SEC S17-W2 || Layer-3 blockchain
 |
|---|
INTRODUCTION |
A layer represents different level or part of something. It is a way to organize and understand complex things by breaking them down into simpler parts.
Let's say we are making a hamburger, each ingredient in the hamburger, like the bread, lettuce, tomato, and cheese, can be thought of as a layers as we stack them on top of each other to create a delicious sandwich with each layer having its own purpose and adding something special to the overall taste and texture.
 |
|---|
In the context of blockchain, a layer is like different level or part of a digital system that work together to make things happen smoothly and securely.
Think of it like the building blocks with each layer having its own specific job and purpose. For example, in the blockchain world, there can be different layers that handle different tasks. One layer might be responsible for recording transactions, another layer might handle security, and yet another layer could focus on verifying and validating information.
These layers work together to create a strong and reliable system while also ensuring that everything is organized, transparent, and trustworthy. So, just like the layers in a sandwich or the layers in a digital system, layers in blockchain help us understand and interact with the technology in a more organized and secure way.
However, to this effect, the blockchain layers are mainly divided into 3, and these different layers in blockchain technology are commonly referred to as Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3 of which our discussion for this week is Layer 3. So without wasting any more of your time, let's us going straight to business.
Describe the architecture of layer 3 blockchains specialized in fractal scalability, highlighting the main components and mechanisms that achieve this objective. Create a chart that illustrates this architecture. |
|---|
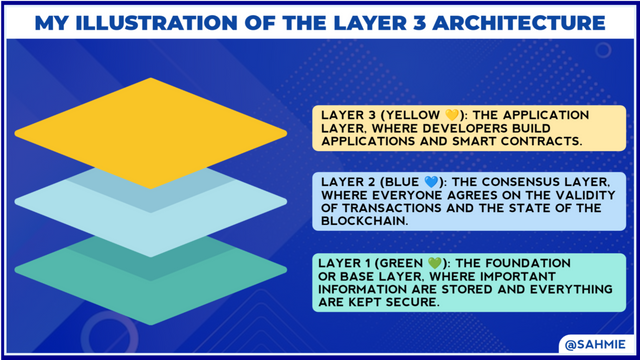
In my introduction, I have started that in blockchain technology, there are typically three main layers which are;
Network Layer (Layer 1):
This layer is known to be the foundation of the blockchain as it is responsible for establishing the network infrastructure and connecting all the participants while also ensuring that all the computers, or nodes, in the blockchain network can communicate with each other securely.
Consensus Layer (Layer 2):
This layer is all about agreement and trust among the participants in the blockchain network. It is responsible for ensuring that everyone agrees on the validity of transactions and the state of the blockchain as it uses algorithms and protocols to make sure that everyone follows the same rules and reaches a consensus on the state of the blockchain.
Application Layer (Layer 3):
This is the layer known to be where all the fun stuff happens as it is where developers build applications and smart contracts as it allows for the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) and enables various use cases like digital currencies, supply chain management, and more. It's where the real-world value and utility of blockchain technology come into play and it is our case study for this week.
In context with the question asked, the Layer 3 blockchains are a type of blockchain architecture that aims to enhance scalability and efficiency an are build upon an already existing layer 1 and layer 2 blockchains by introducing additional layers to improve performance, this is to say that without layers 1 and 2, there is no layer 3.
 |
|---|
Think of layer 3 blockchains like a multi-layered cake with each layer having its own special role to make the whole system work smoothly.
The first layer is the main blockchain layer (layer 1), which is like the base of the cake and it is responsible for storing all the important information and keeping everything secure.
On top of that is the layer 2, which is like the frosting layer, adding some extra sweetness to the cake by introducing techniques like state channels which allows participants to do lots of transactions privately and quickly, without overloading the main blockchain.
With the layer 3 being the cherry on top of the cake bringing with it some exciting features like sharding, sidechains, and cross-chain communication to make transactions faster and more flexible.
Imagine we have a big puzzle, but instead of putting all the pieces together in one go, we break it down into smaller puzzles, or "shards" where each shard can handle its own set of transactions, making things faster and more scalable.
But that's not all as Layer 3 blockchains also have something called state channels which is like having private communication channels between specific participants, so instead of recording every single transaction on the main blockchain, participants can conduct multiple transactions off-chain, which reduces the load on the main blockchain and speeds things up.
