Android version history
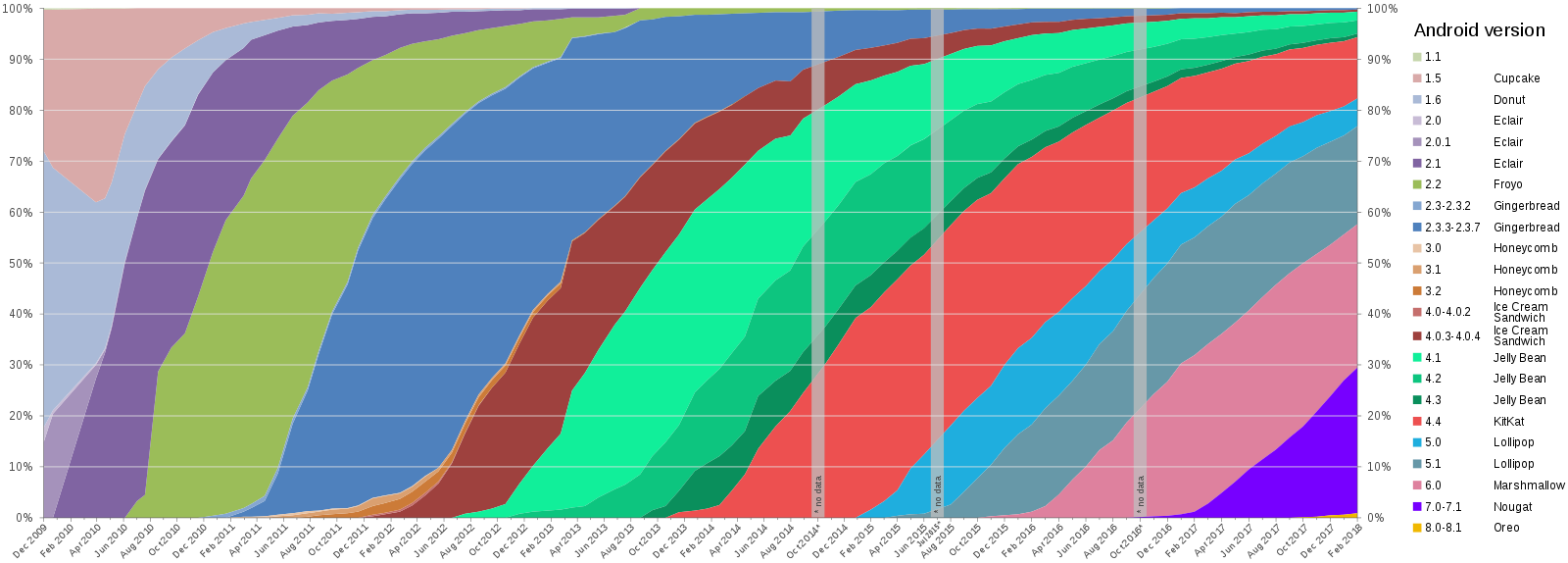
Global Android version distribution since December 2009, as of April 2018. Android Marshmallow the oldest supported version has running on 26.0% of all Android devices accessing Google Play; Android Nougat the most popular versions on 30.8% (while Nougat 7.0 only, is a little less popular at 23.0%), and all supported including Oreo on 61.4%.
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of the Android beta in November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008. Android is continually developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance, and it has seen a number of updates to its base operating system since the initial release.
Versions 1.0 and 1.1 were not released under specific code names. Android code names are confectionery-themed and have been in alphabetical order since 2009's Android 1.5 Cupcake, with the most recent major version being Android 8.1 Oreo, released in December 2017.
A version of Android KitKat exclusive to Android Wear devices was released on June 25, 2014, with an API level of 20, and it has since been renamed to Wear OS.
Pre-commercial release versions
The development of Android started in 2003 by Android, Inc., which was purchased by Google in 2005.[17]
Alpha
There were at least two internal releases of the software inside Google and the OHA before the beta version was released.[18][19]
To avoid confusion, the code names "Astro Boy" and "Bender" were only known to be tagged internally on some early pre-1.0 milestone builds, and thus were never used as the actual code names of the 1.0 and 1.1 release of the OS, as many people are mistakenly calling and repeating on the web.[2] Dan Morrill created some of the first mascot logos, but the current Android logo was designed by Irina Blok.[20] The project manager, Ryan Gibson, conceived the confectionery-themed naming scheme that has been used for the majority of the public releases, starting with Android 1.5 Cupcake.
Beta
The beta was released on November 5, 2007, [21][22] while the software development kit (SDK) was released on November 12, 2007.[23] The November 5 date is popularly celebrated as Android's "birthday".[24] Public beta versions of the SDK were released in the following order:[25]
November 12, 2007: m3-rc20a (milestone 3, release code 20a)[26]
November 16, 2007: m3-rc22a (milestone 3, release code 22a)[27]
December 14, 2007: m3-rc37a (milestone 3, release code 37a)[28]
February 13, 2008: m5-rc14 (milestone 5, release code 14)[29]
March 3, 2008: m5-rc15 (milestone 5, release code 15)[25]
August 18, 2008: 0.9 Beta[30][31]
September 23, 2008: 1.0-r1[32][33]
Hardware requirements
See also: Android (operating system) § Hardware
The main hardware platform for Android is the ARM architecture (ARMv7 and ARMv8-A architectures; formerly also ARMv5), with x86[c] and MIPS[d] architectures also officially supported in later versions of Android, but MIPS support has since been deprecated.[237]
Unofficial Android-x86 project used to provide support for the x86 and MIPS architectures ahead of the official support.[238][239] In 2012, Android devices with Intel processors began to appear, including phones[240] and tablets. While gaining support for 64-bit platforms, Android was first made to run on 64-bit x86 and then on ARM64.[241][242] Since Android 5.0 Lollipop, 64-bit variants of all platforms are supported in addition to the 32-bit variants.
Requirements for the minimum amount of RAM for devices running Android 7.1 depend on screen size and density and type of CPU, ranging from 816 MB–1.8 GB for 64-bit and 512 MB–1.3 GB for 32-bit meaning in practice 1 GB for the most common type of display (while minimum for Android watch is 416 MB).[243] The recommendation for Android 4.4 is to have at least 512 MB of RAM,[244] while for "low RAM" devices 340 MB is the required minimum amount that does not include memory dedicated to various hardware components such as the baseband processor.[146] Android 4.4 requires a 32-bit ARMv7, MIPS or x86 architecture processor (latter two through unofficial ports),[238][239] together with an OpenGL ES 2.0 compatible graphics processing unit (GPU).[245] Android supports OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0, 3.0, 3.2 and since Android 7.0 Vulkan (and version 1.1 available for some devices[246]). Some applications may explicitly require a certain version of the OpenGL ES, and suitable GPU hardware is required to run such applications.[245]
Android used to require an autofocus camera, which was relaxed to a fixed-focus camera[247] if present at all, since the camera was dropped as a requirement entirely (except for smartphones) when Android started to be used on set-top boxes.
possible source
Not indicating that the content you copy/paste (including images) is not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
Some tips to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
Thank You! ⚜
If you are the author, please reply and let us know!
Reply to this comment and I will auto upvote and resteem your post to my 36,000+ followers. @a-0-0