What is an ATM or Asynchronous Transfer Mode?
As we said in the previous series, one of the infrastructure, or better, is the technology of data transmission on widespread WAN or ATM technology. Read almost everywhere before speaking about the nature and reason for using the service, it's just a word translation, but ITPRO differs from that. Normally, the cost of maintaining networks that are specifically used to transfer and pass traffic to computers, audio and video is high. ATM technology gives you the ability to reduce your costs by integrating these services from different networks on a single network and turning it into a single infrastructure.
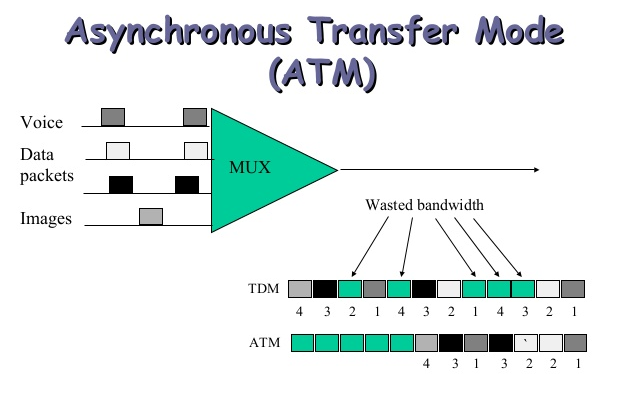
The ATM mechanism is a dedicated or Dedicated communication that divides digital data into small sections of 53 bytes and sends it to physical media into these small cells or cells, and sometimes in some cases The type of data transfer mechanism is also referred to as Cell Switching. Take note of the ATM translation. Asynchronous Transfer Mode means asynchronous transfer mode, each cell being processed separately before it is split up and transferred to the media, and this processing is done without communication and the need for other cells asynchronously and asynchronously. Gets Due to the fact that the ATM operating mechanism is designed to be easily implemented using hardware, processing and speed switching are possible, and its settings are easy to do, unlike software mode. In packet-switched packet-based communications such as Internet and Intranet networks, each packet will have different sizes depending on the different locations used, but in Cell Switching, the cell's size is always the same.
The predefined speed that ATM technology offers on optical fiber is 155.520 Mbps or 622.080 Mbps, which we call it the default Bit Rate but speeds in ATMs can be up to 10 Gigabits per second, and in this regard, this transmission technology is considered as the fastest broadband network service. Apart from other technologies like Synchronous Optical Network or SONET as well as some other technologies, ATM is a key component of ISDN Broadband or BISDN networks. Note that the ATM stands for the Automatic Teller Machine, which means that there is no connection between the two. ATM is the main core protocol for SONET networks in ISDN networks.
The cell structure used in the ATM causes the routers not to process the various sizes of the packets, hence the processing speed increases, and the delay or delay in the path decreases. That's why experts believe that ATM is a solution to increase the bandwidth of the Internet. On the ATM, the path between the start and end point at the start of the work is determined and the two points begin after the path is created, and therefore, the routing will become very simple and fast after the creation of this initial path, because We would no longer be involved in creating intelligence packets and routing them individually, since in the closed mode each packet would route a duplicate somewhere to reach the destination. But the problem with ATMs is that if the network is disrupted, other traffic may not be properly targeted. ATM operates in the second layer or data layer of the OSI model. The ATM can be combined with two Packet Switching and Small Circuit Switching networks, which are ideal for real-time, non-delayed communications such as VoIP and video. In fact, between the origin and destination, the virtual circuit or virtual circuit is always created.
