A QUICK AND EASY GUIDE TO SETTING PROJECT SUCCESS CRITERIA
Overview
In any project or experiment in particular, the first step is defining objectives or what the project aims to accomplish. Success definition differs from one assessor to the other, therefore assessment tends to be subjective. Typically, in the industry wherein a single project involves a cross-functional team and each member though united by one goal will have different focus and contribution. To be objective, improvement criteria must be based on the latest data gathered and agreed by the whole team. Important to note that an alteration in one process must not have negative impact to other processes, for the case of product alteration the customer’s specifications must be met or exceeded. Therefore, evaluation criteria must consider both improvement and comparability. Improvement at the directly affected process or product while comparability for indirectly or unaffected process or product.Before we go into details of setting up criteria, let’s briefly discuss some basic concepts of statistics.
What are the types of data?
There are mainly two types of data, quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data or numerical data are expressed in numbers and is further classified into continuous, discrete and ordinal data. On the other hand, qualitative data or language data are expressed in letters or words and is classified into several types. Allow me to give emphasis on numerical data particularly continuous data.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous | Data acquired through measurement | Dimension, Weight, Viscosity, Temperature, Pressure, pH |
| Discrete | Data acquired through counting | Defective amount, Conforming quantity, No. of students, No. of employees, No. of machines, No. of steemit users |
| Ordinal | Data acquired through comparison relative to its order or ranking | Defective mode rank, sales rank per item, production output rank per line |
Measure of central tendency
The three measures of central tendency are mean (average), median and mode. These numbers represents a different central value in the data distribution.
Median – middle score of a dataset that has been sorted in order of magnitude.
Mode – most frequently occurring value in a dataset.
Measure of variation
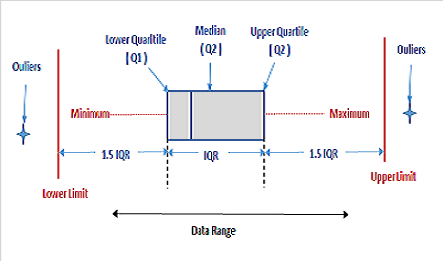
Variation is the extent to which data are dispersed with respect to the mean. Dispersion can be measured in several ways including but not limited to range, inter-quartile range and standard deviation.
Range – is simply the difference between the maximum and minimum value in a dataset.
Inter-quartile range – is a measure that represents the extent to which the central 50% of values in a dataset are dispersed.
Standard deviation – is am measure that consolidates the extent by which each value in a dataset varies from the mean.
How can we use these concepts in setting criteria?
Above concepts are only applicable to continuous data, discrete and ordinal has a different approach entirely. Additionally, improvement and comparability are treated separately. Comparable results implies that the implemented alteration gave results that falls within the reference data set and not in outlier region.For improvement criteria, both quartile and sigma method will still be applied. To better understand, let's take a case where we have a project that aims to improve yield by reducing non-conforming products. Evaluation result will be in terms of percent non-conforming quantity (%NC). If majority of the %NCs in all trials are within 0% to Q2 or median (quartile method) or 0% to mean (sigma method), then we've achieved an improvement.
Over-all judgement will then be "Project Successful".
If result is otherwise, go back to "Define,Measure and Analyze" of the DMAIC problem solving approach and try again.References
Text reference1. Deborah J. Rumsey, P. (2011). Statistics for Dummies (2nd ed.). Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc.
Image reference1. Improvement. (n.d.). Retrieved 2 7, 2018, from https://www.shutterstock.com/th/image-vector/improvement-chart-keywords-icons-279454157?src=pgl6q9pSlInR6iCyMPvROA-1-84
2. Pierce, Rod. (3 May 2017). "Definition of Range (statistics)". Math Is Fun. Retrieved 7 Feb 2018 from http://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/range-statistics-.html
3. Unit 1. Describing and Summarizing Data and the Normal Model. (n.d.). Retrieved 2 7, 2018, from https://sites.google.com/a/pottstownk12.org/statistics/6-rad-fns-rat-exp
Upvoted ☝ Have a great day!
thank you very much!
This is great @jeebee0331 :) you are starting to work on your field of strength. I hope you'll keep on motivating yourself in writing with the passion in you. :)