Avalanche Blockchain - Crypto Academy / S5W8 - Homework post for pelon53
1.- Explain in detail X-Chain, C-Chain and P-chain.
As explained in the lecture by prof @pelon53, the chains of the Avalanche network work as 3 different blockchains that carry out certain functions on which the overall avalanche network functions. Let’s talk about the chains in detail.
X Chain
This chain is mostly also known as the eXchange chain and functions as a decentralized platform where asset creation, exchange and trading happens. It is also where cross-subnet transfers are handled.
It utilizes the Avalanche Virtual Machine (AVM) and the X chain API to create assets on the X chain and allows for the trading of the created assets.
With the X chain API, we can create assets like we can create ERC20 tokens on Ethereum blockchain, check how many shares of the asset are controlled by which addresses, send the asset and check the transaction status.
The assets traded or exchanged on the X chain are smart assets representing real life assets and are governed by rules like ERC20 token standards. Transactions involving the creation, trading or exchange of these smart assets attract transaction fees payed with the AVAX token(native token of the Avalanche network).
C chain
This is one of the three chains of the Avalanche network known as the Contract chain. Developers on the Avalanche network create and deploy smart contracts for Dapps using the C chain using the C chain’s API like the X chain uses the X chain API .
It utilizes the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This gives developers the advantage of being able to fork over other decentralized apps compatible with the EVM. Whiles the X chain uses the Avalanche consensus protocol, the C chain uses a the snowman consensus protocol.
P chain
This is the last of the 3 chains of the Avalanche network. This chain is known as the Platform chain. This chain allows us to create new subnets, track active subnets and coordinates metadata between avalanche network validators.
Subnets consist of a number of validators whose function is to provide consensus for a blockchain. Each subnet of a blockchain has the ability to validate more than one blockchain, but a single blockchain can only be validated by one subnet.
The P chain utilizes the P chain’s API to carry out these functions. Like the C chain, the P chain uses the snowman consensus protocol.
2.- Explore the Avax Network platform . Screenshots required.
To explore the Avax Network platform, I visit the Avax Network. On the homepage, I am greeted with an introduction to some advantages of the Avax network and a demonstration of how it works using the three chains of the network.

Scrolling a little down, I am shown some things that are possible with the Avalanche Network:
Fast Ethereum compatible dapps that operate with low-cost fees, capable of confirming and processing thousands of transactions per second.
Build and deploy your own blockchain and virtual machine and dictate how the blockchain should work or run.
Staking your AVAX token to speed up transaction processing time and secure network against attacks with as minimal hardware as possible.