Then again, layer 3 blockchains also uses sidechains. These are like separate puzzle boards that connect to the main puzzle with each sidechain capable of handling specific tasks or applications, thereby making the whole system even more flexible and scalable.
Therefore, the main components and mechanisms of Layer 3 blockchains that helps it achieve its objectives include;
Sharding:
Sharding is the process of handling an individual parts of something in bulk to help spend up the process. let us say we have a big puzzle, but instead of solving it all at once, we break it down into smaller puzzles called shards to help us work faster. But then, each shard have the ability to handle its own set of transactions to make the process faster and more efficient.
State Channels:
State channels are like private communication channels between specific participants, so instead of recording every single transaction on the main blockchain, it allows participants to conduct multiple transactions off-chain within these channels, hence reducing the load on the main blockchain and speeds up the process.
Sidechains:
Sidechains are like separate blockchain that are connect to the main blockchain to handle specific tasks or applications to allow for more flexibility and scalability. It is like having different areas to work on different things without overcrowding the main blockchain.
Cross-Chain Communication:
This mechanism enables different blockchains to communicate and share information with each other. Therefore, it is like having bridges connecting different different blockchains which allows them to exchange data and work together seamlessly.
Overall, these components and mechanisms work together to create a more scalable and efficient blockchain system in Layer 3 Blockchains. Some examples of Layer 3 Blockchains includes:
- Polkadot
- Cosmos
- Avalanche
- Near Protocol
- Elrond
How do layer 3 blockchains specializing in fractal scalability use horizontal sharding to improve transaction processing capacity, and how does this differ from the Steem blockchain approach? |
|---|
Going back the puzzle analogy, imagine we have a big puzzle to solve, and it's taking a lot of our time and effort to put all the pieces together, where thus context of blockchain, the puzzle pieces represent transactions, and solving the puzzle means processing those transactions.
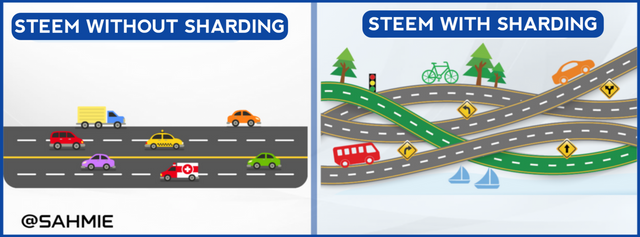
Now, layer 3 blockchains specializing in fractal scalability uses horizontal sharding to make solving the puzzle (transactions) faster. This is like having multiple people working on different sections of the puzzle (transactions) at the same time bringing about a division in labour with each person focusing on their assigned section, which we call a shard. Therefore, by dividing the work among multiple shards, the overall transaction processing capacity increases due to the division of labour.
But then, how does is this different from the Steem blockchain approach? Well, the Steem blockchain takes a different approach, where instead of dividing the work horizontally into shards, it uses a different method called "Vertical Scaling" which is like having one super-fast person solving the whole puzzle all by himself.
To fully understand how this Vertical Scaling works on the Steem Blockchain, let us magine the Steem Blockchain as a big highway where people share and interact with content, hence Vertical scaling of the Steem Blockchain involves making that highway wider and faster to accommodate more people and their activities.
To achieve this, the Steem Blockchain can add more powerful computers or servers to handle the increasing traffic. This could be seen as adding more lanes to a highway to allow more cars to pass through at the same time.
With vertical scaling, each computer or server becomes more capable of handling a larger number of transactions and interactions just like giving each car on the highway a bigger engine to handle more passengers and cargo.
This process of vertical scaling helps the Steem Blockchain handle a higher volume of transactions and activities, making it more efficient and responsive. However, it's important to note that vertical scaling has its limitations as there is a maximum capacity for each computer or server, just like there's a limit to how many cars can fit on a widened highway. Some of the limitations of vertical scaling includes;
Maximum Capacity:
Vertical scaling involves adding more power to a single computer or person to handle tasks. However, there is a limit to how much one computer or person can handle. It's like carrying groceries - there's only so much you can carry before it becomes too heavy. Similarly, a computer can only handle a certain number of transactions before it becomes overwhelmed and slows down.
Cost:
To make a computer more powerful, you usually need to upgrade its hardware, which can be expensive. It's like buying a bigger, faster car to accommodate more passengers. This can become costly, especially if you need to keep upgrading as the demand for transactions increases.
