Ruby Programming Tutorial - Lesson 30 - Implementing Linked Lists, simple blockchain
Singly Linked List
Linked lists is a data structure which is widely used across many applications, you can think of blockchain as a linked list too. Where each block contains information about transactions and information about next node ..
Linked list are similar data structure where it consists upon Nodes chained together in a way that each node contains information about next node.
Create a singly linked list, Where each node of list has connection to next node
Note that every chain of linked list has a head node, where it has no previous node.. you can also call it genesis node that's head will be nil, null or 0x000000, what that means is, it has no previous node, it is start of the node.
Every chain would also have a tail node, which has no information about next node because next node does not exists and in between head and tail nodes, you will find rest of the nodes which are linked together
When you are writing blockchain applications, most of the times you need to make sure once a node is completed, its no more update-able but that's not always the case you can always leave few data entries to be always editable.
e.g you are writing a blockchain where user needs to recover his password
Most of times once a block is completed it is locked. and its no more editable.. you can only retrieve information from it :)
but what linked list we are Implementing here, we will allow user to update the data in any node, anytime they want
Identifying the Entities
By studying blockchains and linked lists for a while, we came to conclusion that it has two entities
- Block/Node
- Chain/Nodes connected together
lets create a class for Node
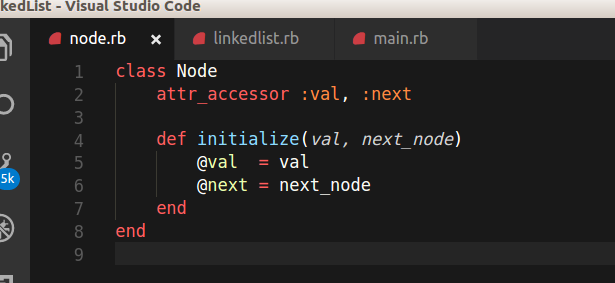
class Node
attr_accessor :val, :next
def initialize(val, next_node)
@val = val
@next = next_node
end
end
attr_accessor :val, :next
attr_accessor is used to create getter and setter methods for instance variables @val and @next, which allows to get and set values of these variables easily ..
we can do like node.val = "This value" and puts node.val to get the value and display it..
It is similar to writing methods like so
def val
@val
end
def val=(value)
@val = value
end
def next
@next
end
def next=(value)
@next = value
end
Once we have Node created, that has a data variable which can hold data, and a variable which holds the next Node
We are ready to create a linked list.
This linked list will be able to create as many lists as you want, you can always instantiate a new object from it, and create a list that serves your purpose.
This linked list has following properties
- Create a new list
- Add a node to existing list, node will be added at the tail of list
- Display all the nodes information, contained within them
- Get all the node references
require_relative 'node'
class LinkedList
def initialize(val)
@head = Node.new(val, nil)
puts @head.val
end
def add(val)
current = @head
while current.next != nil
current = current.next
end
current.next = Node.new(val, nil)
end
def return_list
elements = []
current = @head
while current.next != nil
elements << current
current = current.next
end
elements << current
end
def display_list
current = @head
while current.next != nil
puts current.val
current = current.next
end
puts current.val
end
end
1 - Initialize
Initialize method will take a genesis Node and will create a new list. you can add anything into the data variable.
We learned to create hashes, so we are going to take a hash to insert into the node.
note that whenever a new chain/linkedlist is created, it contains only 1 node that is genesis node. that's node's next variable is nil, so a new chain's head and its tail are the same node :)
2 - add (val)
This method allows us to add a new node in our chain, it starts from the root node. and traverse the list until it finds the tail. and then it adds new node there, and link it with existing chain
3 - return_list
This method will return the node's reference information to us
4 - display_list
This method allows us to see the values contained within the list nodes.