Keep scrolling further down and we will find some organizations and platforms that are currently building on the Avalanche network.
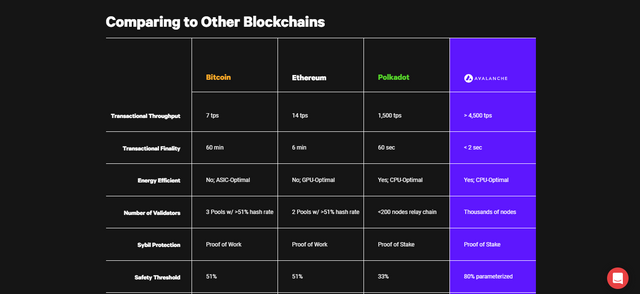
Further down the homepage, Avalanche goes further to show us how confident they’re of their network by providing statistical comparisons with other blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum and Polkadot. Avalanche compares Transactional Throughput, Transactional Finality, Number of Validators, Safety Threshold and other parameters as can be seen from the screenshot above.
Now let’s talk about the main features of the Avalanche Network. I will be exploring the following main features or sections of the network.
- Developers
- Individuals
- Avalanche-X
- Press
- Community
- Contact
- Developers
This section is where developers get to explore and use the avalanche network for developer functions. Developers can either start building or become validators of the network.
- Start Building
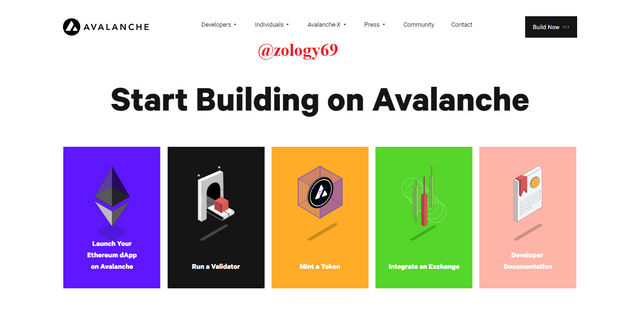
Like you probably already guessed, the start feature allows users to start building on the avalanche network. Developers can launch their own Ethereum dApp, Run a validator, Mint a token, integrate an exchange, or document their work. These can be seen in the screenshot above.
- Validators
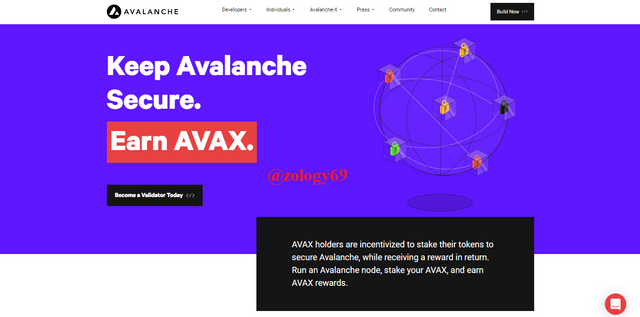
Under this developer option, developers can check validator statistics including total staked AVAX assets, staking ratio, staking rewards, total number of validators and total delegations.
In the screenshot above, we can also see some pretty convincing reasons why it would be best to stake on avalanche and become a validator: high ROI as much as 11% APY on staked AVAX, securing the avax network and becoming a part of their growing network, low hardware requirements.
- Individuals
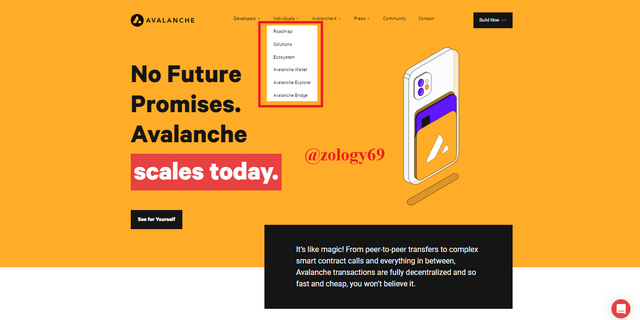
This section features 6 very important features, including Avalanche Roadmap, Solutions, Ecosystem, Avalanche Wallet, Avalanche Explorer, Avalanche Bridge.
- Roadmap

This section under Individuals is where you will find information on the plans of the avalanche network team including their goals. This will give investors and people who want to join in on their projects a view of what they’re getting into and tell them whether or not the platform has potential. In the screenshot below, we can explore the major milestones and ecosystem projects from January 2021- June 2021.
- Ecosystem