Lack of Flexibility:
Vertical scaling may not be as adaptable or flexible as other approaches, like horizontal scaling. With vertical scaling, you're limited to the capabilities of that single computer or person. If there's a sudden increase in demand or if you need to handle different types of tasks, it may be challenging to quickly adjust and meet those needs.
Single Point of Failure:
When relying on a single powerful computer or person, there is a risk of a single point of failure. If that computer or person experiences a problem or goes offline, it can disrupt the entire system. It's like if the only car available breaks down, then nobody can get around.
With this in mind, we can say that layer 3 blockchains with horizontal sharding can scale more effectively because they distribute the work among multiple shards, allowing for greater transaction processing capacity as the network grows.
Explain how Sidechains and Rollups are essential elements of layer 3 blockchains to ensure fractal scalability, and how these concepts could be applied to the Steem blockchain to improve its performance. |
|---|
Before going into full details of how Sidechains and Rollups are essential part of Layer 3 Blockchains, let us get to know how these components work.
Sidechains:
Think of a sidechain as a separate blockchain that runs alongside the main blockchain. It's like having an additional lane on a highway. Sidechains are designed to handle specific tasks or transactions, which helps relieve the congestion on the main blockchain. By moving these tasks to Sidechains, the main blockchain can focus on more complex operations, resulting in improved scalability.
Rollups:
Now, imagine we have a bunch of small transactions that we need to record on the blockchain which we will have to record individually, however instead of directly adding each transaction to the main blockchain, Rollups helps by bundling up these multiple transactions together and submit them as a single entity, were it is like putting several items in a box before shipping them and by compressing and grouping these transactions into one, Rollups help reduce the amount of data that needs to be processed and stored on the blockchain, thereby enhancing scalability.
Hence, the combination of Sidechains and Rollups brings significant benefits to layer 3 blockchains in ways such as;
Fractal Scalability:
Layer 3 blockchains achieve fractal scalability by leveraging the power of Sidechains and Rollups as they offload specific tasks to sidechains and compressing transactions with rollups, thereby greatly ehancing the overall capacity and efficiency of the blockchain system. It is like having multiple highways (sidechains) and optimizing the transportation of goods (transactions) by bundling them together (rollups).
Enhanced Performance:
Sidechains allow for parallel processing, enabling multiple tasks to be executed simultaneously. This improves the speed and throughput of the blockchain network. Rollups, on the other hand, reduce the computational and storage requirements for individual transactions, leading to faster processing times and lower fees.
Flexibility and Interoperability:
Sidechains can have their own rules and features, making them flexible for specific use cases, meaning they can be customized to handle different types of transactions or execute specific smart contracts. Moreover, sidechains can communicate and interact with the main blockchain, ensuring interoperability between different chains within the ecosystem.
Security and Trust:
While sidechains operate independently, they are still connected to the main blockchain and this connection ensures that the security and consensus mechanisms of the main blockchain extend to the sidechains, maintaining the overall integrity and trust of the system.
Then, on how these concepts could be applied to the Steem blockchain to improve its performance, let us once again think of the Steem blockchain like a busy road where lots of people are trying to drive their cars (transactions) at the same time. But then, sometimes the road gets really crowded and it takes a long time for everyone to get to their destination.
Hence, to improve the performance of the Steem blockchain, we can use sidechains and rollups where the Sidechains serves like extra lanes added to the road to help ease the traffic by allowing some cars to take a different route, reducing congestion on the main road, meaning that more transactions can be processed quickly and efficiently.
 |
|---|
Now, talking about Rollups, let us say instead of each car driving individually on the road, we join together some of this cars in groups where these groups of cars are bundled up (like a rollup) and counted as a single vehicle (transaction) on the road (blockchain). This makes it faster and more efficient to process a bunch of transactions at once, just like delivering a big package instead of many small ones.
Therefore, by using sidechains and rollups on the Steem blockchain, we can make it faster and smoother for transactions to be processed even as the Steem Blockchain is already fast as it is, meaning that more people can use the Steem blockchain without having to wait too long for their transactions to be confirmed.
Hence, sidechains and rollups are like tools that can help improve the performance of the Steem blockchain, making it faster and more efficient for everyone to use.
How do Layer 3 blockchains handle the challenges of decentralized governance while maintaining fractal scalability, and how does this compare to the governance structure of the Steem blockchain? |
|---|
When we talk about decentralized governance, all we are talking about is making decisions together as a community, rather than having a central authority in charge just like having a group of friends deciding where to go for dinner by discussing and voting on it.
