SELF-MEDICATION FROM DIARRHOEA PERSPECTIVE
The use of medicines by individuals for the treatment of self-diagnosed or recognised signs and symptoms is termed as self-medication. Self-medication (although may seem to be a rapid way to get rid of an infection ) is a slow and dangerous way to harm the human body. In developing countries where the cost and access to good health care are considered to be expensive, self-medication might probably be considered a normal way of life.

Why do we engage in self-medication, is it because it is easier to procure over-the-counter drugs than seeing a consultant? Or perhaps because we think it is expensive and time-consuming (if this is our concern, then it is important that we create time to see the doctor)or because we are scared or ashamed to talk the doctor about our problem?.
Have you felt that urge to rush to the lavatory or toilet where you pass out loose or liquid stools? when there is an urgent urge for the passage of loose or liquid stools for more than three times per day, and in some cases, these feeling is accompanied with abdominal cramps, abdominal pain, blood in the stool, fever or bloating then you can be sure that you have diarrhoea.
So what do you do in this situation? Do you visit the clinic, make use of the first aid or employ self-medication?
If self-medication is your option, Hmmm, you really need to a have rethink.
The increased or frequent bowel movement, this may not be accompanied by fever, in fact most people who experience diarrhoea may not consider the situation a serious one, for the first 12 hours because most individuals presume that diarrhea is self-limiting and therefore allows the immune system to fight against the pathogen involved but after the first day, most individuals decide to visit a nearby patent medicine store where self-medication is employed most commonly with the metronidazole.
Why diarrhoea?
I decided to discuss self-medication using diarrhoea because, according to the World Health Organisation, there are about 1.7 billion people affected with diarrhoea each year and of these individuals, about 760,000 children under the age of five die each year as a result of diarrhoea, hence a need to bother. Or don't you think there is a need to be worried that a diarrhoea disease which can be notably prevented just by drinking safe water, adequate sanitation and hygiene is killing scores of people especially children?
Now let's educate ourselves a little about the possible reasons why most people occasionally have diarrhoea, the cause of diarrhoea, the source of the infection; the pathogens involved and severity of the infection
Why do Most People Occasionally have Diarrhoea?
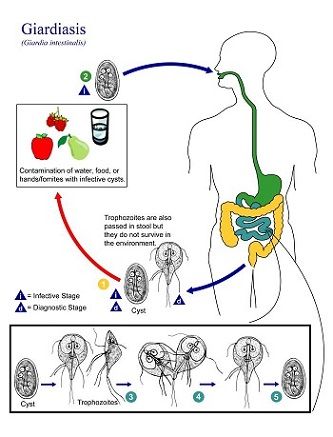
Giardia_lamblia_life_cycle:By PHIL - Public Health Image Library - search for giardia, life, cycle, Public Domain](https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1313043)
Diarrhoea in most cases is a subjective evidence of an infection of the intestinal tract, and this Infection can be transmitted through contaminated drinking water or food, it could also be from person-to-person as a result of poor hygiene.
This means that the consumption of raw vegetables and undercooked shellfishes, forgetting to wash the hands before eating or after using the toilet, improper food handling, particularly on dirty kitchen surfaces, contact and exposure to vomit-stained surfaces without proper washing of hands might results in an infection of the intestinal tract, with diarrhoea as an evidence.
The resulting diarrhoea if not properly managed may result in deaths, stunted growth or malnutrition in children under the age five, electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, renal impairment, poor intellectual development and defective immune system responses.
What are the things in the contaminated food or water that is responsible for diarrhoea?
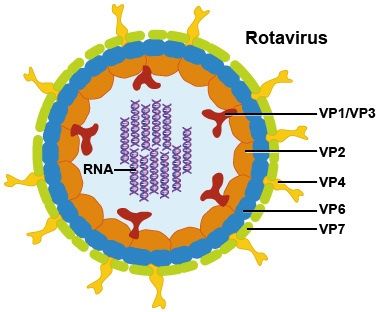
There are some pathogenic organisms that could result in infection when found in the food or water. Diarrhoea is caused by pathogens and these include Bacteria (Escherichia coli, Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella and Salmonella), Viruses (Rotavirus, Norovirus which could in acute diarrhoea) and Protozoa (Cryptosporidium, Giardia lamblia). From the Figure above, it is evident that Giardiasis results when water has been contaminated with the infective cyst of Giardia lamblia.
How then do we know what we need to get rid of this pathogens? Or do we just assume based on what suits us? Treatment of infection depends on the organism involved. For example, Antibiotics are used to either inhibit or kill bacteria agents while an antiviral agent is indicated for viral pathogens.
