You are viewing a single comment's thread from:
RE: 71-year-old male presents to the emergency department with the complaint of progressive shortness of breath and peripheral edema for one weeks' duration...
fluid with a low protein level and low specific gravity
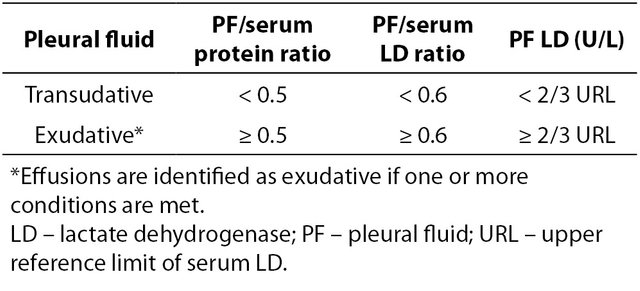
Pleural effusions are classified as either exudative or transudative.
A pleural effusion qualifies as an exudate with the one or more of the following criteria:
- pleural to serum LDH ratio of >0.6,
- pleural: serum protein ratio >0.5,
- total protein >3 g/dL, or
- pleural fluid LDH >2/3 the normal upper limit of serum LDH (200 - 300).
- normal serum LDH? 140 units per liter (U/L) - 280 U/L
Transudative effusions usually are due to a change in hydrostatic or oncotic pressure, as in conditions such as:
- congestive heart failure
- liver cirrhosis, and
- nephrotic syndrome.
The patient in the above scenario has pleural effusions secondary to congestive heart failure, which makes transudative fluid the correct statement.