In a Layer 3 blockchain, the community members have a say in how the blockchain is governed, making it more democratic and inclusive.
Talking about scalability on the other hand, we are talking about the ability of the blockchain to handle a large number of transactions without slowing down. However, fractal scalability takes it a step further by allowing the blockchain to scale not just at one level, but in a recursive and self-similar way, just like having multiple layers of highways that can handle more traffic as needed.
So then, how does Layer 3 handle the challenges of decentralized governance while maintaining fractal scalability?
Well, Layer 3 blockchains achieve this by implementing innovative solutions like Off-chain solutions, Sidechains, Sharding and Layer 2 Solutions that enable decentralized decision-making while ensuring the scalability of the blockchain.
These solutions also involve things like consensus algorithms that allow for efficient and secure voting, governance protocols that ensure fair representation of community members, and layering techniques that enable the blockchain to scale both horizontally and vertically.
Therefore, by combining decentralized governance and fractal scalability, Layer 3 blockchains aim to create a system where the overall community has a say in how things are run, while also ensuring that the blockchain can handle a growing number of transactions without sacrificing performance.
But then, how does this compare to the governance structure of the Steem blockchain?
In Steem Blockchain, the governance structure is a bit different from Layer 3 blockchains, where instead of a fully decentralized governance model, Steem has a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) system.
In this system, instead of everyone having an equal say in decision-making, certain individuals or entities called "witnesses" are chosen to validate transactions and make governance decisions. It is like having a group of trusted friends representing every other persons and they are responsible for making important choices on behalf of the community.
These witnesses are however elected by the Steem community through voting, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the blockchain's operations as they are responsible for validating transactions, securing the network, and proposing changes to the blockchain's rules.
Now, when it comes to scalability, Steem has its own approach as it uses a single-layer blockchain structure. This means that it does not have the same recursive (repeats or refers back to itself) layering as Layer 3 blockchains. However, Steem has implemented various optimizations to handle a large number of transactions efficiently.
One of the key optimizations is the use of a fast block generation time. STEEM has a block generation time of 3 seconds, which means new blocks are created every 3 seconds, therefore this allows for quicker transaction confirmations and helps the blockchain handle a high volume of transactions efficiently.
Another optimization is the implementation of a hierarchical structure called "witnesses" were this witnesses are responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the blockchain as they are elected by the community to play a crucial role in the governance and scalability of the STEEM blockchain.
To further enhance scalability, STEEM has implemented a mechanism called "bandwidth" or "resource credits" to ensure that users have a fair share of network resources based on their stake in the blockchain (Steem Power), which helps to prevent abuse and ensures that the network can handle a large number of transactions without becoming overwhelmed.
Additionally, STEEM has also implemented a system called "dynamic resource allocation", A system that allows users to allocate their resources based on their needs. This ensures that users can adjust their resource usage dynamically, depending on the current demand and network conditions.
Therefore, by combining these optimizations, the STEEM blockchain provide a scalable and efficient platform for handling a large number of transactions.
How could the introduction of new technologies such as sharding and interoperable blockchains influence the future of layer 3 blockchains specialized in fractal scalability, and how could the Steem blockchain adapt to these developments? |
|---|
Sharding like I explained earlier is about dividing a bulk into smaller sections, so different people can work on different sections at the same time to help speed up the process.
Similar, in the world of blockchains, sharding involves splitting the network into smaller parts called shards, where each shard can process its own set of transactions, making the overall system faster and more scalable.
Interoperable blockchains, on the other hand is like having different networks that can be connected together, which allows different blockchains to communicate and share information with each other, thereby opening up new possibilities for collaboration and making it easier for people to use different blockchain platforms together.
When it comes to layer 3 blockchains specialized in fractal scalability, these are blockchains that are designed to handle a huge number of transactions and scale up as needed.
In this context, the Steem blockchain could adapt to these developments by incorporating sharding and interoperability features. Sharding could help the Steem blockchain process transactions more quickly by dividing the workload among different shards bringing about division of labour which would make the blockchain more scalable and able to handle larger number of users and transactions.
To incorporate sharding into the STEEM Blockchain, the network would need to be divided into smaller parts called shards, where each shard would be responsible for processing a subset of transactions, which would help improve scalability and increase the overall transaction processing speed.
By implementing sharding, the STEEM Blockchain could distribute the workload across multiple shards, allowing for parallel processing of transactions at the same time, and this would enable the network to handle a higher volume of transactions and accommodate a larger user base without sacrificing performance.
