¡¡ TONSILLITIS !!
What are the tonsils?
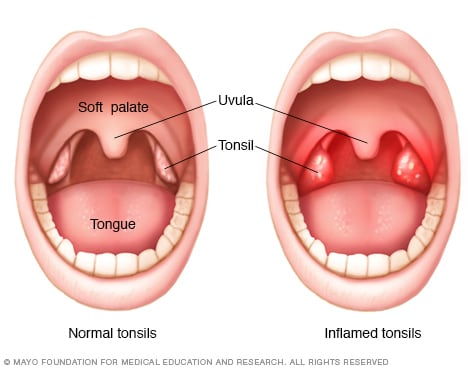
Tonsils are masses of tissue in the back of the throat. There are two of them, one on each side. Along with the adenoids, the tonsils are part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system eliminates infections and keeps body fluids balanced. The adenoids and tonsils trap germs that enter through the mouth and nose.
What is tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils. Sometimes, along with tonsillitis, the adenoids also swell.
What causes tonsillitis?
The cause of tonsillitis is usually a viral infection. Bacterial infections such as strep throat can also cause tonsillitis.
Who gets tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is more common in children older than two years. Almost all children in the United States suffer from it at least once. Tonsillitis caused by bacteria is more common in children aged five to 15 years. Tonsillitis caused by a virus is more common in younger children. Adults can get tonsillitis, but it is not very common.
Is tonsillitis contagious?
Although tonsillitis is not contagious, the viruses and bacteria that cause it are. Frequent hand washing can help prevent the spread or contraction of these infections.
What are the symptoms of tonsillitis?
Throat pain, which can be serious
Red and swollen tonsils
Difficulty to swallow
A white or yellow layer on the tonsils
Swollen glands in the neck
Fever
Bad breath
When should I seek medical help for my child?
Have a sore throat for more than two days
He has difficulty or pain to swallow
He feels very sick or very weak
He has difficulty breathing
Start drooling
Have many problems swallowing
What are the treatments for tonsillitis?
The treatment of tonsillitis depends on the cause. If the cause is a virus, there is no medicine to treat it. If the cause is a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, your child will need to take antibiotics. It is important for your child to finish antibiotic treatment even if he feels better. If the treatment stops too soon, some bacteria can survive and re-infect your child.
Regardless of what is causing the tonsillitis, there are some things you can do to help your child feel better:
Get a lot of rest
Drink a lot of liquid
Try soft foods if it hurts to swallow
Try to consume hot liquids or cold foods such as popsicles of ice cream to soothe the throat
It is free of cigarette smoke or anything else that can irritate the throat
Sleep in a room with a humidifier
Gargle with salt water
Suck a throat pill (except for children under four years of age, as they can choke on them)
Take an over-the-counter pain reliever such as acetaminophen. Children and adolescents should not take aspirin
The difference between a sore throat, pharyngitis and tonsillitis
The terms sore throat, pharyngitis and tonsillitis are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing.
Tonsillitis refers to the tonsils that are inflamed.
Pharyngitis is an infection caused by a specific type of bacteria, streptococcus. When your child has pharyngitis, the tonsils often become very inflamed, and inflammation can affect the surroundings of the throat.
Other causes of sore throat are viruses, and these can only cause inflammation of the throat around the tonsils but not the tonsils themselves.
Sore throat
A specific virus (called Coxsackie virus), which is seen more often in the summer and fall, can cause a slightly higher fever, more difficult to swallow and more discomfort in general. If your child has a Coxsackie virus infection, you may also have one or more blisters on your throat and on your hands and feet (so it is usually called hand-foot-mouth disease). Infectious mononucleosis can cause sore throat, often with marked tonsillitis; however, most children who have a mononucleosis virus infection have few or no symptoms.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is caused by a bacteria called Streptococcus pyogenes. To some extent, the symptoms of pharyngitis depend on the age of the child.
.
Babies : may have only a low fever and a thick or bloody nasal discharge
Young children: may also have a thick or runny nose with blood and fever. These children are often irritable, lose their appetite and often have inflamed lymph nodes in their necks. Sometimes young children complain of stomachache and not sore throat.
Children over three years: usually have stronger symptoms; the sore throat can be extremely painful, the fever rises above 102 degrees Fahrenheit (38.9 degrees Celsius), there are swollen nodes in the neck and pus in the tonsils.
It is important to be able to distinguish a pharyngitis (streptococcal infection) from a viral infection, because streptococcal infections are treated with antibiotics.