These Pathogens could cause various disease and in some cases, the need to seek urgent medical attention is important and necessary. Diarrhoea is a symptom of the many severe conditions, a few of such conditions include:
- Food poisoning
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Appendicitis
- Anthrax
- Ebola virus disease
- Drug allergy
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Derminophen overdose
- Digitalis toxicity
Immunocompromised individuals with diarrhoea should not be tempted to engage in self-medication as this symptom might be at risk of the above-listed conditions. Although some other conditions listed below are considered milder but after 48 hours of the exhibition of symptoms, individuals are advised to seek medical attention to avoid endangering their lives. examples of such condition include:
- Viral gastroenteritis
- Bacterial gastroenteritis
- Giardiasis
- Lactose intolerance
- Malabsorption syndrome
- Ulcerative colitis
- Amebiasis
- Crohn's disease
How Severe is Diarrhoea Infection?
Depending on the duration of symptoms, diarrhoea could be Acute or Chronic.
Acute diarrhoea will last for about two weeks; this type of diarrhoea is the leading cause of death in children below four years of age, particularly in the developing world, where self-medication is considered cheaper and faster.
Chronic Diarrhoea that is usually persistent and lasts for about four weeks or longer. Persistent diarrhoea might be as a result of dietary changes, the intake of certain medicines, stress, irritable bowel syndrome, although persistent diarrhoea might be a symptom of a more serious condition, such as a malabsorption syndrome, colorectal cancer, chronic infection or inflammatory bowel disease.
When considering the number of loose stools, Diarrhoea can be classified as :
Mild diarrhoea: the experience of a few diarrhoea stools in 24 hours.
Moderate diarrhoea: visiting the lavatory more than a few times but with not more than 10 diarrhoea stools in 24 hours.
Severe diarrhoea: The increase in the number of diarrhoea stools to more than 10 loose, watery stools in 24 hours.
Conclusion
Although self-medication in the treatment of diarrhoea in otherwise healthy adults could be considered as safe, medical intervention is recommended for the management of diarrhoea in children, weak and delicate individuals, pregnant women, the elderly (> 65 years), persons with the presence of concurrent or underlining chronic disease.
The benefits associated with appropriate self-medication cannot be compared with the risk involved with one or more of the following :
- Incorrect self-diagnosis
- Masking of a severe disease
- Risk of dependence and abuse
- Delay in seeking medical advice when it is needed urgently.
- Infrequent but severe adverse reactions
- Incorrect dosage and dangerous drug interactions
- Incorrect choice of therapy
- Incorrect administration
Please do seek medical intervention when there is no decline in the symptoms (when the diarrhoea stool does not stop) after 48 hours, or when the condition is becoming progressively worse with situations such as dehydration, abdominal distension, or the onset of dysentery with fever (temperature > 37.5 degrees C ) and (or) with bloody stools.
References
- https://patients.gi.org/topics/diarrhea-acute-and-chronic/
- https://web.archive.org/web/20140717205014/http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs330/en/
- https://www.medicinenet.com/rotavirus/article.htm#rotavirus_infection_facts
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/infections-and-poisoning/norovirus
- https://www.healthline.com/symptom/diarrhea
)
@ugonma , thanks for enlighten us on diarrhea, and deleterious effect of self medication. I think this phenomenal is rampant in the third world countries, and serious awareness should be done to educate people. Most victims also leaves in a dirty environment. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you for reading.Creating awareness to educate people is a collective goal of everyone including you and I.
You are welcome, the post is quite informative
Hahaha , what a paradox,
You try to treat your self and eventually, you destroy your own body. That shows the level of confusion in man. I think like you said, that it's common in developing countries, however, it's not only peculiar to developing countries, but also peculiar in some developed countries too. Many people resolve to do self medication because of poverty and poor orientation. Well done @ugonma for giving us this piece of information.
Thank you for reading and this important input,
I believe diarrhea has grades. I once had one during which I needed nobody to tell me to go to a hospital. While some could be mild and easily handled with OTC drugs, severe ones should be handled by capable hands.
Then, what is the best choice of drug to treat mild diarrhea? How safe or effective is the metronidazole/tetracycline combination to treat mild diarrhea that is quite popular among Nigerians?
Is there any difference between diarrhea and dysentary?
I agree with you that diarrhoea has grades and that is why I described it's severity based on the number of stools as mild, moderate and severe. how safe or effective? Using antibiotics in the treatment of mild diarrhoea without prescription should be discouraged to combat the increase in antibiotics resistance, interestingly, most mild diarrhoea infection are caused by viruses and the symptoms are self-limiting. (resolves after a couple of days, whether you take drugs or not) .
Yes, there is a difference between diarrhoea and dysentery.
Diarrhoea and dysentery can be differentiated in any of the following ways:
Diarrhoea involves the frequent passage of watery stool with no blood or mucus, although dysentery also involves frequent passage of stool, the presence of mucoid and sometimes blood differentiates it.
Fever, cramps and pain are less common in diarrhoea but these symptoms are usually associated with dysentery.
Diarrhoeal is an infection that targets only intestinal lumen and upper epithelial cells (affects the small bowel). Dysentery targets not only upper epithelial cells but colon ulceration also results.
Diarrhoea is usually a viral infection although others pathogens listed in the article can also cause watery diarrhoea. Dysentery is bacterial, Escherichia coli, Shigella, and Salmonella are the most common causative organisms