to.
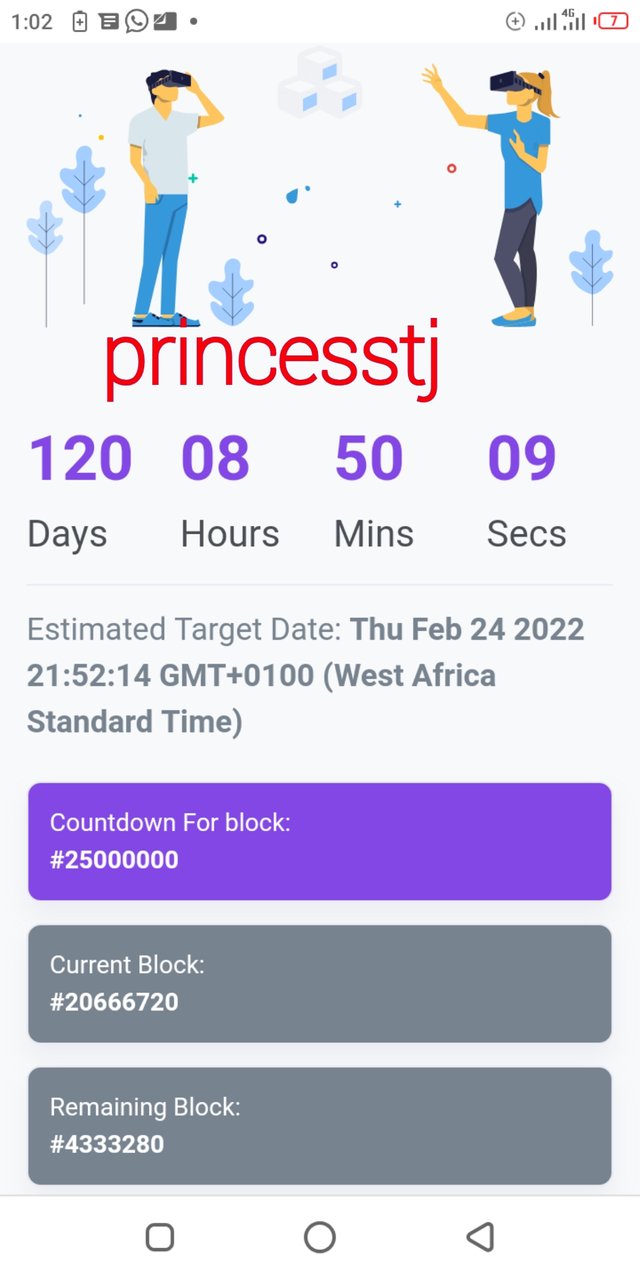
The estimated date is Thursday, February 24, 2022 at 21:52:14 GMT +1 (West African time).
I also typed in block 12,000,000 and the time it was generated was shown. That was 227 days, 2 hours ago. The date was March 14, 2021 at 9:35:48 AM UTC.
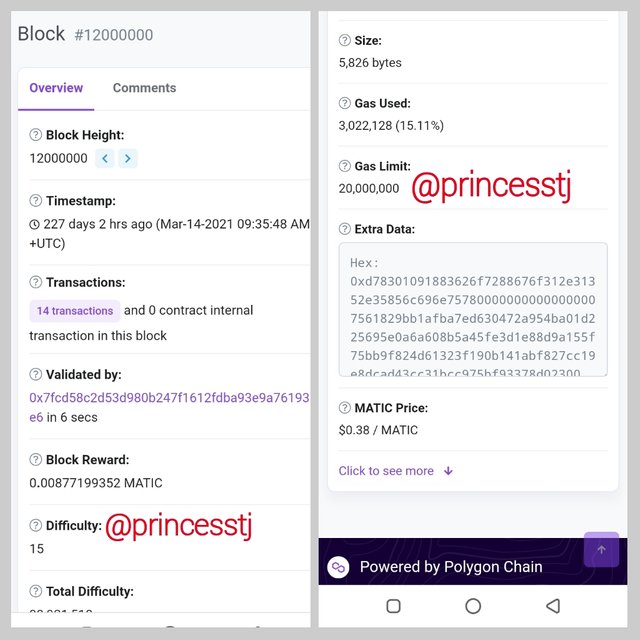
The size of the block was 5,826. The gas limit and gas used were 20,000,000 and 3,022,128 respectively. The price of MATIC at that time was $0.38
CONCLUSION
Sidechains operate parallel to the main blockchain. They are alternative chains used in carrying out faster transactions that scale. ZK-Rollups is an Ethereum sidechain just as Liquid Network is to the Bitcoin Blockchain. With sidechains, major blockchain scalability problems have been given a place as many transfers can be done without much limitations. I once again appreciate professor @pelon53 for this opportunity.