WHAT IS RAID(REDUNDANT ARRAY OF INDEPENDENT DISKS)
HY ALL MEET AGAIN WITH ME, THIS TIME WILL EXPLAIN THE RAID DEFINITION AND LEVEL RAID.
RAID DEFINITION
Raid is data that is absorbed by data storage which some physical disk drive components become a single logical unit for purposes of data redundacy and enhancement of work,which is used to implement application or feature fault tolerance in computer storage media,especially on hardisk by using redudancy or data stacking,either by using software or unique hardware RAID or separate hard drive RAID.Raid is used for Computer System to do the process of mirroring and striping.
The levels in the RAID are divided into three characteristics:
---RAID as a collection of multiple hard disks (physical disk drives) which by the operating system are only seen as a logical drive.
---For all multiple hard disks in the array.
---Redundant disk used to store parity information, its function to save data one of the damaged data hard disk.
LEVEL-LEVEL STANDART RAID
Raid can be devided into 8 different levels,level is level 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,0+1,and also level 1+0.Each level has its shortcomings and advantages.as follows:
RAID LEVEL 0
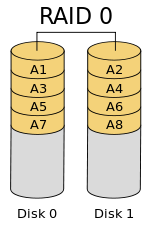
RAID on level 0 uses a set of disk with striping at blok level,without redundancy.Therefore,it only stores and strips the data bloks within a number of disks.This level 0 is not really included in the RAID group,this is because level 0 does not use redundancy in performance improvement
RAID LEVEL 1

Raid level 1 is disk mirroring,forging or duplicating on each disk.This step can provide improvements to disk performance,but the number of disk in need is also change to 2-fold.therefore his funds become very
expensive.
RAID LEVEL 2
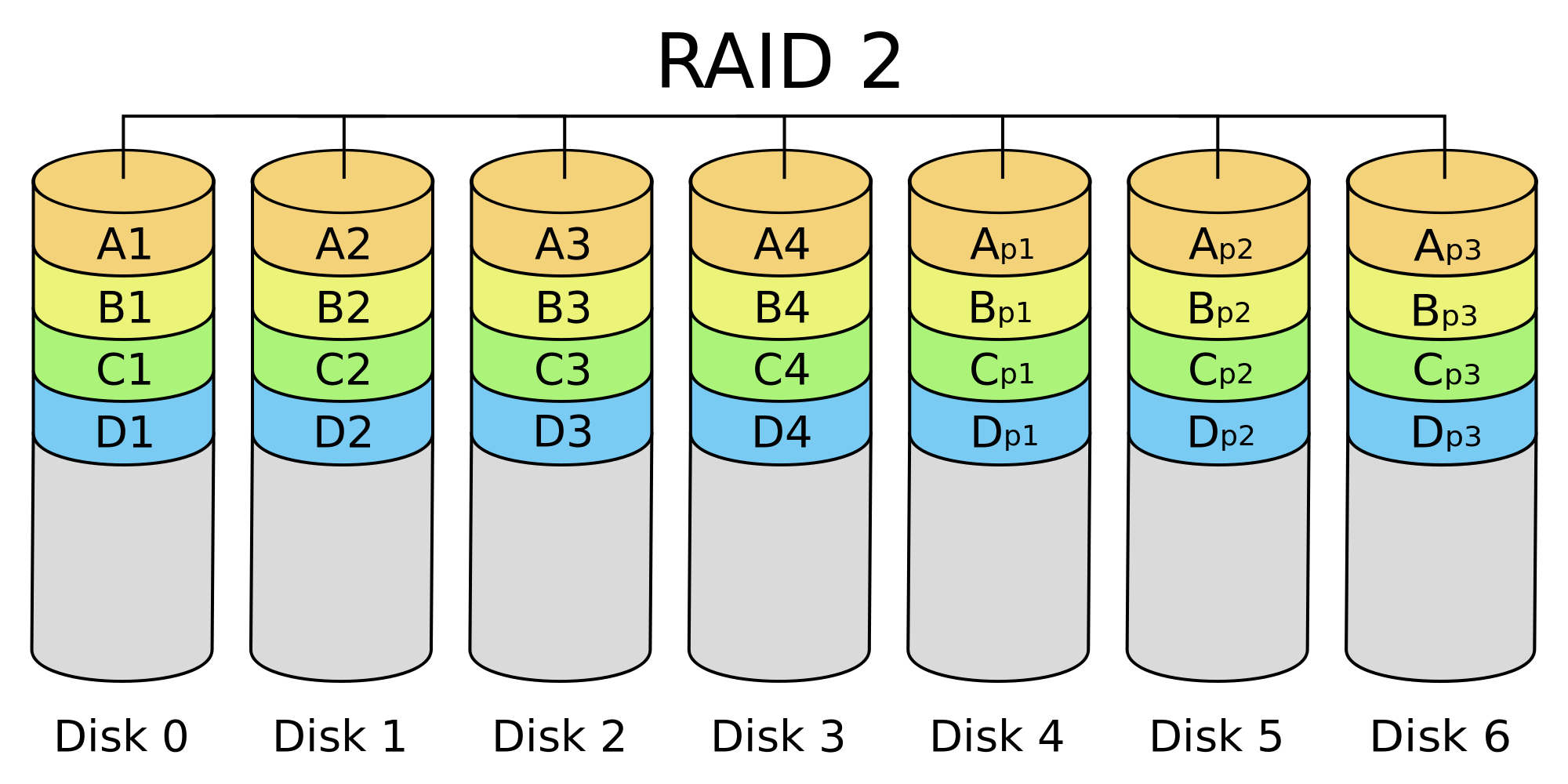
This level 2 RAID is organizing with error - correcting - code (ECC). As in the EEC memory server where the detection point of error using parity bits. In each data byte each has a corresponding parity that represents the number of bits in the byte of the data, where the parity bit = 0 if the number of bits parasite = 1 or odd or parasity bit = 0 is even.
So if one of the bits in the data is changed, the parasity changes and does not match the parity of the already saved or stored bit. That way, if there is a problem or failure on one disk, data can be reshaped by detecting or reading error - correction bits on another disk.
RAID LEVEL 3