However, it's important to note that implementing sharding is a complex process that requires careful planning and consideration as it involves designing protocols and mechanisms to ensure that shards can communicate and coordinate with each other effectively.
Therefore, the STEEM development team would need to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and challenges of sharding and devise a strategy to implement it in a way that maintains the integrity and security of the blockchain.
As for interoperability, the Steem blockchain could benefit from connecting and collaborating with other blockchains, which would enable users to interact with different blockchain platforms, share information, and access a wider range of services and applications.
By embracing these new technologies, the Steem blockchain could enhance its scalability, speed, and usability, making it even more attractive for users and developers alike.
CONCLUSION |
In conclusion, Layer 3 solutions offer exciting possibilities for the Steem Blockchain network. Enabling a decentralized decision-making and improving scalability, solutions like off-chain transactions, sidechains, sharding, and Layer 2 protocols can help Steem handle more users and transactions while maintaining its decentralized nature, whereby these implementations can pave the way for a more efficient and user-friendly blockchain platform, opening up opportunities for growth, innovation, and enhanced user experiences on the Steem network.
I wish to invite @starrchris, @ngoenyi, and @hamzayousafzai.
Thank You for your Time
NOTE: Always have a smile on your face, as you are never fully dressed without one.

@sahmie your detailed breakdown of layer 3 blockchains is truly impressive You have explained everything so clearly and I love how you used the analogy of a puzzle to simplify complex concepts. Best of luck with the contest
Greetings friend,
Thank you so much for your kind words. I'm really glad that my breakdown of layer 3 blockchains was helpful and that you found the analogy of a puzzle to simplify things. It's always my goal to make complex concepts easier to understand. I really appreciate your support and well wishes for the contest. I'll do my best.
Nice, you worked very hard.
Greetings @defender512
I appreciate your kind words. As always, it is never easy here and I have put a lot of time and effort into my work. It feels great to know that my hard work didn't go unnoticed. Thank you for acknowledging it.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. It will make Steem stronger.
Your post has been successfully curated by @kouba01 at 35%.
Thanks for setting your post to 25% for @null.
We invite you to continue publishing quality content. In this way you could have the option of being selected in the weekly Top of our curation team.
Your post provides a great information that helps in understanding the important features of Layer 3 of Blockchain. To explain the various layers of Blockchain in a recent foundation and their benefits, this is an important post from your's sahmie 😊
Greetings friend,
I'm glad you found my post helpful in understanding the important features of Layer 3 of Blockchain. Explaining the different layers of Blockchain and their benefits is really important to get a good foundation.
Thank you for your kind words Understanding the layers of Blockchain is indeed crucial for building a solid understanding of its potential and applications.
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Saludos cordiales estimado amigo sahmie, un placer para mi saludarte y leer tu participación en este reto.
Amigo muy detallada y muy bien explicada tu participación, abordaste cada pregunta con las palabras correctas y adecuadas, las L3 son seguras, rápidas y escalables, ademas su seguridad depende de la L1.
Te deseo una feliz y bendecida noche.
Greetings @yancar
Thank you so much for your kind words and warm greeting. I'm really glad you enjoyed reading my participation in the challenge. It means a lot to me that you found my explanations detailed and clear. L3s are indeed secure, fast, and scalable, and their security relies on L1. I appreciate your well wishes and I wish you the same.
Thank you, friend!


I'm @steem.history, who is steem witness.
Thank you for witnessvoting for me.
please click it!
(Go to https://steemit.com/~witnesses and type fbslo at the bottom of the page)
The weight is reduced because of the lack of Voting Power. If you vote for me as a witness, you can get my little vote.
Hello @sahmie
I'm pleased to have read you because you explain with simple examples.
I don't understand the conclusion. Steem blockchain experience is already several years old. Previously, I saw several innovations but these days I don't see them.
In that sense I feel that Steemit is lagging behind and that the advantages that the good use of layer 3 can have are not being implemented.
Greetings and success!
Greetings @marcybetancourt,
Thank you so much for your time in going through my publication and leaving such a heartfelt remark.
I totally get what you're saying. It seems like Steemit hasn't been keeping up with the latest innovations on the Steem blockchain. It is a bummer when the advantages of layer 3 aren't being utilized. Hopefully, they catch up soon. Greetings and wishing you success too.
Your response is very kind.
I hope it's soon!
Thank you very much for your time.