Structure of matter: elements, compounds and mixtures. Separation methods (basic concepts)
Pure substances and mixtures
There are many pure substances: water, iron, cooking salt, oxygen, sugar, butane, among others. others have less familiar names, such as sulfuric acid, calcium carbonate, benzene, among others.
A pure substance is one that can not be decomposed into other more elementary by simple physical procedures and has a composition and fixed properties throughout its mass. Now, in the world around us, pure substances are not usually found alone, but forming mixtures.
- If the components of a mixture are not distinguished by the naked eye, the mixture is called homogeneous (air, sea water, gasoline). the solutions are homogeneous mixtures. in a chocolate shake, you can not distinguish milk (liquid) from chocolate powder (solid), it is a homogeneous mixture.

Source

Source
Classifying substances according to whether they are considered natural or artificial is a difficult task because the borders between one and the other are very diffuse. It is clear that there are substances that are natural because they exist in nature, as is the case of water. But, next to all of them, today substances are manufactured in the laboratory. They are synthetic substances. Some of these, although they already exist in nature, are synthesized in the laboratory. Others are totally new substances that have no equal reference in nature, as with some plastics or medicines.

Source
The water, sand or wood of the palm tree are examples of natural substances.
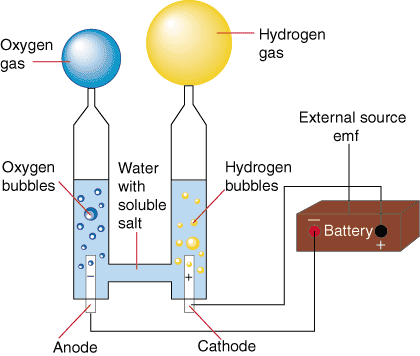
Water is a pure substance, it does not change its composition in the three physical states. When we pass an electric current through it, it is transformed into two gases: oxygen and hydrogen. This procedure is called electrolysis. Therefore, water, which is a pure substance, is also a compound because it can be decomposed into simpler substances.
You can also break down some substances if they get hot. The procedure is called thermal decomposition. For example, if we heat potassium chlorate, which is a solid, we obtain oxygen and potassium chloride, also solid. Pure substances that can be broken down into simpler substances are called compounds (such as water and potassium chlorate).
Pure substances that can not be broken down by any procedure are called elements (such as oxygen or hydrogen).
Source
Thermal decomposition of potassium chlorate.
Source
Water electrolysis.
Mixtures. Separation methods
How can we separate the pure substances that are present in a mixture? We will use different separation methods, depending on the properties of the pure substances that are part of a mixture.
Properties of matter
All matter occupies a volume, has a mass and is at a temperature. Volume, mass and temperature are general properties of matter and do not serve to know the kind of matter of which the bodies are made. Por example:
 |
|.jpeg) |
|Cream Source
Cheese Source
 |
| |
|Milk Source
Oil Source
To differentiate one substance from another, we must resort to other properties, which are called characteristic properties, such as color, smell, magnetism, solubility, density and many others that we will study later.
The characteristic properties of several mixed substances can not be ascertained. To know them it is necessary to separate them; that is, obtain pure substances.
Some properties of matter
General: mass, volume, temperature ...
Characteristics: density, color, solubility ...
Separation of the components
A series of separation methods or methods are used to separate the components of a mixture.
- If we want to separate two solids we use the sieve, which allows the separation of solid particles of different sizes. it is used with heterogeneous mixtures with solid components.
.jpeg)
Source
Sieve.
When the liquids are immiscible decantation is used.
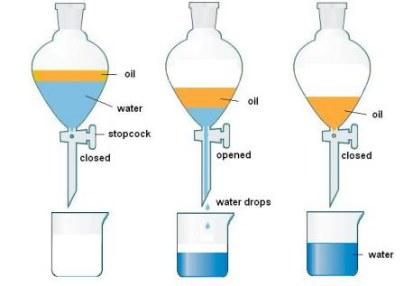
Source
Decanting
When the liquids are miscible, for example alcohol and water, distillation is used.

Source
Distillation