Fluid Mechanics
Today, we will talk about the unique stream of science which is fluid mechanics. In this stream we really deal with the behaviour of the fluid (liquids or gases ) at rest as well as in motion. Thus this branch of science deals with the statics, kinematics and dynamics aspects of fluid. Basically you will deal with the terms like the viscosity, boundary layer, flow of the fluid ,etc.
Now we are talking about the term viscosity .
viscosity is nothing but the measurement of resistance of the fluid and it is primarily describe as the property of a fluid which offers resistance to movement of one layer of fluid over another adjacent layer of the fluid is known as the viscosity.
When two layer of a fluid , a distance 'dy' apart , move one over the other at different velocities, say u+du as shown in the figure., 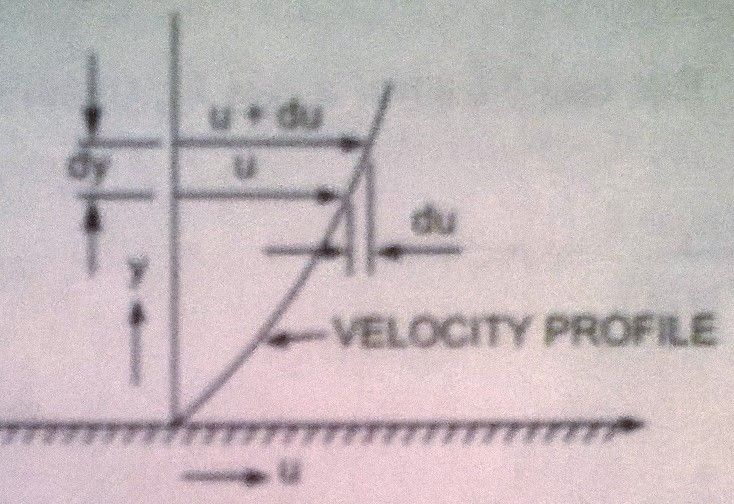
the viscosity together with relative velocity causes a shear stress acting batween the fluid layers.
The top layer causes a shear stress on the adjacent lower layer while the lower causes a shear stree on the adjacent top layer. This shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity with respect to 'y' .it is denoted by symbol τ (Tau).
Mathematically, τ ∝ du/dy
or, τ = μ du/dy
where μ ( called mu) is constant of proportionality and is known as the co-efficient of dynamic viscosity or only viscosity.
du/dy represents the rate of shear strain or rate of shear deformation or velocity gradient. Thus viscosity is also defined as the shear stress required to produce unit rate of shear strain.
Units of Viscosity :- The units of viscosity is obtained by putting the dimensions of the quantities in equation
μ= shear stress/change of velocities/change of distance
= force/area/length/time x 1/length
= force/(length) x (length)/1/Time
= force x time/ length x length
In MKS system, force is represented by kgf and length by meter (m), in cgs system, force is represented by dyne and length by cm and in si system force is represented by Newton (N) and length by meter (m).
therefore, MKS unit of viscosity = kgf-sec/m x m
CGS unit of viscosity = dyne-sec/cm x cm
In the above expression N/m x m is also known as Pascal which is represented by Pa. Hence N/m x m= Pa = Pascal
therefore SI unit of viscosity =Ns / m x m = Pa s.
SI unit of viscosity = Newton-sec/m x m
= N s / m x m
The unit of viscosity in CGS is also called Poise which is equal to dyne-sec/cm x cm.
The numerical conversion of the unit of viscosity from MKS unit to CGS unit is given below:
one kgf-sec/m x m =9.81 n-sec/m x m [ given 1kgf = 9.81 Newton]
But one Newton = one kg (mass) x one(m/sec x sec) (acceleration)
= (1000gm) x (100 cm)/sec x sec
= 1000 x 100 gm-cm/sec x sec
= 1000 x 100 dyne [given :- dyne=gm x cm/sec x sec]
one kgf-sec/m x m = 9.81 x 100000 dyne-sec /cm x cm = 9.81 x 100000 dyne-sec/100 x 100 x cmxcm
= 98.1 x dyne-sec / cm x cm
= 98.1 poise [given dyne-sec/cm x cm = Poise]
Thus for solving numerical problems , if viscosity is given in poise , it must be divided by 98.1 to get its equivalent numerical value in MKS.
But one kgf-sec /m x m = 9.81 N s / m x m = 98.1 poise
one Ns / m x m = 98.1/9.81 poise = 10 poise
or one poise = 1/10 Ns/m x m.
Newton's law of Viscosity :- It states that the shear stress (τ ) on a fluid element layer is directly proportional to the rate of shear strain . The constant of proportionality is called the co- efficient of viscosity .
Mathematically, it is expressed as given by equation
τ = μ du / dy.
Fluids which obeys the above relation are known as Newtonian fluids and the fluids which do not obey the above relation are called Non -Newtonian fluids.
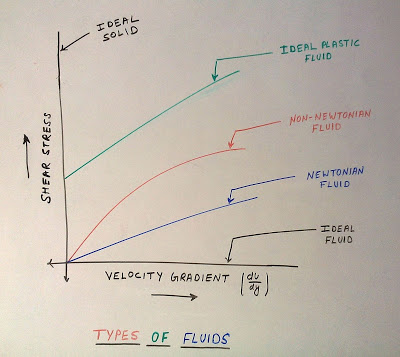
Types of Fluids :- The fluids may be classified into the following five types:-
- Ideal Fluids
- Real fluids
3)Newtonian fluids
4)Non-Newtonian fluids and
5)Ideal plastic fluids
1:- Ideal fluids :- A fluids which is incompressible and is having no viscosity, is known as an Ideal fluid. Ideal fluid is also known as the Imaginary fluids.
2:- Real fluid :- A fluid which possesses viscosity, is known as real fluid. all the fluids, in actual practice, are real fluids.
3:- Newtonian fluid:- A real fluid, in which the shear stress is directly proportional to the rate of shear strain (or velocity gradient), is known as a Newtonian fluid.
4:-Non-Newtonian fluid:-A real fluid , in which the shear stress is not proportional to the rate of shear strain (or velocity gradient), known as a Non-Newtonian fluid.
5:-Ideal plastic fluid:-A fluid , in which shear stress is more than the yield value and shear stress is proportional to the rate of shear strain (or velocity gradient), is known as ideal plastic fluid.
Congratulations @cosmic862! You received a personal award!
Happy Birthday! - You are on the Steem blockchain for 1 year!
Click here to view your Board
Congratulations @cosmic862! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!