How Fast The Universe Is Expanding Still Not Know By Scientist
Since the relationship between distance and motion of a galaxy away from us was first discovered by Hubble, astrophysicists have been measuring how the universe is really expanding. The space fabric itself keep stretching and the gravitationally unbound objects keep rising, which give everyone access in viewing the expanding universe at the same rate. Today in cosmology, the subject of a great debate is actually what the rate is. You measuring the big bang’s afterglow rate, you will discover you will arrive at one value for Hubble’s constant 67km/s Mpc. What if you actually measure it from another perspective like an individual stars, galaxies. You will see that another different value is been given: 74km/s Mpc. Who will be determine right or wrong? Is a big argument in science world.
image
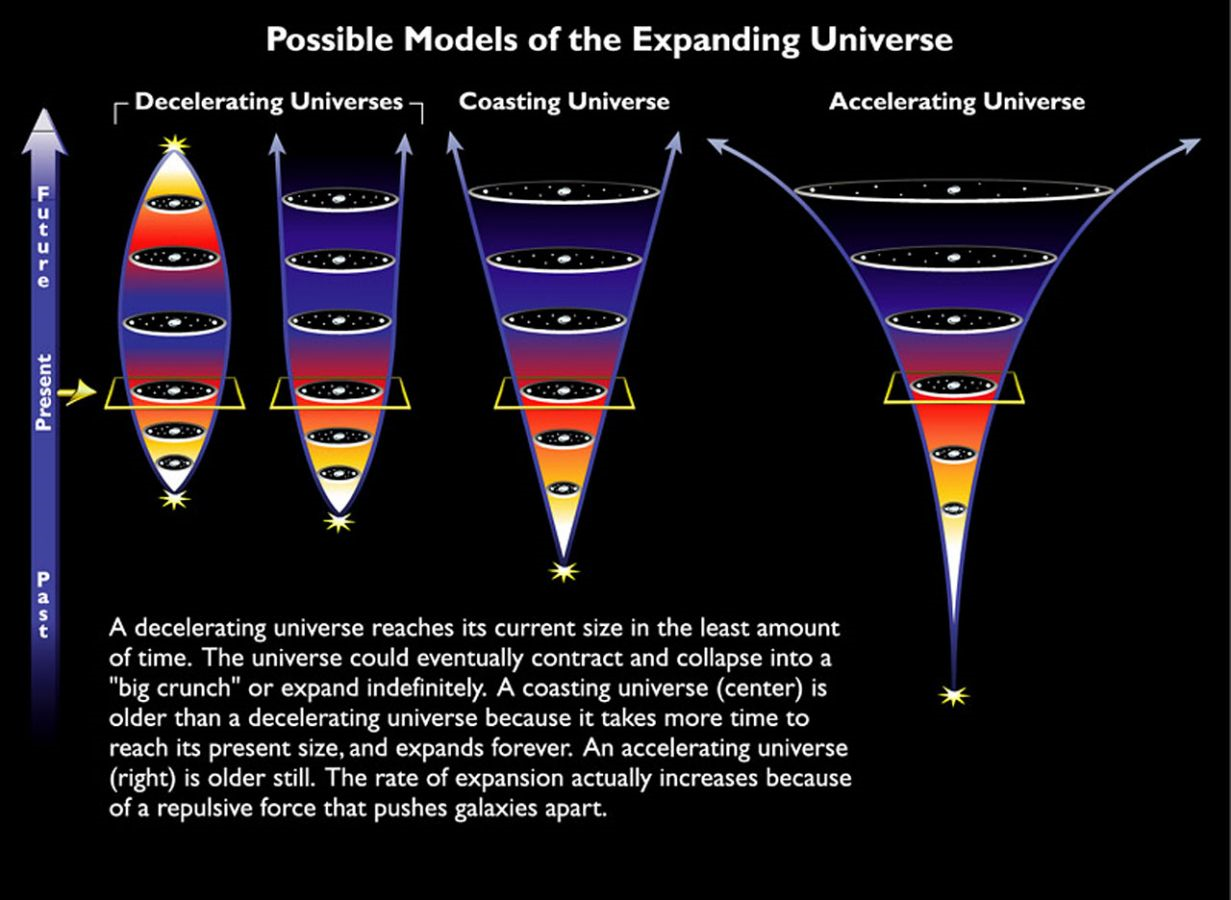
In distant past, the universe may have been more compact or even hotter if viewed based on how it is expanding today. If things are getting more farther apart nowadays, then it means long time ago they may be close together. You can learn a lot of things if you can evaluate today expansion and as well what the universe contains.
If the big bang do occurred (which is yes)
Universe is exactly how old (13.8 billion years)
And if it will expand forever or re-collapse
All this can be learnt if Hubble constant is accurately measure
 (
( )
)This quantity looked straightforward if determined to be measure. If an object distance and the speed it move away from its red shift can be measure, then you can derive the Hubble constant which relates the distance and recession speed but the problem which do arise is based on the different methods the Hubble constant is been measure which do give different results. In fact, two major classes of methods exist that are not compatible with each other due to the results given
Distance Ladder Method
How far away is a distant galaxy when you viewed it, if you can really measure those individual start within the galaxy then you already know how stars work, you can understand the distance to those galaxies. Same deal with supernova. You can read more details of distance ladder method
Leftover Relic Method
During Big Bang incident, the universe came into existence with under dense and over dense regions. Normal matter, dark matter and radiation are the three keys element. The over dense regions grow through the work of gravitation while both dark matter and normal matter fell into them. The work of the radiation is to push that excess matter out, but it interacts with normal matter differently that dark matter.
Recently lot of buzz have been going on that the matter could be settled by colliding neuron stars who will be providing third independent method.
Some of these uncertainties are the same ones that plague the ‘distance ladder’ method. If this ‘standard siren’ method, as it’s coming to be called, agrees with the higher figure of 72–75 km/s/Mpc after, say, 30 detections, that doesn’t necessarily mean the problem is solved. Instead, it’s possible that the systematic errors, or the errors inherent to the method you’re using, are biasing you towards an artificially higher value. It helps to have a third method when the first two give different results, but this third method isn’t entirely independent, and comes along with uncertainties all its own.
Having a good knowledge of how exactly the universe expand quickly is an important ingredient in knowing where everything came from, how it turn to be this way and where it is finally heading. It won’t be needful having a third method with the aim of it been a tiebreaker, it might be a another way of fooling ourselves if we are not careful. The universe wont change what reality entails even if we are misinterpreting it. It is now up to us in making sure we finally get it right.
Interesting read. I have read a little about the ongoing discussion in popular science articles but you provided a lot more detail. Thanks!
keep sharing, more power!
Great Info Thanks for the sharing