Here we find all the different categories of projects running on the avalanche network. We can see that this is a very big list and we also see other functioning projects and exchanges linked to avalanche including some very popular projects we know about like Binance and Metamask.
- Avalanche Wallet
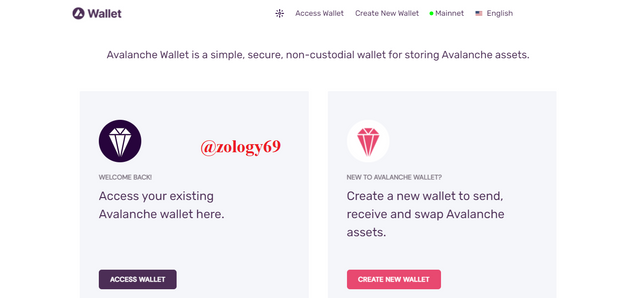
This is where you can access and use the avalanche wallet for transactions. The wallet is a simple and secure non-custodial wallet. In the wallet, you can store your avalanche tokens and manage them. We have the options to create a new wallet if you don’t already have a wallet or to access your existing wallet if you have one.
- Avalanche Explorer
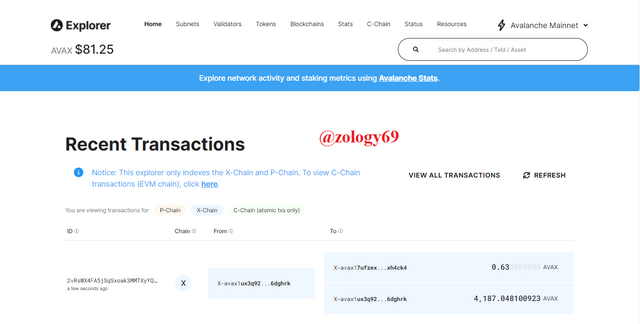
Like block explorers of other blockchains, the avalanche block explorer allows us to view transactions confirmed on the avalanche network. However, it is good to note that this explorer only employs the exploration of X and P chain transactions. To explore C chain transactions which are more of Ethereum Virtual Machine compatible, we use the snowtrace explorer
- Avalanche Bridge
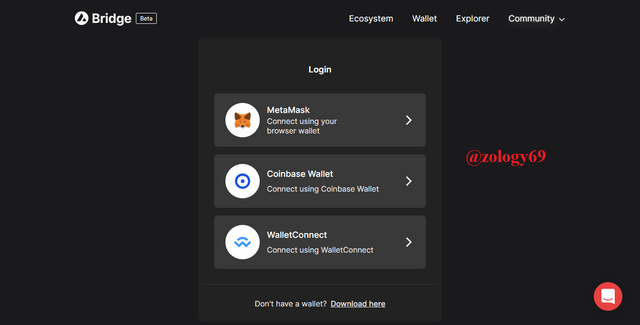
This is the last feature under individuals section and serves as a connecting bridge between the avalanche network’s C chain and the Ethereum network. To transfer ERC20 from the Ethereum blockchain to avalanche’s C chain or vise versa, we use the avalanche bridge. However, this is only possible after connecting to an external wallet.
- Avalanche-X
This section is where we can explore open grants or submit a general proposal. Let’s dive into each of these 2 functionalities.
Explore Open Grants
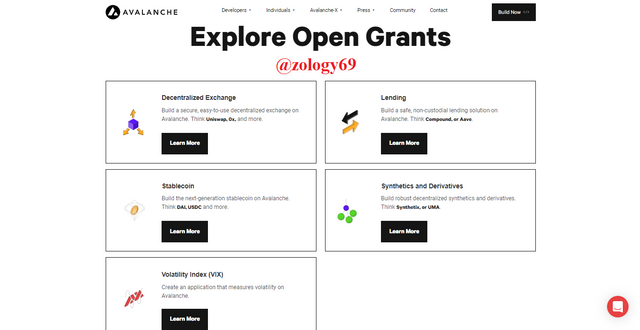
screenshot taken from https://www.avax.network/
Like the feature suggest, we’re able to scan through currently open grants based on the grant’s grouping. We have open grants classified according to : Decentralized Exchanges Grants, Stablecoin grants, Volatility Index Applications grants, Lending Solutions grants, and Decentralized Synthetics and Derivatives grant.Submit a general proposal

This is where the avalanche network gives developers with good project ideas the chance to present their ideas as proposals. They will be informed of requirements that their proposal must meet to get funding, and will go through 3 steps to complete the submission of their proposal.
- Press

This is basically the avalanche network’s own version of the newspaper and captures or tracks avalanche network activities in the news. Here, you can see whether crypto-based media like coindesk, Bloomberg and The Block talk about or mentions avalanche in their articles.
- Community

The avalanche community spreads out across popular social media apps like facebook, twitter, telegram, discord, and reddit. Under the community feature, avalanche therefore allows people join the avalanche community and connects members from across these social media together.

3.- Show the last contract verified in the C-Chain network and show the Smart Contract that was generated at that address. Screenshots required.