lets create a main.rb file. where we can create a new list, or a simple blockchain application
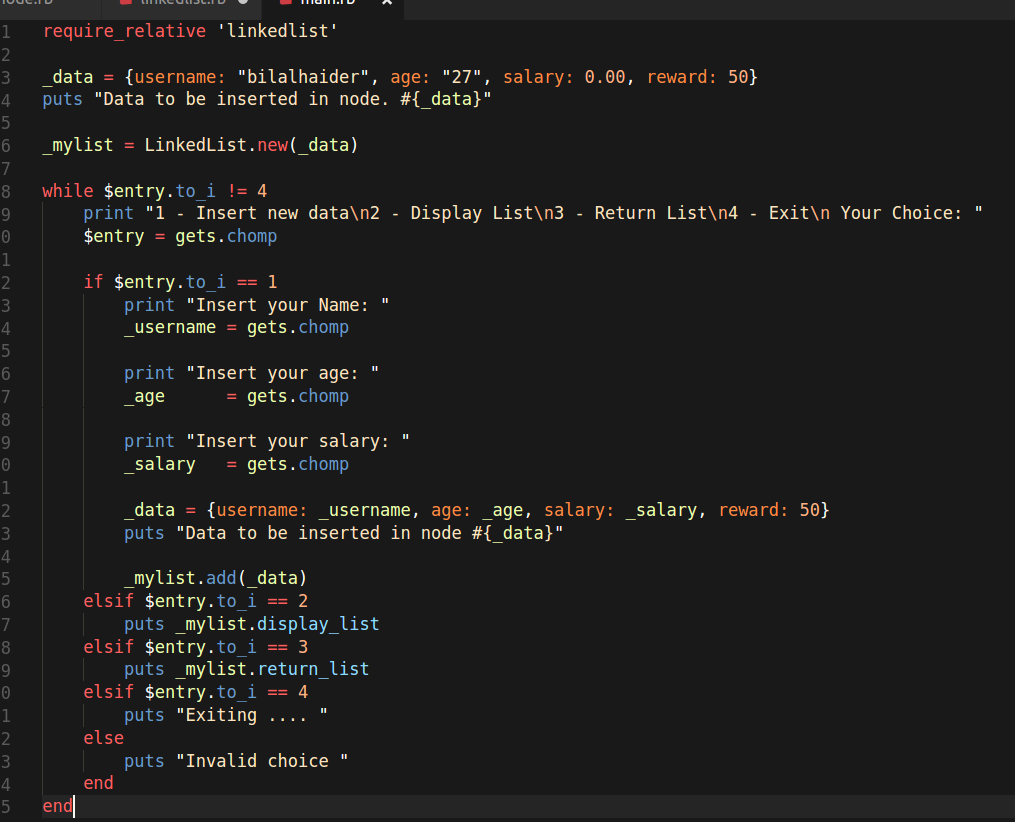
require_relative 'linkedlist'
_data = {username: "bilalhaider", age: "27", salary: 0.00, reward: 50}
puts "Data to be inserted in node. #{_data}"
_mylist = LinkedList.new(_data)
while $entry.to_i != 4
print "1 - Insert new data\n2 - Display List\n3 - Return List\n4 - Exit\n Your Choice: "
$entry = gets.chomp
if $entry.to_i == 1
print "Insert your Name: "
_username = gets.chomp
print "Insert your age: "
_age = gets.chomp
print "Insert your salary: "
_salary = gets.chomp
_data = {username: _username, age: _age, salary: _salary, reward: 50}
puts "Data to be inserted in node #{_data}"
_mylist.add(_data)
elsif $entry.to_i == 2
puts _mylist.display_list
elsif $entry.to_i == 3
puts _mylist.return_list
elsif $entry.to_i == 4
puts "Exiting .... "
else
puts "Invalid choice "
end
end
Above program, provides us a command line interface, where we have 4 options to choose from. If you have followed my previous articles you should be able to understand all the code.
we are constantly displaying choices to user .. when user selects an option we call methods accordingly to perform required task
In this example, we learned to create a simple blockchain application, which does not persist data. e.g it will lost all the data as soon as the program is exited.
In upcoming articles, we will learn different methods to persist data :)
We can use files, we can use database systems.. We will explore many different ways to persist data
For future
- Persist data, and store it in files
- Encrypt and Sign data, so that it can't be duplicated
- Create Peer to Peer network , so that we can push data to other people



Wow! This is great content! You have received a free upvote from the Minnows Freedom Project for being a good Steemian and posting original content. To learn more about us or to support us, please visit @minnows-freedom. You can also find us on Discord. Stay cool, create good content and have a nice day!
Great explanation! I started learning Ruby when Ruby on Rails became popular but have since stopped. Maybe I need to pick it back up.
most definitely bro, get back on track :)
It has become a beast now :D