RAID LEVEL 3 is an organizing with bit interleaved parity. In organizing this level almost the same thing with RAID level 2, only on RAID Level 3 it requires a redundant disk, no matter how much or the amount of its disk collection.
RAID LEVEL 4
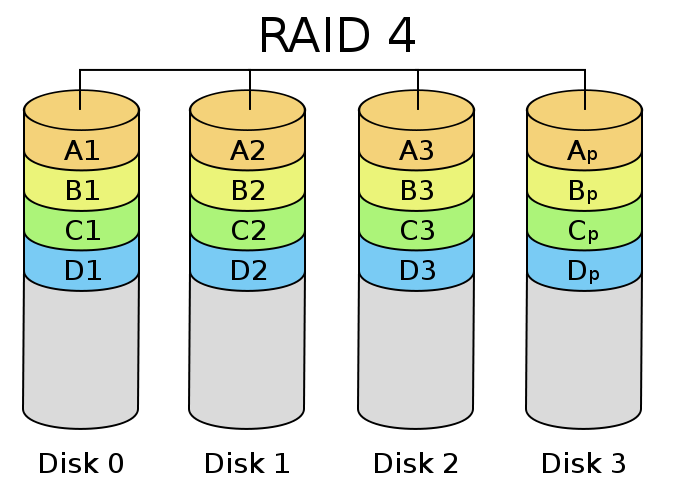
RAID Level 4 is an organizing with blocked interleaved parity, which uses striping data at block level, by saving or storing a parity block on a different disk for each data block on another compatible disk.
RAID LEVEL 5

RAID Level 5 is an organizing with scattered interleaved blocked parity. Parity as well as data that is spread across the disk including on an additional disk.
RAID LEVEL 6
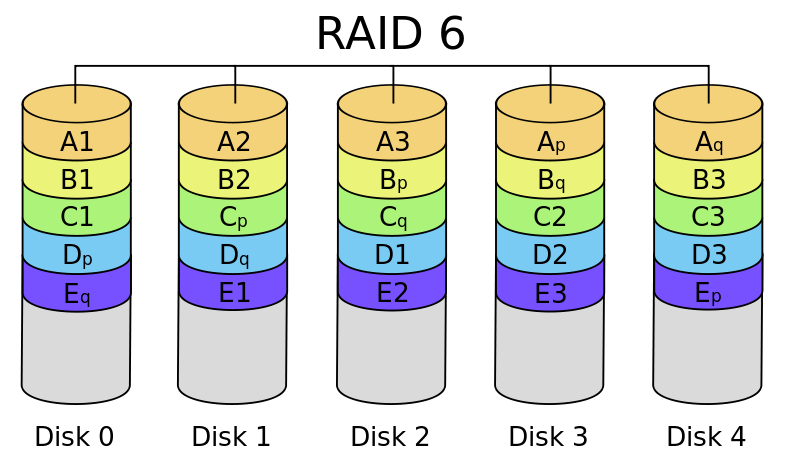
For RAID Level 6 it is also called redundancy p + q, as it does on RAID level 5, but it stores an additional redundant information that will be useful in anticipating the occurrence of multiple disk failures simultaneously.
RAID LEVEL 10

The usual RAID 10 is also called RAID 1 + 0 or RAID 1 and 0, similar to RAID 0 + 1, only difference is the use of its RAID level is reversed. RAID 10 is not a standard RAID level created for Linux MD drivers. RAID 10 requires at least 4 hard drives.
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 (data striping) and RAID 1 (mirroring). Has the highest read / write performance & data redundancy (has damage tolerance up to several hard drives). RAID 10 has a damage tolerance of 1 hard disk per mirror stripe.
RAID 10 is usually widely implemented in databases, web servers & application servers or servers that require high-performance hard drives.
RAID has remained a solid piece of data storage ever since, and. IBM has released IBM Distributed RAID with Spectrum Virtualize V7.6, which promises to improve RAID performance. Use RAID to protect three simultaneous drives. Using NetApp ONTAP uses RAID to protect three simultaneous drives. The Dell EMC Unity platform also supports RAID 1/0, RAID 5 and RAID 6.