Like I mentioned earlier in my presentation, https://snowtrace.io/ is the explorer for avalanche’s C chain.
- So in my task to explore the last contract verified in the c chain network and show the smart contract that was generated at that address, I open https://snowtrace.io/
.png)
- Then from the options on the top of the snowtrace homepage, I hover my pointer over “Blockchain” and clicked on verified contracts
.png)
- A list of the recently verified contracts is shown in order of time verified, with the most recent or last block on the top of the list.
.png)
We can pick the following details about the last contract verified by clicking on the contract. From the screenshot below, we know the following about the last verified transaction at the time.
Contract address : 0x16ce3645E96D3D3e7c09f6aFfeda163D8e5a0c3a
Contract creator address : 0x2554fe74a448750efa63b5bf249C5b20Af18545C
.png)

4.- Explore the last block generated in the C-Chain network. Screenshots required.

Since we’re still exploring the C chain, we will still use snowtrace since it is the block explorer for the C chain.
- So to explore the last block generated in the C chain network, I open snowtrace
.png)
- Then again, I hover my mouse over blockchain and this time, I select view blocks. This will show me the blocks generated on the C chain network.
.png)
- Now I see a list of blocks created on the C chain network according to the times created, with the lalst block created on the top of the list.
.png)
- If we tap on the last block created which was block #9314795 at the time of my writing, we will find information about this last block. These are some important details we can find about the last block at the time of my writing.
Block Height : 9314795
Transaction Hash :0x7ec4b55bf87b4608466512277e740d89b2c6f4a7a56c0e9fa1a16f405eb4b7a0
.png)
.png)

5.- Explain in detail the Avalanche consensus protocol and the Snowman consensus protocol.

Avalanche Consensus Protocol
The avalanche protocol is a relatively new consensus protocol that solves certain shortcomings of the Nakamoto and classical consensus protocols that preceded it. While the Nakamoto protocol saw it okay to compromise a chance of probability to improve performance, the avalanche protocol capitalized on probability and greatly reduced the chance of errors so much that how it is described is incredible.
We all know how difficult it is to find SHA-256 hash collision. Some people describe it as nearly impossible. Now what if I said avalanche has drastically reduced the chances of finding an error so much that it would be easier to find a SHA-256 collision than to find an error. This is merely a description of how safe the avalanche consensus protocol is.
The avalanche consensus protocol is also superfast because unlike what we see with the older consensus protocols, transactions with the avalanche consensus protocol do not have to wait for transactions to confirm because transactions are confirmed in less than a second.
How the avalanche consensus protocol works
Validators on avalanche vote on whether a transaction is to be accepted or denied. In avalanche, there is no lead validator so each validator is a completely independent body and can vote freely whether to accept or reject transactions if they find them malicious. With voting protocols, the collective vote of agreement among the validators on the blockchain determines whether or not the transaction gets accepted. This is the same for the avalanche network, except that the voting among validators is on a much larger scale on the avalanche network.
Each validator votes to accept or reject a transaction. Other validators that meet this transaction see the number of validators that have accepted and how many have rejected this transaction. After enough validators agree on accepting or rejecting a transaction, if the transaction is accepted, it is sent to the virtual machine to be processed and sealed as accepted. However, if a transaction is rejected by the validators, it is removed from consensus. This process of accepting or rejecting transactions is done through repeated random subsampling.
Snowman Consensus Protocol
Earlier in my presentation, I mentioned that some 2 chains of the avalanche network uses a category of the snowman consensus protocol, the snowtrace protcol. These are the P and C chain. The snowman consensus protocol is created as an improvement to the avalanche protocol.
The difference between the two being that the snowman uses a linear ordering technique. Some people even describe the snowman protocol as a linear avalanche protocol. The snowman is linear because the C chain and P chain requires that transaction be linearly ordered and so parallel lines of the avalanche protocol using a partially ordered technique can not be used here.


Avalanche is able to perform a variety of functions due to the 3 different chains it possesses. These are the X chain, C chain and P chain. The X chain is where AVA assets are traded or exchanged, the C chain manages smart contracts, and the P chain is the main chain or the Platform chain.
The 3 chains of the avalanche network also have varying consensus protocols, with the X chain using the avalanche protocol, and the P chain and C chain using the snowman protocol. The snowman protocol is a modification of the avalanche consensus protocol that makes it easier to handle smart contracts.
Combining them all together makes the avalanche network faster, more secure and improves scalability of the network. This lecture and assignment has detailed on avalanches potential.
CC: prof @pelon53