Magnus Effect: What happens when we throw a spinning ball
If you were to throw a beach ball straight without any movement, whosoever, the results would be very predictable. It would move in the direction in which you threw slightly deviating if there was a wind. But what if we added a spin to it?
The deviation would be way more, and if done in very specific direction, it would literally float in the air like a frisbee travelling further away horizontally than you would've imagined. But why is that?
This is due to an interesting phenomenon known as the "Magnus effect", that separates flow of air based on the direction of its spin. In order to understand, let us look at a diagram below.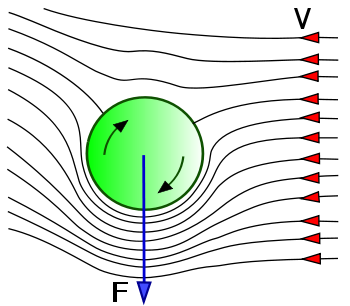
SourceVeritaseum GIF
A wind with velocity V is flowing from the right. If we imagined the ball to be separated into two portions horizontally from the middle, then the upper portion is rotating against the direction of wind, whereas the lower is moving in the wind's direction. The result is that the lower portion, removes air molecules from its vicinity, creating a low-pressure vacuum zone, whereas the upper portion is compressing air creating a high pressure zone compressed with air molecules.
The resulting differential in pressure pushes the ball in the vertically low direction, as indicated by the arrow F.
Verisateum explains this with a practical interesting example.

The spinning ball goes much farther than expected.
@point Yes. That's what I said.
Congratulations @xmachina! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP